Term 2 Unit 1 | Geography | 7th Social Science - Resources | 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 2 Unit 1 : Resources
Chapter: 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 2 Unit 1 : Resources
Resources
GEOGRAPHY
Unit – I
Resources

Learning Objectives
• To know the importance of
resources
• To describe the renewable
resources
• To understand the non-renewable
resources
• To identify the fossil fuel
resources
Introduction
A country’s social, economic and political strength
lies in the distribution, utilization and conservation of its resources. Anything
which can be used for satisfying the human needs I called resource. Natural resources
are resources that exist without action of humankind. Natural resources are obtained
from environment. Many natural resources are essential for human survival. Resources
always cannot be consumed in their original form, but they must be processed into
usable commodities and usable things.
Importance of resource
• Natural resources satisfy daily needs of man such
as food, clothing and shelter.
• Natural resources also contribute immensely to boost up nation’s economy.
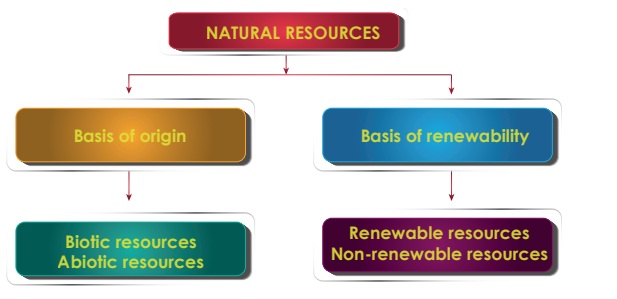
On the basis of origin, resources may be divided into
two types. They are:
1. Biotic resources
2. Abiotic resources
1. Biotic resources
Biotic resources are found in the biosphere which are
obtained from living and organic materials. It includes forests, crops, birds, animals,
fishes, man and materials that can be obtained from them. Fossil fuels such as coal
and petroleum are also included in this category because they are formed from decayed
organic matter.
2. Abiotic resources
Abiotic resources are the non-living parts of an environment.
Examples of abiotic resources include land, water, air, sunlight and heavy metals
including ores such as gold, iron, copper, silver etc.
On the basis of renewability, resources can be divided
into two types. They are:
1. Renewable resources
2. Non - renewable resources
1. Renewable resources
A renewable resource is a resource which
can be used repeatedly and replaced naturally. Renewable resources harvested and
used rationally will not produce pollution. The use of renewable resources and energy
sources is increasing worldwide.
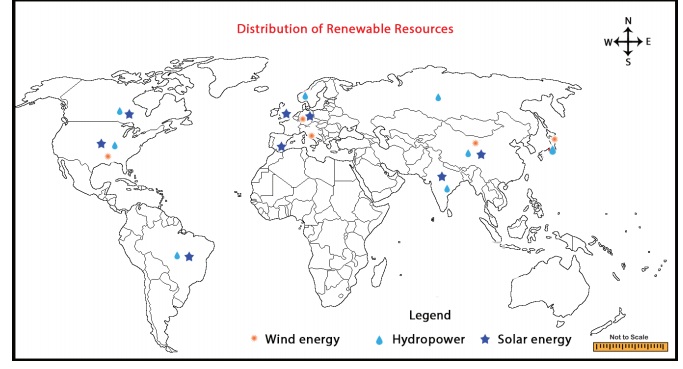
Example: solar energy, wind energy, and hydropower.
Solar energy
The sun produces energy in the form of
heat and light. Solar energy is not harmful to the environment. Photovoltaic devices
or solar cells, directly convert solar energy into electricity. Individual solar
cell in group panel can perform small applications from charging calculator, watch
batteries, to large such as to power residential dwellings. Photovoltaic power plants
and concentrating solar power plants are the largest solar applications covering
acres. India, China, Japan, Italy and States of America are major utilizers of solar
energy in the world.
