Magnetism | Chapter 7 | 8th Science - Points to Remember, Glossary, Concept Map | 8th Science : Chapter 7 : Magnetism
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 7 : Magnetism
Points to Remember, Glossary, Concept Map
Points to Remember
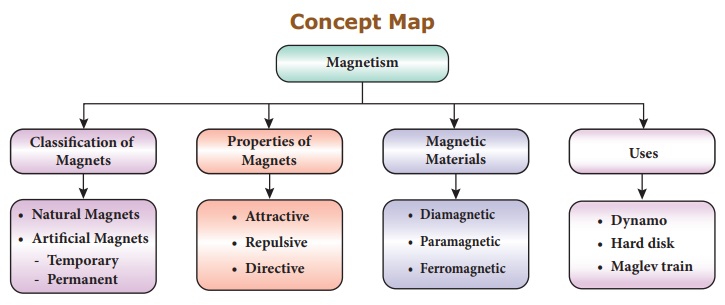
ŌĆó Magnets are classified into two types.
They are: natural magnets and artificial magnets.
ŌĆó Magnets attract things made of
magnetic substances such as iron.
ŌĆó The force of attraction of a
magnet is maximum at the poles.
ŌĆó A freely suspended magnet always
comes to rest along the geographic north-south direction.
ŌĆó Like poles of magnets repel while
unlike poles attract one another.
ŌĆó Materials which are attracted by
magnets are called magnetic materials and those objects which are not attracted
by magnets are called non-magnetic materials.
ŌĆó Based on their behaviour in a
magnetic field magnets can be classified as diamagnetic, paramagnetic and
ferromagnetic materials.
ŌĆó Depending on their ability to
retain their magnetic property, artificial magnets are classified as permanent
or temporary magnets.
ŌĆó The south pole of the imaginary
magnet inside the Earth is located near the geographic north pole and the north
pole is located near the geographic south pole.
ŌĆó In ancient times the magnet in the
form of ŌĆśdirection stoneŌĆÖ helped seamen to find the directions during a voyage.
ŌĆó Magnets, especially electromagnets
are used in day to day life.
ŌĆó Nowadays, magnets are used to
generate electricity in dynamos.
ŌĆó Magnets are used in computers in
the storing devices such as hard disks. They are used in debit and credit cards
also.
GLOSSARY
1.
ALNICO An alloy of
aluminium, nickel and cobalt.
2.
Compass needle A
needle (or plotting compass) which consists of a tiny pivoted magnet, usually
in the form of a pointer, which can turn freely in a horizontal plane.
3.
Magnet A piece of iron or
other material, which can attract things containing iron.
4.
Magnetic axis The
line joining the magnetic poles.
5.
Magnetic field The
space around the magnet, in which the magnetic force is experiencedwithin a
particular region.
6.
Magnetism The branch of
physics which deals with the property of a magnet.
7.
Magnetisation A
process in which a substance is made a permanent or temporary magnet by
exposing it to an external magnetic field.
8.
Magnetite A rock which has
magnetic properties.
Concept Map
REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Electricity and Magnetism -
Brijlal S. Subramanian - S. Chand publications
2. ICSE Physics - Lakmir Singh and
Manjit Kaur - S. Chand publications
3. Physics concepts and connections
- Art Hobson. Edition: Pearson Education
INTERNET RESOURCES
http s : / / w w w. l i ve s c i e n
c e . c om / 3 8 0 5 9 - magnetism.html
https://en.wikipedia. org/wiki/Magnetar
https://www.investopedia. com/terms/m/ magnetic-stripe-card. asp
Related Topics