Chapter: 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 11 : Network Examples and Protocols
Network Examples and Protocols
Network Examples and
Protocols

Introduction
Internet Protocol (IP) is the principle of
communication protocol amoung the Internet protocols for layering on datagram
across boundaries of other networks. Its main function is to allow Internet
working and boost up the Internet.
Internet protocol (IP) will discharge packets from
the source host and it will deliver to the destination host via IP address in
the packet header.
Network protocols is the usual procedures, rules,
formal standards and policies comprised of formats which allows communication
between more than one device which is connected to the network. Network
protocols have to do end-to-end process of secure on time and manage data or
network communication.
All requirements which combine process, on network
protocols so as to carry out the communication between routers, servers,
computers, laptop, and other authorized networked device. Here on network
protocols might be installed and rooters in both sender and receiver to ensure
data or network communication and apply to software and hardware nodes which
communicate on a network.
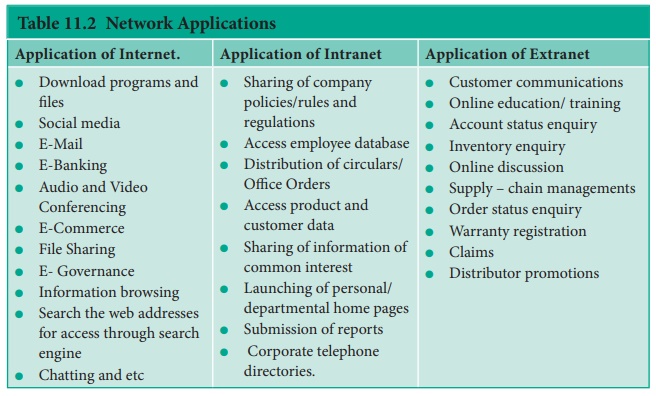
The broad types of networking protocols, including:
● Network
communication protocols is the basic data communication protocol which consist
of HTTP and TCP/IP.
● Network
security protocol is which implement security over network communication and
include HTTP, SFTP and SSL.
● Network management protocol will Provide network
governance and maintenance and include ICMP and SNMP.
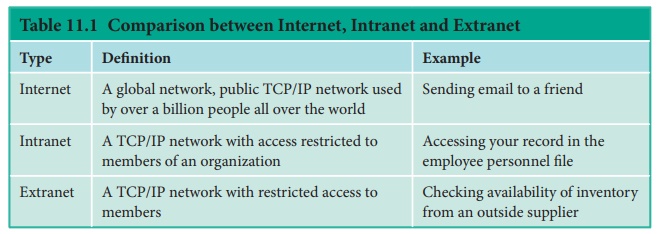
Internet/Intranet/ Extranet
INTERNET:
The Internet, “the Net,” is a worldwide system of computer
networks-A network of networks where the users at any one computer can, if they
have permission, get information from any other computer. The Internet is a
network of global connections – comprising private, public, business, academic
and government networks – linked by guided, wireless and fiber-optic
technologies. It was perceived by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA)
of the U.S. government in 1969 and was first recognized as the ARPANet. The
unique aim was to generate a network that would permit users of a research
computer from one university to “talk to” research computers on other
universities. The jargons Internet and World Wide Web are frequently used
interchangeably, but they are not precisely the same. The Internet denotes to
the global communication system, including infrastructure and hardware, whereas
the web is one of the services interconnected over the Internet. See Figure
11.1
INTRANET:
It is a
private network within an enterprise
to share company data and computing resources between the employees. It may
consist of many interlinked local area networks. It includes connections
through one or more gateway (connects two networks using different protocols
together known as protocol convertor) computers to outside Internet. See Figure
11.2
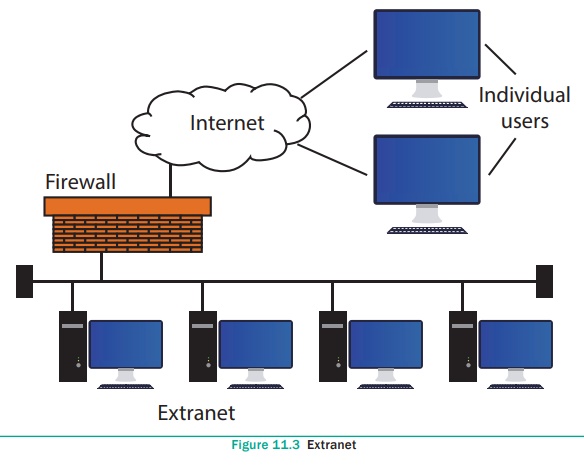
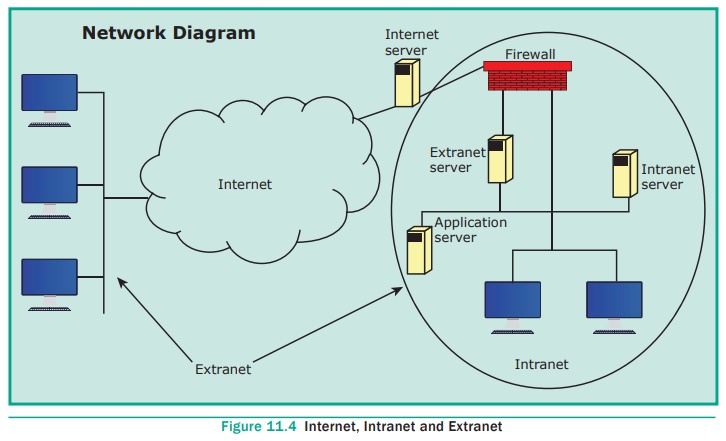
EXTRANET:
It is a
private network that uses Internet
technology and the public telecommunication system to securely share business’s
information with suppliers, vendors, partners, customers, or other businesses.