Kamuthi solar power project is one of
the largest solar powerprojects in the world. It is situated in Ramanathapuram District
in Tamilnadu. The Kamuthi solarower project was completed on 21st September 2016.
Investment of this project is around 4,550 Crores. The installed capacity of this
project is 648 MW.

Hydropower
Water is considered as a great source of energy. At present, water is used for producing hydroelectric power. Hydroelectricity is generated from moving water with high velocity and great falls with the help of turbines and dynamos. Hydroelectricity power is the cheapest and most versatile source of energy out of all the known energy. Hydroelectric power is a renewable resource. China, Canada, Brazil, United States of America, Russia, India, Norway and Japan are some countries producing hydroelectricity. China is the largest producer of hydro-electricity.

S. No. Hydro - electricity project Installed Capacity(MW) State
1. Tehri Dam - 2,400 MV - Uttarakhand
2. Srisailam Dam - 1,670 MV - Andhra Pradesh
3. Nagarjuna Sagar Dam - 960 MV - Andhra Pradesh
4. Sardar Sarovar Dam - 1,450 MV - Gujarat
5. Bhakra Nangal Dam - 1,325 MV - Punjab
6. Koyna Dam - 1,960 MV - Maharashtra
7. Mettur dam - 120 MV - Tamil Nadu
8. Idukki dam - 780 MV - Kerala
S.No. Name of the Project Country River Installed Capacity in MW
1. Three gorges Dam - China - Yangtze River - 22,500 MV
2. Itaipu Dam - Brazil and Paraguay - Parana River - 14,000 MV
3. Xiluodu Dam - China - Jinsha River - 13,860 MV
4. Guri Dam - Venezuela - Caroni River - 10,235 MV
5. Tucurui Dam - Brazil - Tocantins River - 8,370 MV
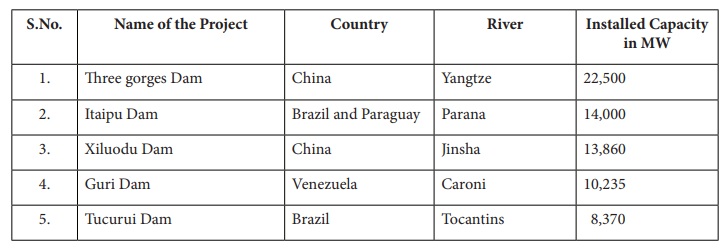
Three Gorges Dam in China is the largest hydroelectricity project in the world. It’s construction started in 1994 and ended in 2012. The installed capacity ofthe dam is 22,000MW.

Wind energy
Wind
power is clean
energy since wind
turbines does not
produce any emissions.
In recent years,
wind energy has
become one of the
most economical and renewable energy technologies. The Classic Dutch windmill harnessed
the wind’s energy
hundreds of years
ago. Modern wind turbines with three blades dot the landscape today,
turning wind into electricity. Major wind energy producing countries are United States,
China, Germany, Spain,
India, United Kingdom, Canada and
Brazil.

Major wind farms in India
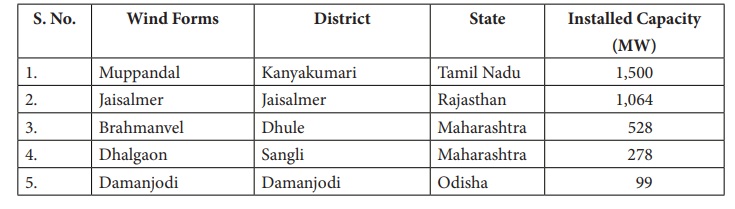
2. Non-renewable resources
Natural
resources that once consumed and cannot be replaced is called non-renewable resources.
Continuous consumption of non-renewable resources ultimately leads to exhaustion.
