Types, Manufacturing Process, Finishing Process, Properties, Uses| Man-Made Fibres - Nylon Fibre | 11th Textiles and Dress Designing : Chapter 3 : Man-Made Fibres
Chapter: 11th Textiles and Dress Designing : Chapter 3 : Man-Made Fibres
Nylon Fibre
NYLON
Nylon is a generic name given to a group of
related compounds classified as Polyamides, just like cotton, linen and wool.
Nylon is a long chain of linear con-centrated polymer made from haxamethy-lene
diamine and adipic acid. Nylon is the first synthetic fibre made in 1928 during
a research at Dupont Company.
Nylon was invented by E.I.Du Pont de Nemours
& Co. The credit of the dis-covery of the nylon goes to Dr.Wallace H.
Carothers and his staff of organic chem-ists who worked in Du Pont’s chemi-cal
department. Realizing that there is a need of more active program of research
to provide new developments, Du Pont began a long range of programme in 1928.
Du Pont now shifted from applied research to fundamental research, which
primarily aimed to develop knowledge of chemicals, materials and processes.
After many months of research, Dr.Carothers
assistant discovered a poly-mer, which was a clear, heavy molasses when molten
and could be drawn out into filament. This was a polymer. It was called 6.6,
because there were six carbon atoms per molecule. Later it was called Nylon. It
is also known a polyamide.
Nylon is actually a group of related chemical
compounds. It is composed of hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and carbon in
controlled proportions and structural arrangements. Variations in the chemi-cal
structures can result in formation of compounds like plastic. The two types of
nylon are nylon 6.6 and nylon 6.
Types of Nylon Yarns
The diameter of the nylon yarn filament can be
determined by the rate of delivery from the pump to the spinneret and the rate
by which the yarn is drawn away from the spinneret. The size of yarn, which is
measured in denier, can be determined by the diameter and the number of
filaments in the yarn. Based upon this nylon can be divided as Nylon 6.6, Nylon
6.12, Nylon 4.6, Nylon 6, Nylon 12 and so on.
·
Monofilament Yarns.
·
Multifilament Yarns.
·
Stretch Yarns.
·
Textured Yarns.
·
Spun Yarns.
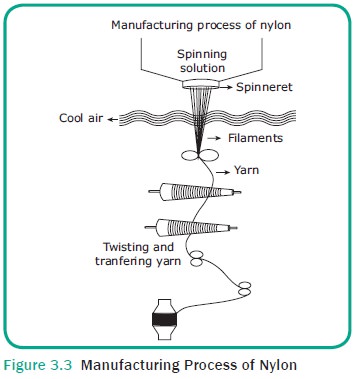
Manufacturing Process of Nylon
Required amount of hexamethylene diamine and
adipic acid are mixed to form nylon salt. This salt is dissolved in water at
the spinning mill and heated to get a con-centrated nylon salt solution. The
solution is placed in an autoclave under high pressure and heat which results
in giant chain links structure called “Linear Superpolymers”. The solution is
slowly passed over the auto-clave and a molten nylon resin is deposited on
wheel. This is sprayed with cold water to harden into opaque ribbon, flakes or
pellets. On melting this pellets or flakes are passed through the spinneret to
form nylon yarns (Figure 3.3).
Properties of Nylon
Shape :
Can be
modified as per requirement.
Size : Thin
long filament.
Density
: 1.1 g /
ccm
Lustre
: Varies
from brightness to dullness
Strength
: Good
Elongation
: Good
Elastic
recovery : 100%
Resiliency
: Good
Moisture
absorption : 8%
Dimensional
stability : Excellent
Resistance
to acid : Poor
Resistance
to alkalies : Good
Sunlight
: Affected
by sunlight
Insects
: Normally
damages the fibres
Resistance
to flame : Self extinguishing
Finishing Nylon Fabrics
Nylon fabrics can be given various finishes.
Antistatic
finish : For reduction of electrostatic build up
Embossing
: For
patterns or designs
Heat
setting : For permanent shape
Moireing
: For
shimmer effect
Molding
: For
shaping fabrics
Nylonizing
: For
increased absorbency
Water
repellence : For added protection against water
Dyeing : For imparting colour to the fabric
Uses of Nylon Fabric
·
Nylon is used in women’s stockings or hosiery. It
is also used as a mate-rial for producing socks, swimwear, shorts, track pants,
active wear, draperies and bedspreads.
·
Nylon is used for making fishing nets, ropes,
parachutes and tyre cords.
·
Nylon is used in cookware since it has a
relatively high continuous ser-vice temperature.
·
Nylon is used for making plastic machine parts as
it is low cost and long lasting. It is often commonly used in the electronics industry
for its non-conductivity and heat resistance.
Related Topics