Chapter: Human Nervous System and Sensory Organs : Brain's Cerebrovascular and Ventricular Systems
Superficial Cerebral Veins
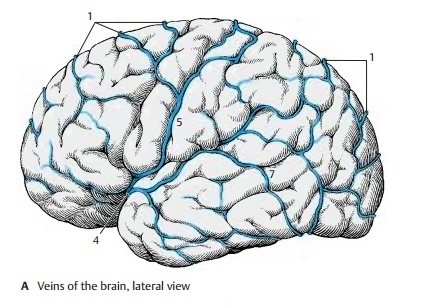
Superficial Cerebral Veins
We distinguish between the group of superior cerebral veins and the group of inferior cerebral veins. The superior cerebral veins (AC1), totaling about 10 – 15 veins, collect the blood from the frontal and parietal lobes and carry it into the superior sagittal sinus (BC2). They run within the subarachnoid space and empty into the lateral lacunae (BC3), pouchlike cavities of the superior sagittal sinus. For a short distance, they pass through the subdural space. Here, the thin-walled veins can easily rupture during head injury and bleed into the subdural space (subdural hematoma). Strangely, the veins empty into the superior sagittal sinus at an oblique angle against the dominating blood flow in the sinus.
The inferior cerebral veins receive the blood from the temporal lobe and from the basal regions of the occipital lobe; they empty into the transverse sinus and the su-perior petrosal sinus. The largest and mostconsistent of these veins is the superficialmiddle cerebral vein (AC4) located in thelateral sulcus; it often consists of several venous trunks. It drains the blood from most of the lateral aspect of the hemisphere into the cavernous sinus.
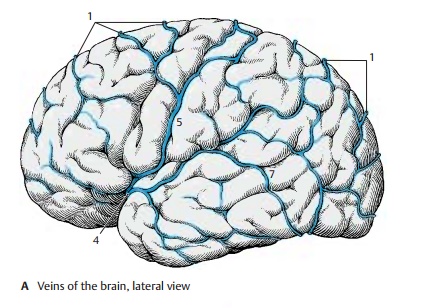
The superior and inferior cerebral veins are interconnected only by a few anastomoses. The most important one is the superior anastomotic vein (Trolard’s vein) (AC5); itempties into the superior sagittal sinus and is connected with the superficial middle cerebral vein. The central vein (C6) located in the central sulcus may also form anasto-moses with the middle cerebral vein. The inferior anastomotic vein (Labbé’s vein,Browning ’s vein) (AC7) connects the super-ficial middle cerebral vein with the trans-verse sinus.
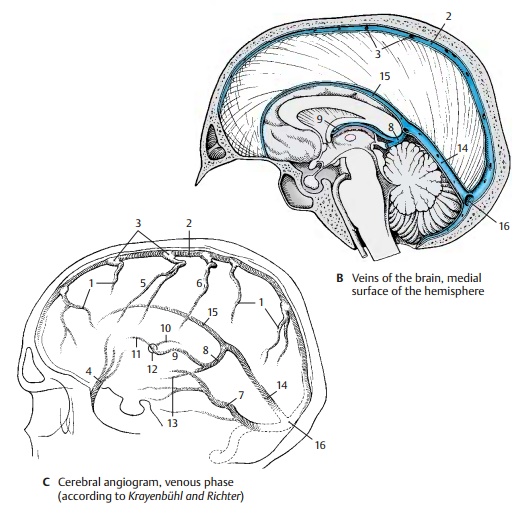
Carotid angiogram (venous phase).A dia-gram of the venous phase of a carotid angio-gram is shown in C (for arterial phase, see p. 272). A radiograph taken only seconds after injection of the contrast medium shows its drainage via the venous vascular tree. Superficial and deep veins are seen in a single plane.
C9 Internal cerebral vein.
C10 Thalamostriate vein (terminal vein).
C11 Vein of the septum pellucidum
C12 Interventricular foramen (foramen of Monro).
C13 Basal vein (Rosenthal’s vein).
BC14 Straight sinus.
BC15 Inferior sagittal sinus.
BC16 Confluence of sinuses.
Related Topics