Chapter: Biochemistry: Biomolecules
Biomolecule: Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates
Importance
Carbohydrates are widely distributed in both
plant and animal tissues. They are indispensible for living organisms and serve
as skeletal structures in plants and also in insects and crustaceans. They
occur as food reserves in the storage organs of plants and animals. They are
the important source of energy required for the various metabolic activities of
the living organisms.
Definition
Carbohydrates are defined as polyhydroxy
aldehydes or ketones and are generally classified as follows.
Classification
Carbohydrates are generally classified into 4
major groups :
·
Monosaccharides
·
Disaccharides
·
Oligosaccharides
and
·
Polysaccharides
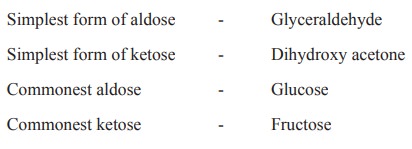
Monosaccharides
These are carbohydrates that cannot be
hydrolysed into more simpler form. These are otherwise known as simple sugars.
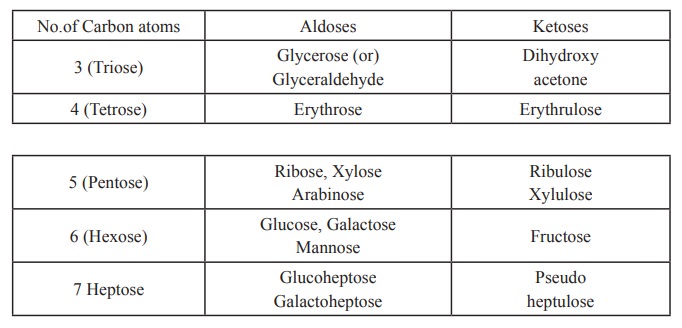
The general formula is Cn(H2O)n. They may be
subdivided into trioses, tetroses, pentoses and hexoses depending upon the
number of carbon atoms they contain and also subdivided as aldoses and ketoses
depending upon the presence of aldehyde or ketone groups (eg).
Functions
·
Ribose
is a structural element of nucleic acids and also of some coenzymes.
·
Glucose
on oxidation yield energy which is required for various metabolic activities.
·
Fructose
is found in fruits, honey etc.which are responsible for sweetness and can be
converted to glucose and utilised in the body.
·
Galactose
is a component of milk sugar-lactose, glycolipids and glycoproteins
·
Mannose is a constituent of mucoproteins and
glycoproteins which are essential for the body.
Disaccharides
These are carbohydrates that yield two
molecules of same or different types of monosaccharides on hydrolysis. The
general formula is Cn(H2O)n-1 (eg) Lactose,
Maltose and Sucrose. The monosaccharide units are united by a glycosidic
linkage.
Functions
1. Lactose is otherwise called as milk sugar.
It is present in milk and is made up of monosaccharides - glucose and
galactose.
Glucose + Galactose - - > Lactose
2. Maltose is otherwise known as ‘malt sugar’
and is present in germinating cereals, malt etc.It is the intermediate product
in the hydrolysis of starch by amylase in the alimentary canal. It is made up
of 2 molecules of glucose.
Glucose + Glucose - - > Maltose
3. Sucrose is otherwise called as ‘table sugar’
or ‘cane sugar’. It is the common sugar and is widely distributed in all
photosynthetic plants. It does not exist in the body but occurs in sugarcane,
pineapple, sweet potato and honey. It is made up of glucose and fructose.
Glucose + Fructose - - > Sucrose
Oligosaccharides
These are carbohydrates that yield 2-10
monosaccharide units on hydrolysis.eg. Maltotriose.
Polysaccharides
These carbohydrates yield more than 10
monosaccharide units on hydrolysis. They are further classified into
homopolysaccharides and heteropolysaccharides.
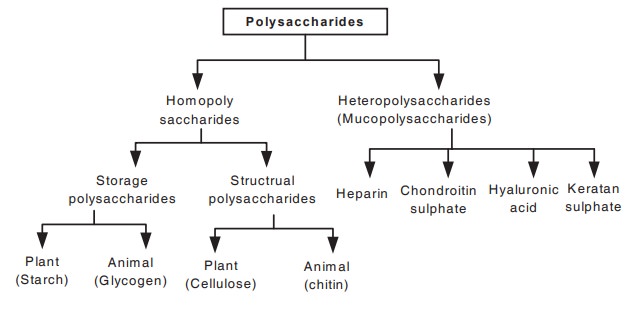
Homopolysaccharides
These on hydrolysis yield same type of
monosaccharide units.
(eg). starch, glycogen, cellulose, inulin,
pectin and hemicellulose yield only glucose on hydrolysis.
Heteropolysaccharides
These on hydrolysis yield a mixture of different types of monosaccharides. The heteropolysaccharides situated in extra cellular matrix are called as mucopolysaccharides.
(eg). hyaluronic acid, heparin,
keratan sulphate and chondroitin sulphate.
Hyaluronic acid is made up of glucuronic acid and N-acetyl glucosamine
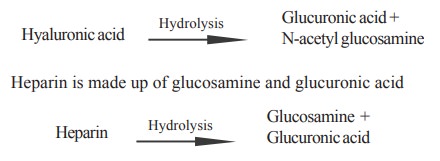
Chondroitin sulphate is made up of either glucuronic
acid (A and C type) or Iduronic acid (B type) and

Keratan sulphate consists of N-acetyl
galactosamine, galactose and sulphuric acid
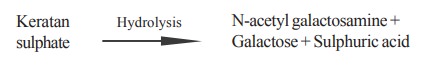
Functions
·
Starch
is made up of repeated units of glucose moiety. It is the most important source
of carbohydrate in our food. Such a compound which produces only glucose on
hydrolysis is called a glucosan, and is found in cereals, potatoes, legumes and
other vegetables.
·
Glycogen
is the major carbohydrate reserve in animals and is often called animal starch.
It is stored in liver and muscle of animals.
·
It is
also found in plants which have no chlorophyll system [eg. fungi and yeasts]
but not in green plants.
·
Cellulose
is widely distributed in plant sources. It occurs in the cell walls of plants
where it contributes to the structure. It is the main consituent of the supporting
tissues of plants and forms a considerable part of vegetables.
·
Pectin
and hemicellulose are present in fruits of many plants and serve as jelling
agents.
·
Hyaluronic
acid occurs in synovial fluid, in skin and in tissues. It acts as a cementing
substance in tissues and also acts as a lubricant. It is also present in
vitreous humor.
·
Heparin
is used in medicine as an anticoagulant and prevents blood clotting.
·
Keratan
sulphate is an important component of cartilage and cornea.
Related Topics