Universe and Space Science | Chapter 8 | 8th Science - Rockets | 8th Science : Chapter 8 : Universe and Space Science
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 8 : Universe and Space Science
Rockets
Rockets
The universe is a great mystery to
all of us. Our mind always tries to know about the space around us.
Understanding the space will be helpful to us in many ways. Space research
provides information to understand the environment of the earth and the
changing climate and weather on the earth. Exploring the space will help us to
answer many of the challenges we are facing these days. Discovery of rockets
has opened a small portion of the universe to us.
Rockets help us to launch space
probes to explore the planets in the solar system. They also help us to launch
space-based telescopes to explore the universe. More than all rockets enable us
to put satellites, which are useful to us in a number of ways. Our country has
effective rocket technology and has applied it successfully to provide so many
space services globally.
Rockets were invented
in China, more than 800 years ago. The first rockets were a cardboard tube
packed with gunpowder. They were called fire arrows. In 1232 AD, the Chinese
used these ŌĆśfire arrowsŌĆÖ to defeat the invading Mongol army. The knowledge of
making rockets soon spread to the Middle East and Europe, where they were used
as weapons.
1. Parts of Rockets
A rocket is a space vehicle with a
very powerful engine designed to carry people or equipment beyond Earth and out
into space. There are four major parts or systems in a rocket. They are:
* Structural system
* Payload system
* Guidance system
* Propulsion system
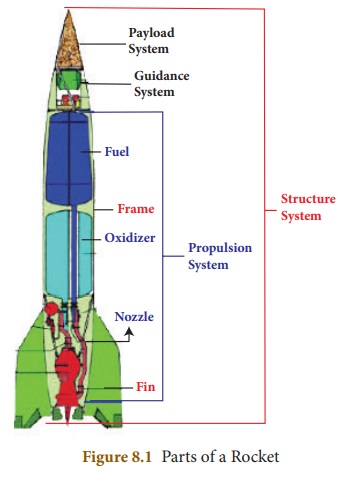
Structural
system (Frame)
The structural system is the frame
that covers the rocket. It is made up of very strong but light weight materials
like titanium or aluminum. Fins are attached to some rockets at the bottom of
the frame to provide stability during the flight.
Payload
system
Payload is the object that the
satellite is carrying into the orbit. Payload depends on the rocketŌĆÖs mission.
The rockets are modified to launch satellites with a wide range of missions
like communications, weather monitoring, spying, planetary exploration, and as
observatories. Special rockets are also developed to launch people into the
EarthŌĆÖs orbit and onto the surface of the Moon.
Guidance
system
Guidance system guides the rocket in
its path. It may include sensors, on-board computers, radars, and communication
equipments.
Propulsion
system
It takes up most of the space in a
rocket. It consists of fuel (propellant) tanks, pumps and a combustion chamber.
There are two main types of propulsion systems. They are: liquid propulsion
system and solid propulsion system.
Polar Satellite Launch
Vehicl (PSLV) and Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) rockets are
IndiaŌĆÖs popular rockets.
Activity 1
Make a model of a
rocket using the low cost materials available to you. Also prepare an album of
the rockets launched by India.
2. Types of Propellants
A propellant is a chemical substance
that can undergo combustion to produce pressurized gases whose energy is
utilized to move a rocket against the gravitational force of attraction. It is
a mixture, which contains a fuel that burns and an oxidizer, which supplies the
oxygen necessary for the burning (combustion) of the fuel. The propellants may
be in the form of a solid or liquid.
a.
Liquid propellants
In liquid propellants, fuel and
oxidisers are combined in a combustion chamber where they burn and come out
from the base of the rocket with a great force. Liquid hydrogen, hydrazine and
ethyl alcohol are the liquid fuels. Some of the oxidizers are oxygen, ozone,
hydrogen peroxide and fuming nitric acid.

b.
Solid propellants
In solid rocket propellants, fuel
and oxidiser compounds are already combined. When they are ignited they burn
and produce heat energy. Combustion of solid propellants cannot be stopped once
it is ignited. Solid fuels used in rockets are polyurethanes and poly
butadienes. Nitrate and chlorate salts are used as oxidizers.
c.
