Chapter: 12th Computer Science : Chapter 7 : Core Python : Python Functions
Python Functions: Book Back Questions and Answers
Computer Science : Core Python : Python Functions
Evaluation
Part – I
Choose the best answer: (1 Mark)
1.A named blocks of code that are designed to do one specific job is called as
(a) Loop
(b) Branching
(c) Function
(d) Block
2.A Function which calls itself is called as
(a) Built-in
(b) Recursion
(c) Lambda
(d) return
3. Which function is called anonymous un-named function
(a) Lambda
(b) Recursion
(c) Function
(d) define
4. Which of the following keyword is used to begin the function block?
(a) define
(b) for
(c) finally
(d) def
5. Which of the following keyword is used to exit a function block?
(a) define
(b) return
(c) finally
(d) def
6. While defining a function which of the following symbol is used.
(a) ; (semicolon)
(b) . (dot)
(c) : (colon)
(d) $ (dollar)
7.In which arguments the correct positional order is passed to a function?
(a) Required
(b) Keyword
(c) Default
(d) Variable-length
8.Read the following statement and choose the correct statement(s).
(I) In Python, you don’t have to mention the specific data types while defining function.
(II) Python keywords can be used as function name.
(a) I is correct and II is wrong
(b) Both are correct
(c) I is wrong and II is correct
(d) Both are wrong
9.Pick the correct one to execute the given statement successfully. if ____ : print(x, " is a leap year")
(a) x%2=0
(b) x%4==0
(c) x/4=0
(d) x%4=0
10. Which of the following keyword is used to define the function testpython(): ?
(a) define
(b) Pass
(c) def
(d) while
Part – II
Answer the following questions: (2 Marks)
1. What is function?
Ans.
Functions are nothing but a group of related statements that perform a specific
task.
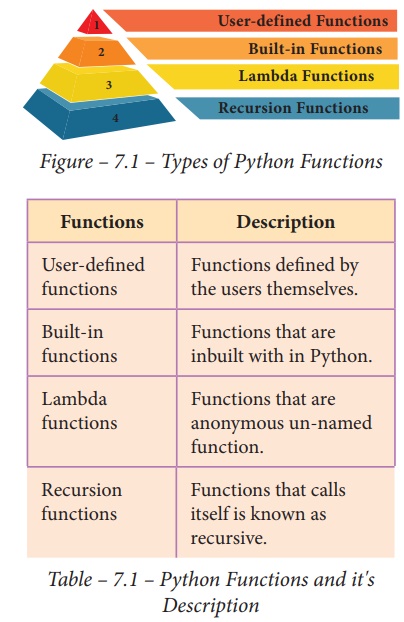
2. Write the different types of function.
Ans.
Functions : Description
User - defined functions
: Functions defined by the
users themselves
Built in functions
: Functions that are inbuilt with in Python.
Lambda functions : Functions that are anonymous
un-named function.
Recursion functions : Functions that calls itself is known as
recursive.
3. What are the main advantages of function?
Ans. Main advantages of functions are
(i) It avoids repetition and makes high degree of code reusing.
(iij It provides better modularity for your application.
4. What is meant by scope of variable? Mention its types.
Ans.
Scope of variable refers to the part of the program, where it is accessible,
i.e., area where the variables can refer (use). The scope holds the current set
of variables and their values. The two types of scopes - local scope and global scope.
5. Define global scope.
Ans. A variable, with global scope can be used anywhere in the
program. It can be created by defining a variable outside the scope of any
function/block.
6. What is base condition in recursive function
Ans. (i) A recursive function calls itself. Imagine a process would
iterate indefinitely if not stopped by some condition. Such a process is known
as infinite iteration.
(ii) The condition that is applied in any recursive function is
known as base condition.
(iii) A base condition is must in every recursive function
otherwise it will continue to execute like an infinite loop.
