Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Language : Inheritance
The Object Class - Java
The
Object Class
There is
one special class, Object, defined
by Java. All other classes are subclasses of Object. That is, Object
is a superclass of all other classes. This means that a reference variable of
type Object can refer to an object
of any other class. Also, since arrays are implemented as classes, a variable
of type Object can also refer to any
array.
Object defines the following methods, which means that they are available
in every object.
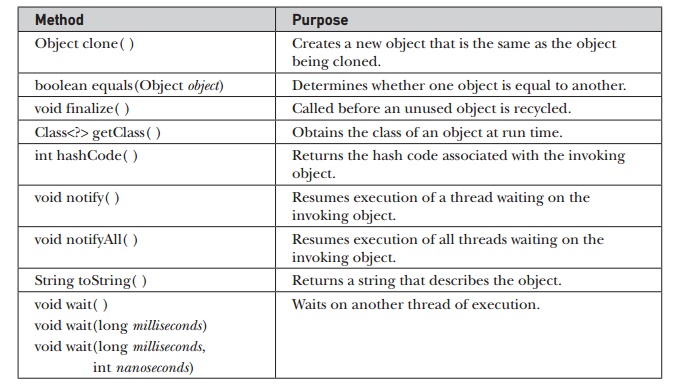
The methods getClass( ), notify( ), notifyAll( ),
and wait( ) are declared as final. You may override the others.
These methods are described elsewhere in this book. However, notice two methods
now: equals( ) and toString( ). The equals( ) method compares two objects. It returns true if the objects are equal, and false otherwise. The precise definition
of equality can vary, depending on the type of objects being compared. The toString( ) method returns a string
that contains a description of the object on which it is called. Also, this
method is automatically called when an object is output using println( ). Many classes override this
method. Doing so allows them to tailor a description specifically for the types
of objects that they create.
One last point: Notice the
unusual syntax in the return type for getClass(
). This relates to Java’s generics
feature, which is described in Chapter 14.
Related Topics