Chapter: Biochemistry: Biomolecules
Nucleic acids: Definition, Classification, Functions
Nucleic acids
Nucleic acids are a polynucleotides consisting
of repeated units of mononucleotides.
Definition
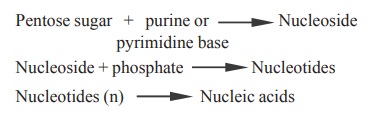
Nucleic acids are the polymers of nucleotides.
A nucleotide is a nucleoside containing phosphate group. A nucleoside is made
up of a purine or pyrimidine nitrogenous base linked to a pentose sugar.
Classification :
Nucleic acids are classified into
1. Deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA)
The most important consistuent of chromosome
and exist as double stranded helix. The nitogenous bases present are adenine,
guanine, cytosine and thymine and the pentose sugar is deoxyribose.
2. Ribonucleic acids (RNA)
RNA is a polymer of purine and pyrimidine
ribonucleotides linked together by 3’, 5’ phosphodiester bridges. The
nitrogenous bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil and the pentose
sugar is ribose.
Types of RNA - There are 3 main classes of RNA
molecules exist in all prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms - They are
messenger RNA (mRNA).
transfer RNA (t RNA)
ribosomal RNA (r RNA)
Functions of DNA
·
DNA
serves as genetic material in cells.
·
DNA
provides information inherited by the daughter cells and is also a source of
information for the synthesis of proteins and it produces mRNA essential for
protein biosynthesis.
Functions of RNA
·
It
primarily functions in the cytoplasm of the cell as template for the synthesis
of protein.
·
It
carries genetic information from DNA to the site of protein biosynthesis.
·
It is an
essential component of ribosome
·
Some RNA
has enzymatic activity
·
It
serves as genetic material for viruses such as tobacco mosaic virus, polio
virus etc.
Related Topics