Examples of non-renewable resources include fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum,
natural gas and mineral resources such as iron, copper, bauxite, gold, silver and
others. Non-renewable resources can be divided into three types. They are:
•
Metallic resources
•
Non - Metallic resources
•
Fossil fuel resources
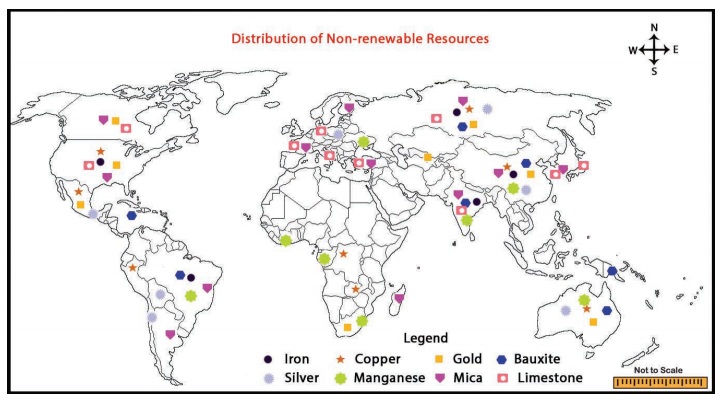
Metallic resources
Metallic resources are the type of resources
that are composed of metals. These are hard substances, which are the good conductors
of heat and electricity. Example for metallic resources are iron, copper, gold,
bauxite, silver, manganese, etc.
Iron
Iron is the fourth most common element
in the Earth’s crust and the most widely available metal. Magnetite and hematite
are the common ore for iron, which occurs normally in the rocks of the crust. Iron
ore is the key raw material in making steel and 98% of the iron ore extracted is
used to make Steel. Pure iron ore is very soft, but its strength is increased many
folds by adding small amount of carbon and manganese. It’s low cost and high earth
strength makes it usable in engineering applications, such as the construction of
machinery and machine tools, automobiles, construction of large ships, structural
components of building, bridges etc.
Iron ore is mined in about 50 countries.
Among the iron ore producing countries China, Australia, Brazil, India and Russia
are the principal producers accounting for 85% of the world’s total output of iron
ore. These countries have 70% of the total reserves of the world. Jharkhand, Odisha,
Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka and Goa account for over 95 per cent of
the total reserves of India. Iron ores found at Kanjamalai in Tamil Nadu.
Copper
Copper is one of the first metals known
and used by man. Copper ranks as the third most consumed industrial metal in the
world after Iron and Aluminium. Copper is good conductor of heat and electricity.
About three quarters of copper is used to make electrical wires, telecommunication
cables and electronics.
Chile is the world’s number one country
in the production of copper. Other copper producing countries are Peru, China, United
States, Congo and Australia.
Gold
It is a rare and precious metal. Hence,
it has high demand in world markets. Formerly, it was used for minting coins, but
now it is used for making ornaments and in dentistry. It is regarded as a symbol
of prosperity and a form of wealth.
China is the world’s largest producer
of gold. Also, Australia, Russia, United States, South Africa and Canada are the
major producers of gold. Among these countries, Australia has 9500 tons reserves
of gold ore and it is world’s leading country in gold ore reserves. Karnataka is
the largest producer of gold in India. Kolar Gold Field is one of the deepest mines
of the world.

Bauxite
Aluminium is produced from bauxite ore.
There are several ores that contain aluminium but bauxite contains more aluminium.
Aluminium has wide range of uses compared to other metals. Aluminium is light in
weight, tough and cheaper, which makes it popular metal for constructional purpose.
It is mainly used in the construction of aircrafts, ship, automobiles, railway coaches
and etc. Aluminium is a good conductor of electricity and heat, hence, it is used
for making electrical cables. It is highly resistant to corrosion. By the addition
of small quantities of other metals to aluminium, it creates superior alloy than
pure aluminium.E.g: Duralumin.
Australia is the world’s leading bauxite
producer. Apart from that, China, Brazil, India, Guinea, Jamaica and Russia also
play an important role in bauxite production. One fourth of the bauxite mineral
deposits found in Guinea alone. Odisha, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh,
Tamil Nadu and Madhya Pradesh are the main bauxite producing states in India. The
bauxite deposits are mainly found in the Shervaroy hills of Salem district, Tamil
Nadu.