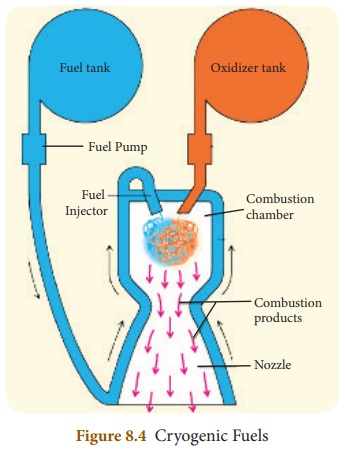
Cryogenic propellants
In this type of fuel, the fuel or
oxidizer or both are liquefied gases and they are stored at a very low
temperature. These fuels do not need any ignition system. They react on mixing
and start their own flame.
3. Launching of Satellite
Activity 2
Take a balloon and
blow air into it. Now let the air inside the balloon to come out. What do you
observe? You can see the balloon moving in a direction opposite to the
direction of the air. Rocket also moves almost similar to this.
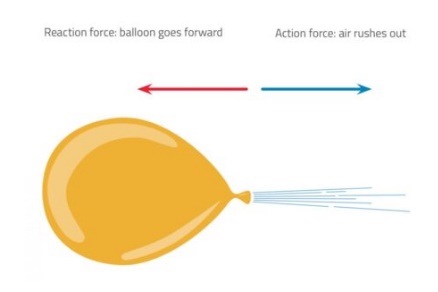
In this experiment, a rocket launch is illustrated by blowing up
a balloon and letting it go. The escaping air exerts a force on the balloon,
and the balloon reacts by pushing in the opposite direction with the same
force, as described by NewtonŌĆÖs third law of motion (for every action, there is
an equal and opposite reaction). The opposing force (as with rocket thrust)
propels the balloon forward (figure 1). To make the demonstration more
controlled, the balloon is attached to a line made from string.
Before being launched into the
space, rockets will be held down by the clamps on the launching pad. Manned or
unmanned satellites will be placed at the top of the rocket. When the fuel in
the rocket is burnt, it will produce an upward thrust. There will be a point at
which the upward thrust will be greater than the weight of the satellite. At
that point the clamp will be removed by remote control and the rocket will move
upwards. According to NewtonŌĆÖs third law, for every action there is an equal
and opposite reaction. As the gas is released downward, the rocket will move
upward.
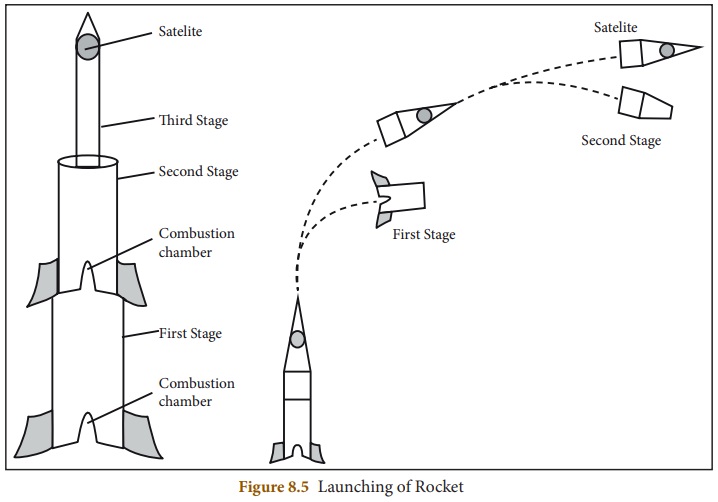
To place a satellite in a particular
orbit, a satellite must be raised to the desired height and given the correct
speed and direction by the launching rocket. If this high velocity is given to
the rocket at the surface of the Earth, the rocket will be burnt due to air friction.
Moreover, such high velocities cannot be developed by a single rocket. So,
multistage rockets are used. To penetrate the dense lower part of the
atmosphere, initially the rocket rises vertically and then it is tilted by a
guidance system.
Related Topics