Python - Python Variables and Operators: Book Back Questions and Answers | 12th Computer Science : Chapter 5 : Core Python : Python Variables and Operators
Chapter: 12th Computer Science : Chapter 5 : Core Python : Python Variables and Operators
Python Variables and Operators: Book Back Questions and Answers
Computer Science : Core Python : Python Variables and Operators
Evaluation
Part – I
Choose the best answer (1 Marks)
1.Who developed Python ?
A) Ritche
B) Guido Van Rossum
C) Bill Gates
D) Sunder Pitchai
2. The Python prompt indicates that Interpreter is ready to accept instruction.
A) >>>
B) <<<
C) #
D) <<
3. Which of the following shortcut is used to create new Python Program ?
A) Ctrl + C
B) Ctrl + F
C) Ctrl + B
D) Ctrl + N
4. Which of the following character is used to give comments in Python Program ?
A) #
B) &
C) @
D) $
5. This symbol is used to print more than one item on a single line.
A) Semicolon(;)
B) Dollor($)
C) comma(,)
D) Colon(:)
6. Which of the following is not a token ?
A) Interpreter
B) Identifiers
C) Keyword
D) Operators
7.Which of the following is not a Keyword in Python ?
A) break
B) while
C) continue
D) operators
8.Which operator is also called as Comparative operator?
A) Arithmetic
B) Relational
C) Logical
D) Assignment
9.Which of the following is not Logical operator?
A) and
B) or
C) not
D) Assignment
10. Which operator is also called as Conditional operator?
A) Ternary
B) Relational
C) Logical
D) Assignment
Part – II
Answer the following questions : (2 Marks)
1. What are the different modes that can be used to test Python Program ?
Ans. The modes that can be used to test Python program are
(i) Interactive mode
(ii) Script mode
2. Write short notes on Tokens.
Ans. Python breaks each logical line into a sequence of elementary
lexical components known as Tokens. The normal token types are
(i) Identifiers,
(ii) Keywords,
(iii) Operators,
(iv) Delimiters and
(v) Literals.
3. What are the different operators that can be used in Python ?
Ans. The operators that can be used in Python
(i) Arithmetic operators
(ii) Relational or Comparative operator
(iii) Logical operators
(iv) Assignment operators
(v) Conditional operator
4. What is a literal? Explain the types of literals ?
Ans. Literal is a raw data given in a variable or constant. In
Python, there are various types of literals.
(i) Numeric
(ii) String
(iii) Boolean
5. Write short notes on Exponent data?
Ans. An Exponent data contains decimal digit part, decimal point,
exponent part followed by one or more digits.
Example: 12.E04, 24.e04.
Part – III
Answer the following questions : (3 Marks)
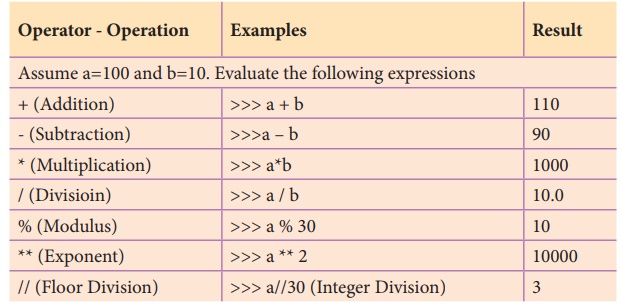
1. Write short notes on Arithmetic operator with examples.
Ans. (i) An arithmetic operator is a mathematical operator that
takes two operands and performs a calculation on them. They are used for simple
arithmetic.
(ii) Most computer languages contain a set of such operators
that can be used within equations to perform different types of sequential
calculations.
(iii) Python supports the following Arithmetic operators.
2. What are the assignment operators that can be used in Python?
Ans. (i) In Python, = is a simple assignment operator to assign
values to variable. Let a = 5 and b
= 10 assigns the value 5 to a and 10
to b these two assignment statement
can also be given as a,b=5,10 that
assigns the value 5 and 10 on the right to the variables a and b respectively.
(ii) There are various .compound operators in Python like +=,
-=, *=, /=, %=, **= and //= are also available.
3. Explain Ternary operator with examples.
Ans. (i) Ternary operator is also known as conditional operator that
evaluate something based on a condition being true or false.
(ii) It simply allows testing a condition in a single line
replacing the multiline if-else making the code compact.
Variable Name = [on_true] if [Test expression] else [on_false]
(iii) Example:
min = 50 if 49 < 50 else 70 // min = 50
min = 50 if 49 > 50 else 70 // min = 70
4. Write short notes on Escape sequences with examples.
Ans. (i) ' In Python strings, the backslash "\" is a
special character, also called the ’’escape”
character.
