Chapter: Civil : Repair and Rehabilitation of Structures : Maintenance and Repairs Strategies
Repair and rehabilitation of Structures
Repair and rehabilitation
Repair is the technical aspect of
rehabilitation. It refers to the modification of a structure, partly or wholly
which is damaged in appearance or serviceability.
The following factors to be considered repair of
concrete structures:
ü The cause
of damage
ü Type,
shape and function of the structure
ü The
capabilities and facilities available with builders
ü The
availability of repair materials
1Stages of concrete repair
Repair of concrete structures is
carried out in the following stages:
ü Removal
of damaged concrete
ü Pre
treatment of surfaces and reinforcement
ü Application
of repair material
ü Restoring
the integrity of individual sections and strengthening of structure as a whole
2 Repair
procedure
A repair
procedure may be selected to accomplish on or more of the following objectives:
ü To
increase strength or restore load carrying capacity
ü To
restore or increase stiffens
ü To
improve functional performance
ü To
provide water tightness
ü To
improve durability
ü To
prevent access of corrosive material to reinforcement
3 Types and classification of repair Types of
repair:
ü Cosmetic
treatments on surfaces
ü Partial
replacement of surface and subsurface material
ü
Additional of reinforcements and bonding materials
to strengthen the element
ü
Total replacement of the structural element
Classification of repair:
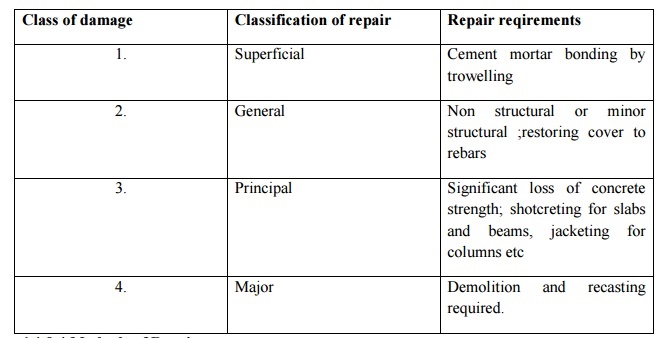
Classification
of repair : Repair reqirements
Superficial
: Cement mortar bonding by trowelling
General
: Non structural or minor structural
;restoring cover to rebars
Principal
: Significant loss of concrete strength;
shotcreting for slabs and beams, jacketing
for columns etc
Major :
Demolition and recasting required.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 4 Methods of Repairs
4 Methods of Repairs
The
following considerations are to be taken care of and observed:
ü Determination
of extent, location and width of cracks
ü Classification
of cracks as structural and non-structural
Dormant cracks:
Dormant cracks are caused by some event in the part, which is
not expected to recur. They remain constant in width, and may be repaired by
filling then with a rigid material.
Active cracks:
Do not remain constant in width, but open and close as the
structure in loaded, or due to thermal and hydras changes in the concrete.
Growth cracks:
Increase in width becomes the
original reason for their occurrence persists.
5 Applications:
The repair of cracks can be achieved with the
following techniques:
ü Resin
injection
ü Routing
and Sealing
ü Stitching
ü External
stressing
ü Bonding
ü Blanketing
ü Overlays
ü Dry pack
ü Vacuum
impregnation
ü Polymer
impregnation
6 Rehabilitations
The success of repair activity
depends on the identification of the root cause of the deterioration of the
concrete structures. The repairs can be done for the improvement of strength
and durability, thus extending the life of the structure, is not difficult to
achieve.
It is the processes of restoring
the structure to service level, once it had and now lost, strengthening
consists in endowing the structure with a service level, higher than that
initially planned by modifying the structure not necessarily damaged area.
The following steps are generally
used in the rehabilitation of distressed concrete structure:
ü Support
the structural members properly as required.
ü Remove
all cracked, spalled and loose concrete.
ü Clean the
exposed concrete surfaces and steel reinforcement
ü Provide
additional reinforcing bars, if the loss in reinforcement is more than 10%
ü Apply
protective coatings over the exposed/repaired surface.
Applications:
ü Shotcrete/Gunite
ü Resin
injection
ü Dry pack
and Epoxy-bonded dry pack
ü Slab
jacking Technique
ü Sprayed
concrete
Related Topics