Chapter: Discrete Time Systems and Signal Processing : Digital Signal Processor
Microprocessor Architectures
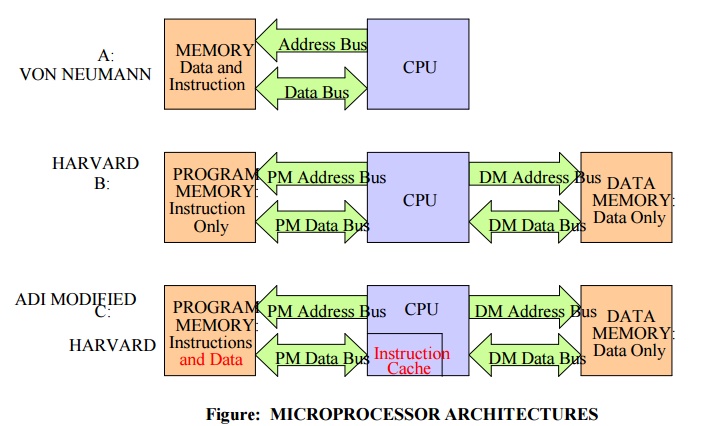
MICROPROCESSOR
ARCHITECTURES
There are
mainly three types of microprocessor architectures present.
1. Von-Neumann
architecture
2. Harvard
architecture
3. Analog
devices Modified Harvard architecture.
1) Von-Neumann Architecture
General
purpose microprocessors uses the Von-Neumann Architectures. (named after the
American mathematician John Von Neumann)
1.It
consists of ALU, accumulator, IO devices and common address and data bus. It
also consists of a single memory which contains data and instructions, a single
bus for transferring data and instructions into and out of the CPU.
2.Multiplying
two numbers requires at leased three cycles, two cycles are required to
transfer the two numbers into the CPU and one cycle to transfer the
instruction.
3.This
architecture is giving good performance when all the required tasks can be
executed serially. 4.For large processing applications like DSP applications
Von-Neumann architecture is not suitable as processing speed is less.
Processing speed can be increased by pipelining up to certain extend which is
not sufficient for DSP applications. In order to perform a single FIR filter
multiply-accumulate, an instruction is fetched from the program memory, and
during the same cycle, a coefficient can be fetched from the data memory. A
second cycle is required to fetch the data word from data memory
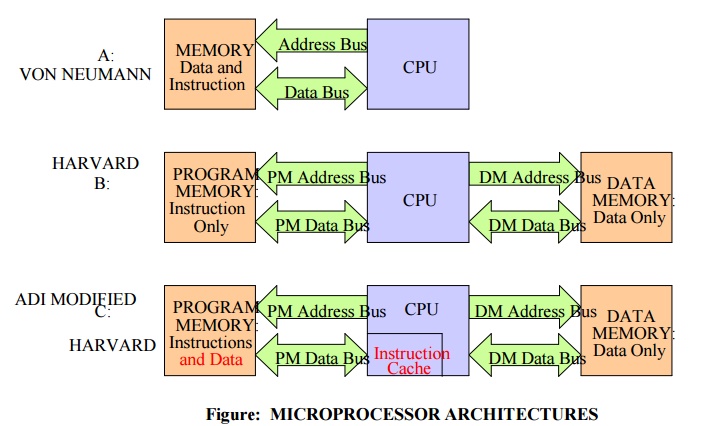
2) Harvard Architecture (named for the work done at
Harvard university)
1. Data and
program instructions each have separate memories and buses as shown. Program
memory address and data buses for program memory and data memory address and
data buses for data memory.
2. Since the
buses operate independently, program instructions and data can be fetched at
the same time. Therefore improving speed over the single bus Von Neumann
design.
3. In order
to perform a single FIR filter multiply-accumulate, an instruction is fetched
from the program memory, and during the same cycle, a coefficient can be
fetched from the data memory. A second cycle is required to fetch the data word
from data memory.
Related Topics