Chapter: Biology: Structure and Nature of Living Cell
Structure and Functions of Golgi bodies/Golgi apparatus
Golgi bodies/Golgi apparatus:
Golgi bodies may be flat, spherical or elongated. Normally they are present near the nucleus. It was first observed by a scientist named Golgi in 1898 AD in the nerve cells of owl and cat. This organelle is afterward named Golgi apparatus after his name. In plant cells their number is small for which it is not always visible under microscope.
Structure: Golgi apparatus is tubular, small vesicle, vacuolar, elongated vessellike or lamillar bodies. They are vacuolar space bounded by double-layered membrane.
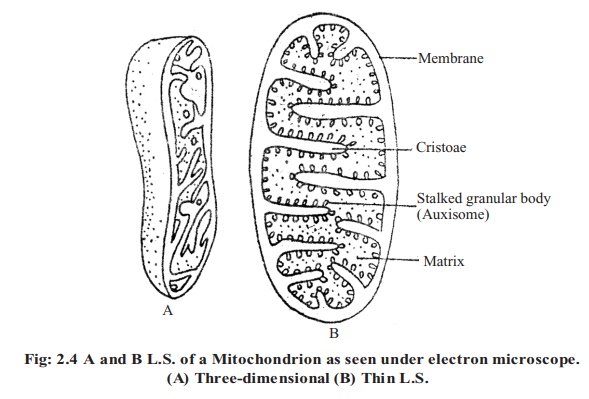
necessary for respiration are well arranged in auxisome. About 70 types of enzymes and 14 types of co-enzymes are present in it. Matrix is also present inside the free space of mitochondria. The main function of mitochondria is to produce energy, like- respiration, oxidative phosphorilation, electron transport system etc.
Function: Function of Golgi bodies are- synthesis of lysosome and non-proteinsubstances, releasing some enzymes, expelling cell water and attaching substances to its membrane produced by endoplasmic reticulum.
Related Topics