Chapter: Operating Systems : Storage Management
Memory Management: Background
MEMORY MANAGEMENT: BACKGROUND
ü In general, to rum a program, it
must be brought into memory.
ü Input
queue – collection of processes on the disk that are waiting to be
brought into memory to run the program.
ü User programs go through several steps before being run
Address binding: Mapping
of instructions and data from one address to another address in memory.
Three different stages of binding:
1 Compile
time: Must generate absolute code if memory location is known in
prior.
2 Load
time: Must generate relocatable code if memory location is not known
at compile time
3
Execution time: Need hardware support for address
maps (e.g., base and limit
registers).
Logical vs. Physical Address
SpaceLogical address – generated
by the CPU; also referred to as “virtual
address“
Physical
address – address seen by the memory unit.
Logical and physical addresses
are the same in compile-time and load-time address-binding schemes
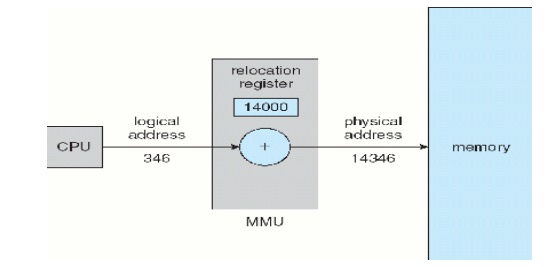
Memory-Management Unit (MMU)
ü It is a hardware device that maps virtual / Logical address to physical address.
ü In this
scheme, the relocation register‘s value is
added to Logical address generated by a user
process.
ü The user
program deals with logical addresses; it never sees the real physical addresses
v Logical
address range: 0 to max
v Physical
address range: R+0 to
R+max, where R—value in relocation.
Dynamic relocation using
relocation register
Dynamic Loading
ü Through
this, the routine is not loaded until it is called.
o Better
memory-space utilization; unused routine is never loaded
o Useful
when large amounts of code are needed to handle infrequently occurring cases
o No special support from the operating system
is required implemented through program design
Dynamic Linking
ü Linking postponed until execution time & is particularly
useful for libraries
ü Small
piece of code called stub, used to locate the appropriate memory resident library routine or function.
ü Stub
replaces itself with the address of the routine, and executes the routine
ü Operating
system needed to check if routine is in processes Memory addresses Shared
libraries.
ü Programs
linked before the new library was installed will continue using the older
library.
Related Topics