Chapter: Pathology: Bone Pathology
Osteoporosis
OSTEOPOROSIS
Osteoporosis is decreased bone mass (osteopenia), resulting
in thin, fragile bones susceptible to fracture. It
is the most common bone disorder in the United States. It most commonly occurs
in postmenopausal Caucasian women and the elderly.
Primary causes of
osteoporosis include the following:
• Estrogen deficiency
(postmenopausal, Turner syndrome)
• Genetic factors (low
density of original bone)
• Lack of exercise
• Old age
• Nutritional factors
Secondary causes include
immobilization, endocrinopathies (e.g., Cushing disease, thyrotoxicosis),
malnutrition (e.g., deficiencies of calcium, vitamins C and D, protein),
corticosteroids, smoking/alcohol consumption, genetic disease (e.g., Gaucher
disease).
• Patients may experience
bone pain and fractures; weight-bearing bones are predisposed to fractures.
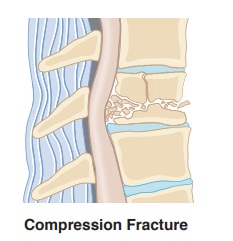
• Common fracture sites
include vertebrae (compression fracture); femoral neck (hip fracture); and
distal radius (Colles fracture).
• Kyphosis and loss of height
may result.
• X-rays show generalized
radiolucency of bone (osteopenia).
Dual-energy x-ray
absorptiometry (DEXA) can measure bone mineral density to
predict fracture risk. Lab
studies may show normal serum calcium, phosphorus, and alkaline phosphatase,
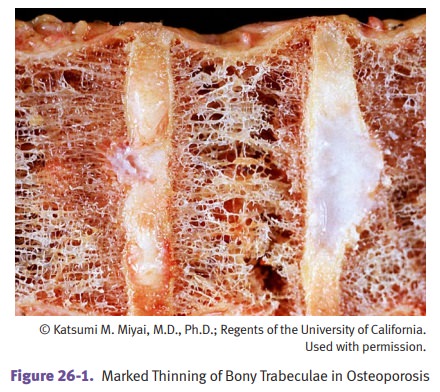
but the diagnosis is not based on labs. Microscopically, the bone has thinned
cortical and trabecular bone.
Treatment can include
estrogen replacement therapy (controversial; not recommended currently);
weight-bearing exercise; calcium and vitamin D; bisphosphonate (alendronate);
and calcitonin.
Related Topics