(ii) It is used in representing certain whitespace characters: ”\t” is a tab, ”\n” is a newline, and ”\r”
is a carriage return.
(iii) For example to print the message "It's raining",
the Python command is
>>> print ("It\'s raining")
It's raining
5. What are string literals? Explain.
Ans. (i) In Python, a string literal is a sequence of characters
surrounded by quotes. Python supports single, double and triple quotes for a
string.
(ii) A character literal is a single character surrounded by
single„or double quotes. The value with triple-quote "' "' is used to
give multi-line string literal.
To test String Literals:
# Demo Program to test String Literals
strings = "This is Python"
char = "C"
multiline_str = "'This is a multiline string with more than
one line code.'"
print (strings)
print (char)
print (multiline_str)
#End of the Program
Output:
This is Python
C
This is a multiline string with more than one line code.
Part – IV
Answer the following questions : (5 Marks)
1. Describe in detail the procedure Script mode programming.
Ans. A script is a text file containing the Python statements.
Python Scripts are reusable code. Once the script is created, it can be
executed again and again without retyping. The Scripts are editable.
Creating Scripts in Python:
(i) Choose File → New File or press Ctrl + N in Python shell
window.
A - A script is a text frame
R - Text file contain
Python script
(1) All text file does not Python scripts
(2) All text file must contain Python script
(3) A is T B
(ii) An untitled blank script text editor will be displayed on
screen.
(iii) Type the code in Script editor
Saving python script:
(i) Choose File → Save or press Ctrl+S
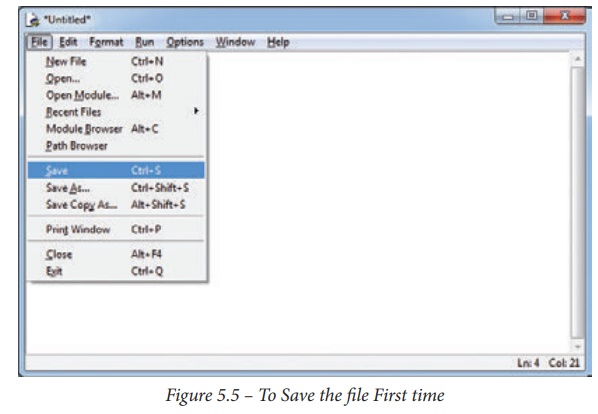
(ii) Now, Save As
dialog box appears on the screen.
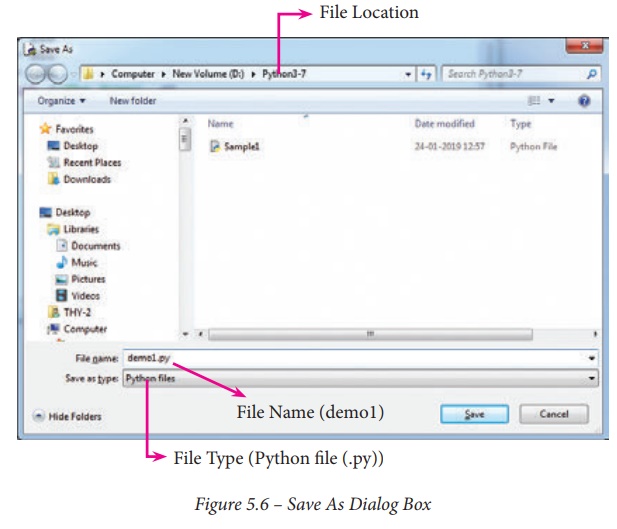
(iii) In the Save As
dialog box, select the location where you want to save your Python code, and
type the file name in File Name box.
Python files are by default saved with extension .py. Thus, while creating Python scripts using Python Script editor,
no need to specify the file extension.
(iv) Finally, click Save button
to save your Python script.
Executing Python Script:
(i) Choose Run→Run Module or
press F5
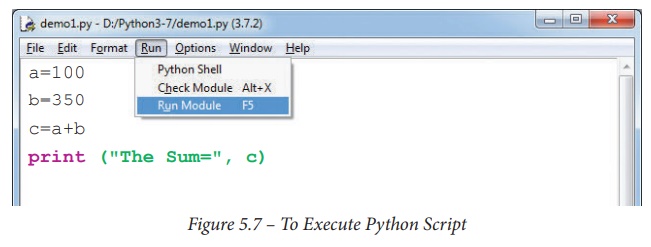
To Execute Python Script
(ii) If code has any error, it will be shown in red color in the
IDLE window," and Python describes the type of error occurred. To correct
the errors, go back to Script editor, make corrections, save the file using Ctrl + S or File → Save and execute it again.