Silver
Silver is also a precious metal like
gold. It has a wider variety of uses than gold. It is used in making jewellery,
dentistry, photographic goods, electroplating industry and in the manufacture of
luxury goods. About two-third of silver is used for monetary purposes. Like gold,
silver also resists corrosion.
Mexico is the world’s leading silver
producer. Following Mexico, Peru, China, Russia, Australia and Chile produce more
silver. More than 50% of silver is found only in South American countries.
Manganese
Manganese is a steel-greyed, hard, shiny
and brittle metal. The common ores of manganese are Pyrolusite Manganese, Psilomelane
and Rhodochrosite. Manganese is essential for the production of good quality Steel.
Manganese is used in making electrical batteries. It is also used as colouring material
in bricks, pottery, floor tiles. Manganese compounds are used in making disinfecting
liquids, bleaching powder, fertilizers etc.
South Africa is the world’s leading producer
of manganese. The significant producers of manganese in the world are China, Australia,
Gabon, Brazil and India. All these producers have large reserves of manganese and
are significant exporters in the world.
Non-metallic resources
Non-metallic resources can be described
as the resources that do not comprise of metals. These are not hard substances,
and are not good conductors of heat and electricity. Example for non-metallic resources
are mica, limestone, gypsum, dolomite, phosphate, etc.
Mica
Muscovite and Biotite are the common
ores of Mica. It is one of the indispensable minerals used in electrical and electronics
industry. It is used as an insulating material in electrical industry. In powder
form, it is used for making lubricating oils and decorative wallpapers.
China is the world’s top producer of
mica. Russia, Finland, United States, Turkey and Republic of Korea also play a major
role in the production of mica. About 95 per cent of India’s mica is found in just
three states of Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan and Jharkhand.
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock, composed
mainly by skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral, foraminifera and
molluscs. About 10% of sedimentary rocks are limestones. Mostly limestone is made
into crushed stone and used as a construction material. It is used for facing stone,
floor tiles, stair treads, windows sills and many other purposes. Crushed limestone
is used in smelting and other metal refining process. Portland cement is made from
limestone.
China produces more than half of limestone
production in the world. Beside this, United States, India, Russia, Brazil and Japan
also produce more Limestone. Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat,
Chhattisgarh and Tamil Nadu Produce over three-fourths of the total limestone of
India. In Tamil Nadu, Large scale limestone reserve found in Ramanathapuram, Tirunelveli,
Ariyalur, Salem, Coimbatore and Madurai districts.
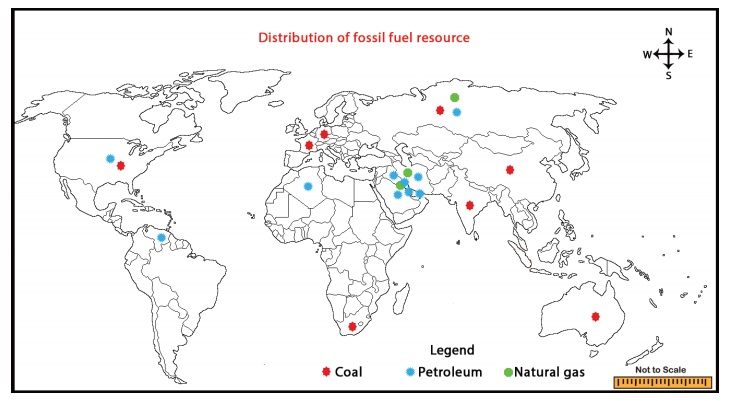
Fossil fuel resources
Fossil fuel resources are normally formed
from the remains of dead plants and animals. They are often referred to as fossil
fuels and are formed from hydrocarbon. When fossil fuels are burned, they become
a great source of heat energy. Example for fossil fuel resources are coal, petroleum
and natural gas.