See Figure 11.3 and 11.4
Internet of Things refers to the digital
interconnection of everyday objects (home applicances, wearable devices or
automobiles) with the Internet. The ‘thing’ in IoT refers to objects that have
been assigned an IP address and have the ability to collect and transfer data
over a network without manual assistance or intervention.

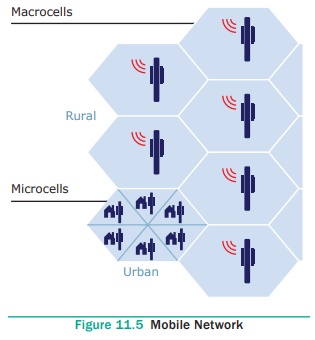
Mobile Networks
A mobile network or cellular network as it is made
up of a large number of signal areas called cells. These cells join to form a
large coverage area. Users can cross into different cells without losing their
connection.
Within each cell there is a base station, which
sends and receives the mobile signals. A mobile device will connect to the
nearest or least base station. The base stations are connected to digital
exchange where the communication is sent to other telephone
or data networks. Cells will often be smaller in
size in large towns, as the number of users in the area is more. Communication
over mobile network is made up of voice, data, images and text messages. See
Figure 11.5
Mobile networking assign to the technology supports
voice/data, network connectivity using via radio transmission solution. The
common application of mobile networks is mobile phones, tablets, etc.. In the
past, wireless communications largely used circuit switching to carry only
voice over a network, but now currently both data and voice are being
transmitted over both circuit via switched networks and packet-switched
networks.
The generation of mobile networks are as follows.
● First Generation(1G) 1981- NMT launch
● Second Generation(2G) 1991-GSM Launch
● Second to Third Generation Bridge (2.5)2000 –
GPRS launch
● Third
Generation( 3G) 2003- UK 3G launch
● Fourth
Generation (4 G) 2007
● Fifth
Generation (5G) 2019+
First Generation (1G) 1981 – NMT launch
During the initial periods the mobile systems were
based on analog transmission. NMT stands for Nordic Mobile Telephone
communication. They had a very low traffic density of one call per radio
channel, and a very poor voice quality, and they used unsure and unencrypted
transmission, which leads to the spoofing of its identities.
Second Generation (2G) 1991 – GSM launch
Later the second generation of mobile systems were
placed on digital transmission with GSM. GSM
stands for (Global System for Mobile
communication) was most popular standard which is used in second
generation, using 900MHz and 1800MHz for the frequency bands. GSM mobile
systems grown digital transmission using SIM. SIM stands for (Subscriber Identity Module) technology
to authenticate a user for identification and billing purposes, and to encrypt
the data to prevent listen without permission (eavesdropping). The transmission
used as TDMA. TMDA stands for (Time
Division Multiple Access) and
CDMA stands for (Code Division Multiple
Access ) method to increase the
amount of information transported on the network. Mobility is supported at
layer 2, which stops seamless roaming across assorted access networks and
routing domains. This means that each operator must cover the entire area or
have agreements in place to permit roaming.
Second to Third Generations Bridge (2.5G) 2000 – GPRS launch
GPRS was introduced here, this is the excess period
of mobile networking development, between 2G and 3G. GPRS stands for( General Packet Radio Service ).GPRS is a data service which enables mobile devices to send and
receive messages, picture messages and e-mails. It allows most popular
operating speeds of up to 115kbit/s, latterly maximum of 384kbit/s by
usingEDGE. EDGE stands for EDGE (Enhanced
Data rates for Global Evolution).
GSM data transmission rates
typically reached 9.6kbit/s.
Third Generation(3G)2003 – First UK 3G launch
This gneration of mobile system merges different
mobile technology standards, and uses higher frequency bands for transmission
and Code Division Multiple Access to deliver data rates of up to 2Mbit/s
supporting multimedia services (MMS: voice, video and data). European standard
is UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunication Systems). Mobile phones systems continue to use digital
transmission with SIM authentication for billing systems and for data
incorruption. Data transmission used a WCDMA. WCDMA stands for (Wideband Code
Division Multiple Access). A technique to obtain data rates between 384kbit/s
and 2048kbit/s. Few 3G suppliers use ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) for ‘over the air’ network with in MPLS
(Multiprotocol Label Switching) or IP for their backbone network.
Li-Fi is a wireless technology which
uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for data transmission whereas Wi-Fi uses
radio frequencies for data transmission. Li-Fi is the short form of Light
Fidelity.
