How the State Government Works | Chapter 1 | Civics | 8th Social Science - The Legislature | 8th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 1 : How the State Government Works
Chapter: 8th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 1 : How the State Government Works
The Legislature
The Legislature
In India, the State Legislature
consists of the Governor and one or two houses. The upper house is called the
Legislative Council while the lower house is called the Legislative Assembly.

Legislative Council
* The Constitution provides that the
total strength of the Legislative Council must not be less than 40 and not more
than 1/3 of the total strength of the Legislative Assembly of the State. The
members of the Legislative Council are elected indirectly.
*
One third of its members are elected by the local government bodies like the
District Panchayat and Municipalities.
*
Another one third is elected by the members of the Legislative Assembly.
* One twelfth is elected by the
graduates of the constituency and another one twelfth by the teachers of
secondary schools, colleges and universities.
At present, only six
states in India have Legislative Council in their legislature. They are Bihar,
Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
*
One sixth of the members of the Legislative Council are nominated by the
Governor of the State.
The Legislative Council is a
permanent house. One-third of its members retire every two years and elections
are held to fill the vacant seats. The members are elected for a term of six
years. To be a member of the Legislative Council, one must be a citizen of
India and should have completed 30 years of age. He cannot be a member of the
Legislative Assembly or either of the houses of the Parliament. The Chairman is
the presiding officer of the Legislative Council. In his absence, the Deputy
Chairman presides over its meetings. They are elected from among the members of
that house.
Legislative
Assembly
The people who make the laws of a
state government are called ‘Members of the Legislative Assembly’ (MLA). MLAs
are chosen from different constituencies. For the election of MLAs the entire
state is divided into different constituencies. These constituencies are called
the legislativeconstituencies. One legislative constituency may have one lakh
or even more people. One MLA is chosen from each legislative constituency to
represent that legislative assembly.
Election to the Assembly
Different political parties compete
in the elections to the legislative assembly. These parties nominate their
candidates from each constituency. The candidate is that person who contests
for the election and asks people to vote for him. A person has to be at least
25 years old to contest for election to the legislative assembly. One person
can stand for election in more than one constituency at the same time. Even if
a person does not belong to any political party, he can contest election; such
candidate is called an independent candidate. Every party has its own symbol.
Independent candidates are also given election symbol. The members of
legislative assembly (MLA) are elected directly by the people. All people
residing in the area of a legislative constituency who are 18 years of age can
cast a vote in the legislative assembly elections.
According to the Constitution, a
Legislative Assembly cannot have more than 500 members and not less than 60
members. Some seats in the Legislative Assembly are reserved for Scheduled
Castes and Scheduled Tribes. The Governor can nominate one member from the
Anglo-Indian community.The members of the Legislative Assembly are elected for
a term of five years. But the Governor can dissolve the house before the expiry
of its term and can call for fresh elections. The meetings of the Assembly are
presided over by the Speaker who is elected from among the members of the
Assembly. In his absence, the Deputy Speaker conducts its meetings.
The States Council of Ministers
The leader of the majority party in
the election is chosen as Chief Minister. In Tamil Nadu there are 234
legislative constituencies. The party with more than 118 elected candidates
(MLA) are invited by the governor to form the Government. The Chief Minister
(who also should be an MLA) chooses his ministers from the MLAs of his party.
Ministers for various departments headed by the Chief Minister is called the
State Government. So it is said that the party which got majority seats in the
election forms the government.
The working of the State
Government
After being elected to the
legislative assembly the MLAs are expected to regularly participate in its
sittings. The legislative assembly meets 2 or 3 times in a year. The main duty
of the Legislative Assembly is to make laws for the state. It can make law on
the subjects mentioned in the state list and the concurrent list. However,
during state emergency, it cannot exercise its legislative power.
The assembly has control over the
State council of Ministers. The State council of ministers are responsible or
answerable to the Assembly for its activities. The Assembly may pass a no
confidence motion against the council of Ministers and bring its downfall if it
is not satisfied with the performance of the council of Ministers. The
legislative Assembly has control over the finances of the state. A money bill
can be introduced only in the Assembly. The government cannot impose, increase,
lower or withdraw any tax without the approval of the Assembly. The elected
members of the Legislative Assembly can take part in the election of the
president of India and all members can take part in the election of the members
of the Rajya Sabha from the state. The Assembly also takes part in the
amendment of the Constitution on certain matters. So the government has three
basic functions: making laws, executing laws and ensuring justice.
How laws are made in
State Government?
Several kinds of rules and laws have
been made for all people of our country. For instance, there is a law that you
cannot keep a gun without having a licence for it. Or that woman cannot marry
before the age of 18 years old and men cannot marry before the age of 21 years.
These rules and laws have not been made just like that. People elected their
government who thought carefully before making such laws. A lot of such laws
are made by the state and central government.
In the legislative assembly
meetings, MLAs discuss a number of topics like public works, education, law and
order and various problems faced by the state. The MLA s can ask questions to
know the activities of ministries, which the concern ministers have to answer.
The legislative assembly makes laws on certain issues. The process of law
making as follows:
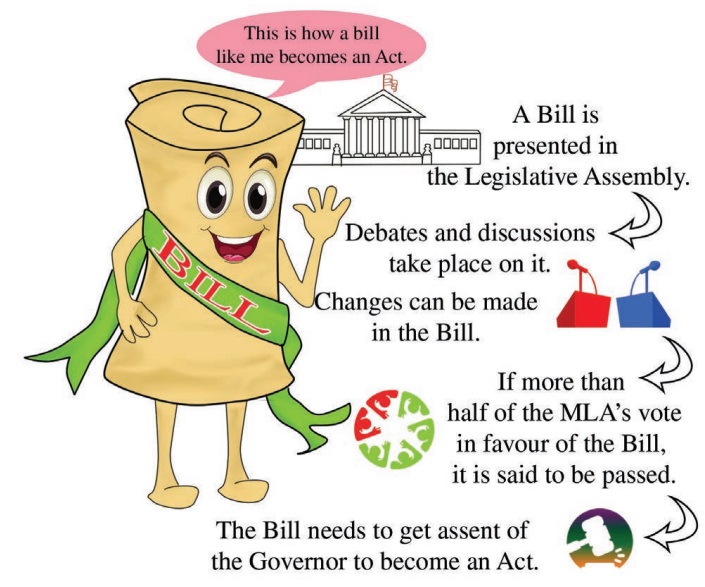
The State legislature
follows the same procedure for passing an ordinary or a money bill like that of
the Parliament. In State legislatures also, the Legislative Assembly which is
the lower house is more powerful than the Legislative Council which is the
upper house.
Executing Laws
It is the job of the state’s council
of ministers to execute the law. The legislative assembly of Tamilnadu is
located at Chennai. The place where a state’s legislative assembly is located
and where its council of ministers function is called the capital of that
state.
The state government has several
lakhs of government employees to execute the laws made by the legislative
assembly- Collectors, Tahsildars, Block Development Officers, Revenue officers,
Village Administrative Officers, Policemen, Teachers and Doctors, etc. All of them
are paid salaries by the state government. They have to follow the orders of
the state government.
Related Topics