Coal
This is the most abundantly found fossil
fuel the then dead plant matter is converted into peat. It is used as a domestic
fuel, in industries such as iron and steel, steam engines to generate electricity.
Electricity produced from coal is called Thermal Power. Coal is classified into
four types based on carbon content. They are:
•
Anthracite
•
Bituminous
•
Lignite
•
Peat.
The leading coal producers of the world
is China. Beside this, India, USA, Australia, Indonesia and Russia also produce
more coal. The coal producing areas of India are Raniganj in West Bengal, Neyveli
in Tamil Nadu, Jharia, Dhanbad, and Bokaro in Jharkhand.
Most of the coal deposite that we use now, where formed about 300
million years ago. Much of the earth was covered with steamy swamps. As the plants
and trees are dead, their remains were buried underneath the swamps. Eventually,
they were transformed into coal beneath the ground due to excessive heat and pressure.

Petroleum
Petroleum is found between the layers
of rocks and is drilled from oil fields located in Offshore and coastal areas. This
is sent to refineries which process crude oil and produce variety of products like
diesel, petrol, kerosene, wax, plastics and lubricants. Petroleum and its derivatives
are called Black Gold as they are very valuable.
The chief petroleum producing countries
are Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq and Qatar. The other major producers are USA, Russia,
Venezuela, Kuwait, UAE and Algeria. The leading producers in India are Digboi in
Assam, Bombay High in Mumbai and the deltas of Krishna and Godavari rivers.

Natural gas
Natural gas is found with petroleum deposits
and is released when crude oil is brought to the surface. It can be used as a domestic
and industrial fuel.
More than 50% of the global natural gas
reserves are found in United States of America, Russia, Iran and Qatar.
In India, Krishna and Godavari Delta,
Assam, Gujarat and some areas of offshore in Mumbai have natural gas resources.
Wrap up
1. Natural resources are obtained from environment.
2 .Renewable resources can be used repeatedly and replaced
naturally.
3. Non-renewable resources once consumed, cannot be
replaced.
4. Solar energy is not harmful to the environment.
5. Hydroelectricity is generated from moving water
with high velocity and great falls with the
help of a turbines and dynamos.
6. Metallic resources are iron, copper, gold, bauxite,
silver, manganese etc.
7. Non-metallicresourcesaremica,limestone, gypsum,
dolomite, phosphate, etc.
8. Fossil fuels resources are normally formed from
the remains of dead plants and animals.
Glossary
1. Biotic
resources: obtained from living and
organic materials உயிரியல் வளங்கள்
2. Abiotic
resources: obtained from non-living, non-organic materials உயிரற்ற வளங்கள்
3. Hydroelectricity:
generated from moving water with high velocitand great falls with the help of
turbines and dynamos நீர் மின் சக்தி
4. Metallic
resources: resources that are composed of metals உலோகக வளங்கள்
5. Non-metallic
resources: resources that do not comprise of metals உலோககம் அல்லாத வளங்கள்
6. Duralumin:
a hard, light alloy of aluminium with copper and otherelements துராலுமின்
7. Fossil
fuel: formed from the remains of dead plants and animals படிம எரிபபோருள்
8. Thermal
Power: Electricity produced from coal அனல் மின் சக்தி
9. Black
Gold: Petroleum and its derivatives ககருப்புத் தங்கம்
10. Precious
metal: a metal that is valuable and usually rare விலை மதிப்பற்ற உலோககம்
References
1. K. Siddartha (2016), Economic Geography, Kitab
Mahal Publications, New Delhi.
2. H.M Saxena (2013), Economic Geography, Rawat
Publications, New Delhi.
3. Majid Husain (2012), World Geography, Rawat
Publications, New Delhi.
4. www.usgs.gov (2015) United States Geological
Survey, Reston, USA
Related Topics