Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Language : Lambda Expressions
Predefined Functional Interfaces
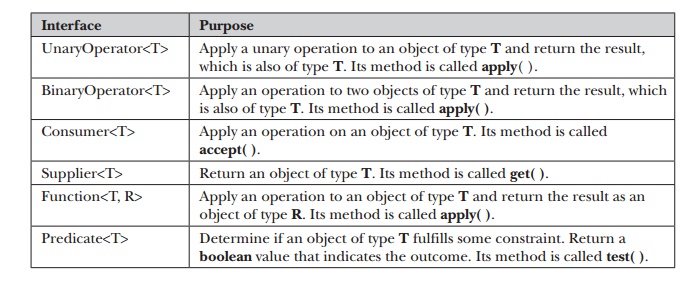
Predefined
Functional Interfaces
Up to this point, the
examples in this chapter have defined their own functional interfaces so that
the fundamental concepts behind lambda expressions and functional interfaces
could be clearly illustrated. However, in many cases, you won’t need to define
your own functional interface because JDK 8 adds a new package called java.util.function that provides
several predefined ones. Although we will look at them more closely in Part II,
here is a sampling:
The following program shows
the Function interface in action by
using it to rework the earlier example called BlockLambdaDemo that demonstrated block lambdas by implementing a
factorial example. That example created its own functional interface called NumericFunc, but the built-in Function interface could have been
used, as this version of the program illustrates:
//Use the Function built-in functional
interface.
//Import the Function interface.
import java.util.function.Function;
class UseFunctionInterfaceDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
//This block lambda computes the factorial of
an int value.
//This time, Function is the functional
interface.
Function<Integer, Integer> factorial =
(n) -> {
int result = 1;
for(int i=1; i <= n; i++) result = i * result;
return result;
};
System.out.println("The factoral of 3 is " + factorial.apply(3));
System.out.println("The factoral of 5 is
" + factorial.apply(5));
}
}
It produces the same output
as previous versions of the program.
Related Topics