Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Creep of Rails
Portions of Track Susceptible to Creep and Measures to Reduce Creep
Portions of Track Susceptible to Creep
The following locations of a track are normally more susceptible to creep.
(a) The point where a steel sleeper track or CST-9 sleeper track meets a wooden sleeper track
(b) Dips in stretches with long gradients
(c) Approaches to major girder bridges or other stable structures
(d) Approaches to level crossings and points and crossings
Measures to Reduce Creep
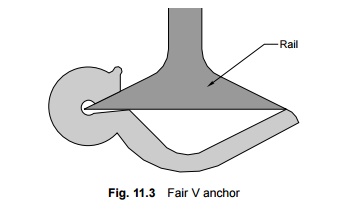
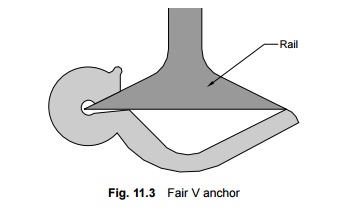
To reduce creep in a track, it should be ensured that the rails are held firmly to the sleepers and that adequate ballast resistance is available. All spikes, screws, and keys should be driven home. The toe load of fastenings should always be slightly more than the ballast resistance. Creep anchors can effectively reduce the creep in a track. At least eight of these must be provided per panel. Out of the large number of creep anchors tried on Indian Railways, the 'fair T' and 'fair V' anchors, have been standardized for use. The fair 'V' anchor, which is more popular, is shown in Fig. 11.3. The creep anchor should fit snugly against the sleeper for it to be fully effective. The following measures are also helpful in reducing creep.
(a) The track should be well maintained-sleepers should be properly packed and the crib and shoulder ballast should be well compacted.
(b) A careful lookout should be kept for jammed joints that exist in series. In the case of a fish-plated track, more than six consecutive continuously jammed joints should not be permitted. In the case of SWR tracks, more than two consecutive jammed joints should not be permitted at rail temperatures lower than the maximum daily temperature (tm) in the case of zones I and II and lower than (tm - 5 o C) in the case of zones III and IV. Regular adjustment may be necessitated on girder bridges.
(c) Anticreep bearing plates should be provided on wooden sleepers to arrest creep, but joints sleepers should have standard canted bearing plates with rail screws.
Creep is the longitudinal movement of rails with respect to sleepers. It is common in all tracks and is a severe type of track defect. In servere cases, it can result in the buckling of the track and can eventually derail the train. Therefore, it is very important to attend to creep immediately after it has been detected. Certain preventive measures can be taken to reduce creep, but it cannot be eliminated completely.
Related Topics