7. How to set the limit for recursive function? Give an example.
Ans.To set the limit for recursive function using sys.
setrecursionlimit (limit _value).
Example:
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(3000)
def fact(n):
if n==0:
return 1
else:
return n * fact(n-1)
print(fact (2000))
Part – III
Answer the following questions: (3 Marks)
1. Write the rules of local variable.
Ans. Rules of local variable :
(i) A variable with local scope can be accessed only within the
function/block that it is created in.
ii) When a variable is created inside the function/block, the
variable becomes local to it.
(iii) A local variable only exists while the function is
executing.
(iv) The formate arguments are also local to function.
2. Write the basic rules for global keyword in python.
Ans. Rules of global Keyword : The basic rules for global
keyword in Python are:
(I) When we define a variable outside a function, it’s global by
default. You don’t have to use global keyword.
(i) We use global keyword to read and write a global variable
inside a function.
(ii) Use of global keyword outside a function has no effect.
3. What happens when we modify global variable inside the function?
Ans. It shows an error, unbound local error.
4. Differentiate ceil() and floor() function?
Ans.
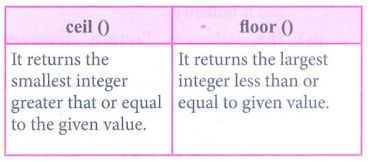
ceil () : It returns the smallest integer greater that or equal to the
given value.
floor () : It returns the largest integer less than or equal to given
value.
5. Write a Python code to check whether a given year is leap year or not.
Ans. y = int(input ("Enter year")
if y%4==0:
print ("The given year is a leap year")
else:
print ("The given year is not a leap year")
6. What is composition in functions?
Ans. (i) Tie value returned by a function may be used as an argument
for another function in a nested manner.
(ii) This is called composition.
For example, if we wish to take a numeric value or an expression as a input
from the user, we take the input string from the user using the function input() and apply eval() function to evaluate its value
7. How recursive function works?
Ans. (i) Recursive function is called by some external code.
(ii) If the base condition is met then the program gives
meaningful output and exits.
(iii) Otherwise, function does some required processing and then
calls itself to continue recursion.
8. What are the points to be noted while defining a function?
Ans. When defining functions there are multiple things that need to
be noted;
(i) Function blocks begin with the keyword "def" followed by function name and parenthesis ().
(ii) Any input parameters or arguments should be placed within
these parentheses when you define a function.
(iii) The code block always comes after colon(;) and is
indented.
(iv) The statement ’’return
[expression]" exits a function, optionally passing back an expression
to the caller. A "return" with no arguments is the same as return
None.
Part – IV
Answer the following questions: (5 Marks)
1. Explain the different types of function with an example.
Ans. Type of functions:
Functions : Description
User - defined functions : Functions defined by the users themselves
Built in functions
: Functions that are inbuilt
with in Python.
Lambda functions :
Functions that are anonymous un-rfamed function.
Recursion functions : Functions that calls itself is known as
recursive.

Syntax for user defined
function:
def<function_name
([parameter 1, parameter 2….. ])>:
<Block of Statement >
return<expression / None>
a
(i) Block : A block
is one or more lines of code, grouped together so that they are treated as one
big sequence of statements while execution. In Python, statements in a block
are written with indentation.
Usually, a block begins when a line is indented (by four spaces) and all the
statements of the block should be at same indent level.
(ii) Nested Block : A block within a block is called nested block. When the first
block statement is indented by a single tab space, the second block of
statement is indented by double tab spaces.
Here is an example of defining a function;
Do_Something():
value = 1 # Assignment Statement
return value #Return Statement
(iii) Lambda function is mostly used for creating small and
one-time anonymous function.
(iv) Lambda functions are mainly used in combination with the
functions like filter(), map() and reduce().
