Meaning, Applicability, Benefits (or) Advantages, Disadvantages | Auditing - Test Checking | 11th Auditing : Chapter 4 : Audit Planning
Chapter: 11th Auditing : Chapter 4 : Audit Planning
Test Checking
Test Checking
Meaning
Test checking is a process of selecting and
checking of a few transactions from a large volume of transactions. If the
entries checked are found to be correct then the auditor assumes that the
remaining entries are also correct. The technique is based on the theory of
sampling which is commonly used as a statistical method. Checking each and every
transaction that occurs during the year is both redundant and uneconomical for
the auditor. Therefore, the auditor verifies and examines a few representative
transactions in order to obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence to base
his opinion. Test checking reduces the volume of work of the auditor, if in
test checking, the auditor finds that the records checked by him are correct
then no further detailed checking is carried out.
Applicability of Test Checking
Test checking can be applied in the following
situations:
1. When there are large volumes of identical or
routine transactions.
2. When transactions are large.
3. When the auditor has to certify the accounts
quickly after the close of the accounting period.
4. When the auditor has past experience about the
nature of transactions of the clients organisation.
5. When a satisfactory system of internal control
and check system exist.
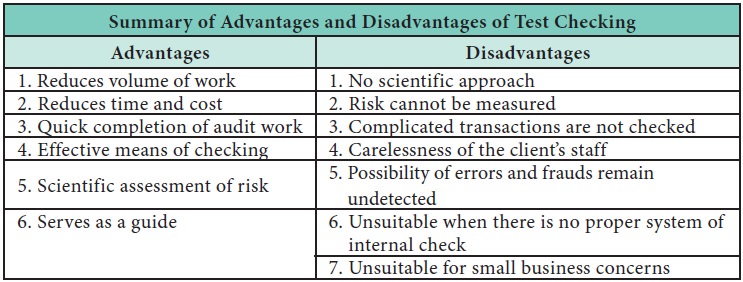
Advantages of Test Checking
Test checking can give the following advantages:
1.
Reduces
Volume of Work: The work of an
auditor is reduced considerable as he checks only few transactions, extra time
available can be utilised for concentrating on areas of considerable
importance.
2.
Reduces
Time and Cost: Test checking
is one of the technique which reduces time, cost and energy of both the
auditor and the client.
3.
Quick
Completion of Audit Work: Test check
enables the auditor to complete the work quickly as the auditor checks only a
few or limited transactions.
4.
Effective
Means of Checking: Test checking
can be effective if the auditor selects the transaction to be checked
carefully.
5.
Scientific
Assessment of Risk: The risk of
material misstatement in the financial statement is assessed by the auditor in
a scientific manner by drawing samples and studying them in detail.
6.
Serves as
a Guide: It serves as a guide for the
auditor to arrive at conclusion regarding the true and fair view of the state
of affairs of business.
Disadvantages of Test Checking
Test checking can give the following dsiadvantages:
1. No Scientific Approach: It is a traditional auditing technique where
no scientific approach is used in selecting the samples, hence the results
drawn on it tends to be incorrect.
2. Risk cannot be measured: It is not
possible to measure the amount of
risk involved.
3. Complicated Transactions are not Checked: The audit
assistants select only simple
transactions for checking and complicated transactions are left omitted.
4. Carelessness of the Client’s Staff: The client’s staff is aware that the
auditor will not check all their work hence they become careless.
5. Possibility of Errors and Frauds Remain Undetected:
When test
check is adopted by the auditor
there are possibility of errors and frauds left undetected.
6. Unsuitable when there is no System of Internal
Check: The auditor cannot adopt test
check when there is no proper system of Internal check and control in
operation.
7. Unsuitable for Small Business Concerns: Test checking is not suitable for small business concerns as the number of transactions involved is not large.
Auditor’s Duty Regarding Test Checking
The following are the auditor’s duty or precautions
to be taken by an auditor while adopting test check:
1.
Entries selected for test checking must be
representative of all transactions and entries on random basis should be
selected for checking.
2.
Auditor should select the test independently
without regard to the suggestions of the client’s staff.
3.
Entries selected for test check should be chosen by
the auditor cautiously by applying his intelligence and professional skill.
4. Test
check should not be adopted in vouching the entries in the cash Book and bank
Pass book.
5. The
auditor should not adopt test check while checking the entries of first and
last month of the year and all the entries must be thoroughly checked.
6. Test
check should be so devised that a sizeable portion of the work done by each
employee is checked.
7.
Auditor should consider his past experiences in
selecting the nature and size of the samples for checking.
Related Topics