(iii) For all error free code, the output will appear in the
IDLE window of Python.
2. Explain input() and print() functions with examples.
Ans. Input and Output
Functions: A program needs to interact with the user to accomplish the
desired task; this can be achieved using Input- Output functions. The input()
function helps to enter data at run time by the user and the output function
print() is used to display the result of the program on the screen after
execution.
The input() function :
(i) In Python, input( ) function is used to accept data as input
at run time. The syntax for input() function is,
Variable = input (“prompt string”)
(ii) Where, prompt string in the syntax is a statement or
message to the user, to know what input can be given.
(ii) If a prompt string is used, it is displayed on the monitor;
the user can provide expected data from the input device. The input( ) takes
whatever is typed from the keyboard and stores the entered data in the given
variable.
(iv) If prompt string is not given in input() no message is
displayed on the screen, thus, the user will not know what is to be typed as
input.
(v) Example 1 : input() with prompt string
>>> city=input (“Enter Your City:”)
Enter Your City: Madurai
>>> print (“I am from “, city)
I am from Madurai
(v) Example 2 : input() without prompt string
>>> city=input
Madurai
>>> print (“I am
from “, city)
I am from Madurai
(vii) Note that in example-2, the input( ) is not having any
prompt string, thus the user will not know what is to be typed as input. If the
user inputs irrelevant data as given in the above example, then the output will
be unexpected. So, to make your program more interactive, provide prompt string
with input().
(viii)The input ( ) accepts all data as string or characters but
not as numbers. If a numerical value is entered, the input values should be
explicitly converted into numeric data type. The int( ) function is used to convert
string data as integer data explicitly. We will learn about more such functions
in later chapters.
(ix) Example 3 :
x = int (input(“Enter Number 1: ”))
y = int (input(“Enter Number 2: ”))
print (“The sum = ”, x+y)
(x) Output:
Enter Number 1: 34
Enter Number 2: 56
The sum = 90
(xi) Example 4: Alternate method for the above program
x,y=int (input("Enter Number 1 :")),
int(input("Enter Number 2:"))
print ("X = ",x," Y = ",y)
(xii) Output:
Enter Number 1:30
Enter Number 2:50
X = 30 Y = 50
The print() function :
(i) In Python, the print() function is used to display result on
the screen. The syntax for print() is as follows :
(ii) Example :
print (“string to be displayed as output ” )
print (variable)
print (“String to be displayed as output ”, variable)
print (“Stringl ”, variable, “String 2”, variable, “String 3”
......)
(iii) Example :
>>> print (“Welcome to Python Programming”)
Welcome to Python Programming
>>>x = 5
>>>y = 6
>> >z = x + y
>>> print (z)
11
>>> print (“The sum = ”, z)
The sum =11
>>> print (“The sum of”, x, “ and ”, y, “ is ”, z)
The sum of 5 and 6 is 11
(iv) The print ()
evaluates the expression before printing it on the monitor.
(v) The print () displays an entire statement which is specified
within print (). Comma (,) is used as
a separator in print () to print
more than one item.
3. Discuss in detail about Tokens in Python
Ans. Python breaks each logical line into a sequence of elementary
lexical components known as Tokens.
The normal token types are
(i) Identifiers,
(ii) Keywords,
(iii) Operators,
(iv) Delimiters and
(v) Literals.
(i) Identifiers :
■ An Identifier is a name used to identify a variable, function,
class, module or object.
■ An identifier must start with an alphabet (A..Z or a..z) or
underscore (_).
■ Identifiers may contain digits (0 .. 9).
■ Python identifiers are case sensitive i.e. uppercase and
lowercase letters are distinct.
■ Identifiers must not be a python keyword.
■ Python does not allow punctuation character such as %,$, @
etc., within identifiers.
(ii) Keywords:
Keywords are special words used by Python interpreter to recognize the
structure of program. As these words have specific meaning for interpreter,
they cannot be used for any other purpose.
(iii) Operators: In
computer programming languages operators are special symbols which represent
computations, conditional matching etc. The value of an operator used is called
operands. Operators are categorized
as Arithmetic, Relational, Logical, Assignment etc. Value and variables when
used with operator are known as operands.
(iv) Delimiters: Python uses the symbols and symbol combinations as delimiters
in expressions, lists, dictionaries and strings. Following are the delimiters.
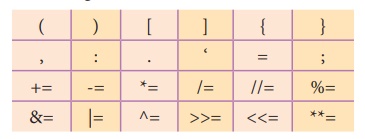
(v) Literals :
Literal is a raw data given in a variable or constant. In Python, there are
various types of literals.
■ Numeric
■ String
■ Boolean.
Related Topics