Syntax of Anonymous Functions:
The syntax for anonymous functions is as follows:
lambda [argument(s)]:
expression
Example:
sun = lambda argl, arg2: argl + arg2
print (The Sum is: ‘, sum(30,40)
print (The Sum is : ‘, sum(-30, 40)
Output :
The Sum is : 70
The Sum is : 10
Built-in Functions : Functions which are using Python libraries are called
Built-in function.
x=20
y=-23.2
print('x =abs(x))
print('y = abs(y))
Output:
x = 20
y = 23.2
Recursive function : A recursive function calls itself. Imagine a process would
iterate indefinitely if not stopped by some condition! Such a process is known
as infinite iteration. The condition that is applied in any recursive function
is known as base condition. A base condition is must in every recursive
function otherwise it will continue to execute like an infinite loop.
Overview of how recursive
function works :
(i) Recursive function is called by some external code.
(ii) If the base condition is met then the program gives
meaningful output and exits.
(iii) Otherwise, function does some required processing and then
calls itself to continue recursion.
Here is an example of recursive function used to calculate
factorial.
Example :
def fact(n):
if n==0:
return 1
else:
return n * fact (n-1)
print (fact (0))
print (fact (5))
Output:
1
120
2. Explain the scope of variables with an example.
Ans. Scope of variable refers to the part of the program, where it
is accessible, i.e., area where the variables refer (use). The scope holds the
current set of variables and their values. The two types of scopes - local
scope and global scope.
Local Scope : A variable declared inside the function's body or in the
local scope is known as local variable.
Rules of local variable :
(i) A variable with local scope can be accessed only within the
function/block that it is created in.
(ii) When a variable is created inside the function/block, the
variable becomes local to it.
(iiii) A local variable only exists while the function is
executing.
(iv) The formate arguments are also local to function.
(v) Example: Create a
Local Variable
def loc():
y=0 # local scope
print(y)
loc()
Output:
0
(vi) Example : Accessing local variable outside the scope
def loc():
y = "local"
loc()
print(y)
(vii) When we run the above code, the output shows the following
error:
The above error occurs because we are trying to access a local
variable ‘y’ in a global scope.
NameError: name 'y' is not
defined
Global Scope : A variable, with global scope can be used anywhere in the
program. It can be created by defining a variable outside the scope of any
function/block.
Rules of global Keyword:
The basic rules for global keyword in Python are:
(i) When we define a
variable outside a function, it’s global by default. You don’t have to use
global keyword.
(ii) We use global keyword to read and write a global variable
inside a function.
(iii) Use of global keyword outside a function has no effect.
Use of global Keyword :
(i) Example : Accessing global Variable From Inside a Function
c = 1 # global variable
defadd():
print(c)
add()
Output:
1
(ii) Example : Accessing global Variable From Inside a Function
c = 1 # global variable
def add():
print(c)
add()
Output:
1
(iii) Example: Modifying Global Variable From Inside the Function
c = 1 # global variable
def add():
c = c + 2 #
increment c by 2
print(c)
add()
Output:
Unbound Local Error: local variable 'c' referenced before
assignment
(iv) Example.: Changing Global Variable From
Inside a Function using global keyword
x = 0 #
global variable
def add():
global x
x = x + 5 # increment
by 2
print ("Inside add() function x value is:”, x)
add()
print ("In main x value is :”, x)
Output:
Inside add() function x value is : 5
In main x value is : 5
(v) In the above program, x is defined as a global variable. Inside the add()
function, global keyword is used for
x and we increment the variable x by 5. Now We can see the change on the global variable x outside
the function i.e the value of x is 5.