The term Li-Fi was first used by
Harald Haas, Professor in Edinburgh University. The computer scientists
achieved speeds of 224 gbps in the lab and research is going on. The biggest
revolution in the Internet world is going to happen
Mobility still supported at layer 2, and hence like
2G it still prohibits seamless roaming beyond heterogeneous access networks and
routing domains. The transmission were band frequencies between 1900 and 2200
MHz. All UMTS license holders at the UK holds a 20 year license with the
condition that 80% population coverage is achieved by 31 December 2007. The
present third generation licensed operators in the UK can be seen below as at August
2004.
Fourth Generation(4G) 2007
4G is at the research stage. 4G was based on an
adhoc networking model where there was no need for a fixed infrastructure
operation. Adhoc networking requires global mobility features (e.g. Mobile IP)
and connectivity to a global IPv6 network to support an IP address for each
mobile device. Logically roaming in assorted IP networks (for example: 802.11
WLAN, GPRS and UMTS) were possible with higher data rates, from 2Mbit/s to
10–100Mbit/s, offering reduced delays and new services. Mobile devices will not
expect on a fixed infrastructure, they will require enhanced intelligence to
self configure in adhoc networks and having a routing capabilities to route
over a packet-switched network.
Fifth Generation (5G) 2019+
5G is the stage succeeds the 4G (LTE/ WiMAx),
3G(umts) and 2G(GSM) syetems. 5G targets to perform the high data rate, reduced
latency, energy saving, cost reduction, higher system, capacity, and massive
device connectivity. The two phases of 5G, First one will be Release-15
complete by March 2019,Second one Release-16 is expected to complete at
March2020, for submission to the ITU(International Telecommunication Union) as
a candidate IMT-2020 technology. The ITU IMT – 2020 provides speed up to 20
gigabits per second it has been demonstrated with millimeter waves of 15
gigahertz and higher frequency. 3 GPP standard includes any network using New
Radio software. 5G New Radio can access at lower frequencies from 600 MHz to 6
GHz. Speed in the lower frequencies are only modest higher than 4G systems,
estimated at 15% to 50% faster.
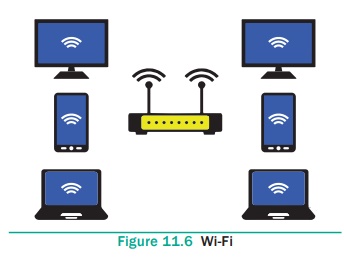
WLANS 802.11
Wi-Fi stands for Wireless Fidelity. It is a
wireless network technology that permits computers and alternative devices to
be connected to every alternative into a local area network and to the net
without wires and cables. Wi-Fi is additionally stated as wireless local area
networkthat stands for wireless local area network, and 802.11, is the
technical code for the protocol. See Figure 11.6
ADVANTAGES: Benefits of Wi-Fi are
● It
provides mobility. Example: I get Internet connection wireless through my
laptop computer at home and at work, because of Wi-Fi, hotspots both at home
and at work can be used.
● It
provides connection to Internet.
● Flexibility
of LAN.
● Ensures
connectivity.
● It
allows remote places to benefit from connectivity.
● Low
cost, high benifts.
RFID
● RFID - Radio Frequency Identification.
RFID is a technology designed to locate objects
(Credit cards, Passports or even livestock) using radio signals.
RFID used radio waves to read and capture
information stored on a tag attached to an object. Tag can be read from several
feet away and does not need to be in direct-line-of-sight of the reader to be
tracked. RFID has been made up of two parts a reader and a tag or a label. RFID
tags are installed with a transmitter and receiver.
RFID component on the tags has two parts: a
microchip which stores and processes the information, and the antenna to
receive and transmit a signal. The Tag replies the information from its memory
bank. The reader will transmit to read the result to RFID computer program.
Two types of RFID tags were Active RFID and Passive
RFID systems.
1. In a passive RFID tag, the power is supplied by
the reader when radio waves from the reader are encountered by a passive RFID
tag, the coiled antenna forms a magnetic field.
2. Battery powered RFID tag is installed with small
battery that powers the broadcast of information
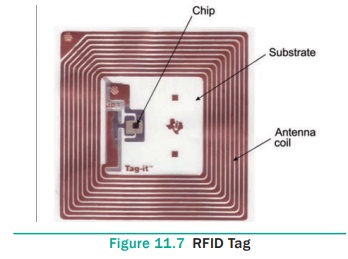
Main Components of a RFID System
● A RFID
tag: It has silicon microchip attached
to a small antenna and mounted on a substrate. See Figure 11.7
● A
reader: It has a scanner with antennas to
transmit and receive signals, used for communication. See Figure 11.8

● A
Controller: It is the host computer with
a Microprocessor which receives the reader input and process the data.
Two types of RFID Systems:
1. Active
RFID system: The tag has its
own power source. These systems are used for larger distances and to track
high value goods like vehicles.
2. Passive RFID system: The tag gets power from a reader antenna to the tag antenna. They are used for shorter range transmission.
Related Topics