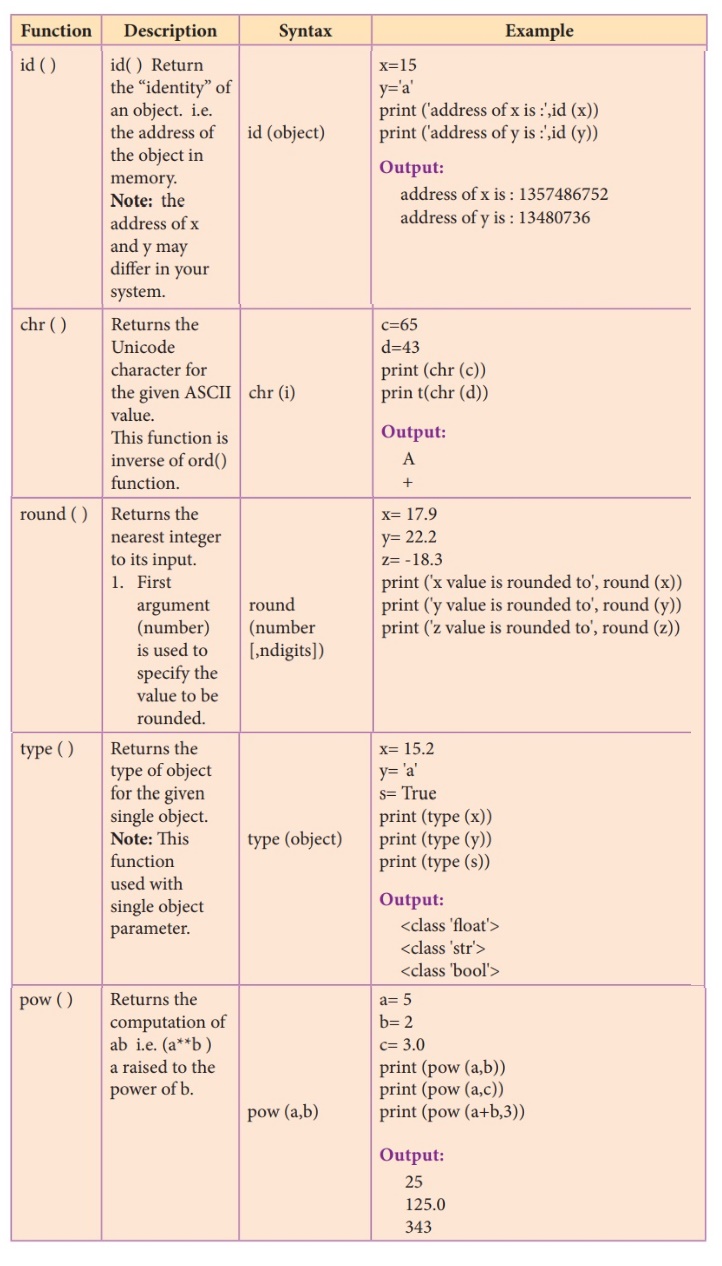
3. Explain the following built-in functions.
(a) id()
(b) chr()
(c) round()
(d) type()
(e) pow()
4. Write a Python code to find the L.C.M. of two numbers.
Ans. Program :
def lcm(x, y):
if x>y:
greater = x
else:
greater = y
while (True):
if ((greater % x == 0) and (greater % y == 0)):
lcm = greater
break
greater + = 1
return 1cm
a = int (input ("Enter number 1"))
b = int (input ("Enter number 2"))
print ("The LCM of", a, "and", b,
"is", LCM(a,b))
5. Explain recursive function with an example.
Ans. (i) A recursive
function calls itself. Imagine a process would iterate indefinitely if not
stopped by some condition.
(ii) Such a process is known as infinite iteration. The
condition that is applied in any recursive function is known as base condition.
(iii) A base condition is must in every recursive function
otherwise it will continue to execute like an infinite loop.
Overview of how recursive
function works :
(i) Recursive function is called by some external code.
(ii) If the base condition is met then the program gives
meaningful output and exits.
(iii) Otherwise, function does some required processing and then
calls itself to continue recursion.
Here is an example of recursive function used to calculate
factorial.
Example :
def fact(n):
if n == 0:
return 1
else:
return n * fact (n-1)
print (fact (0))
print (fact (5))
Output:
1
120
Related Topics