Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 5 : Child Health Nursing
Medical and Special Care of Newborn
Medical and Special Care of Newborn
The first week of life is the most crucial period in the life of
an infant. In India, 61.3 percent of all infant deaths occur within the first
month of life. Of these, more than half may die during first week of birth.
This is because the newborn has to adapt itself rapidly and successfully to an
alien external environment. The risk of death is the greatest during the first
24-48 hours after birth.
Principles of Newborn care
To promote adequate oxygenation
·
To prevent hypothermia
·
To promote early
breastfeeding
·
To prevent neonatal
infections
·
To identify at risk
newborn
·
To facilitate
stabilization of the newborn
Care of newborn
Maintenance of normal respiration and oxygenation
The first cry of the baby after birth is the sign of respiration.
All babies should cry immediately after birth. If the baby doesn’t cry, it
needs immediate attention of the health care personnel. As soon as the baby is
born, the airway should be cleared of mucus and any other secretions within the
labour room. Then continuous monitoring of respiration and heart rate is done
for every 15 minutes for first 2 hours or till adaptation to external
environment. Positioning the baby with its head extended may help in the
drainage of secretions. A gentle suction in the mouth first and nostrils second
can facilitate removal of secretions and amniotic fluid. Resuscitation is
necessary for babies who do not breathe within a minute.
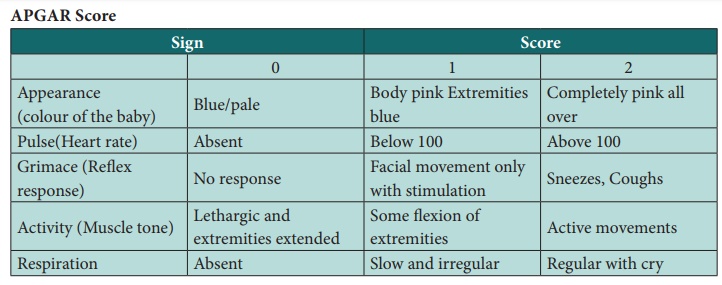
The APGAR score is taken at 1 minute and again at 5 minutes
after birth. It requires immediate and careful observation of the Appearance,
Pulse, Grimace, Activity and Respiration. Each sign is given a score of 0, 1 or
2. It provides an immediate estimate of the physical condition of the baby. A
perfect score should be 9 or 10. A score below 5 needs prompt action.
Maintenance of Body temperature (warmth)
Body heat is lost from the newborn by four ways. They are as
follows:-
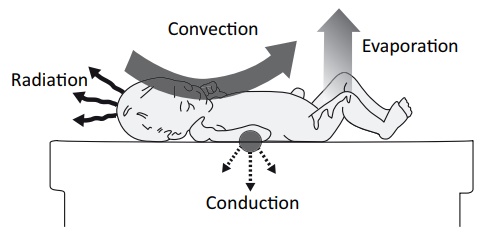
·
Convection- Leaving the
baby in a draught (Cool air)
·
Radiation – If the
baby’s head is not covered, the body heat is able to pass into surrounding air.
·
Conduction – Leaving the
baby on a cold surface
·
Evaporation – Baby not
dried after birth the amniotic fluid evaporate by using by body heat.
The body temperature below 36.5°C is known as hypothermia.
To maintain the temperature of the newborn one must do the following
Provide skin to skin contact to the baby if possible
If skin-to-skin contact is NOT possible:
• Wrap the baby in a
clean dry warm cloth
• Mummify the baby
• Cover the baby’s head
with cap.
• Assess warmth every 4 hours by
touching baby’s feet
• Keep the room warm
• Remove all wet cloths
• Rooming in. The mother
should be encouraged to keep the baby with her.

Breast feeding
It should be initiated as early as possible after birth. The first
milk which is called “colostrum” is the most suitable food for the
baby during early period because it is rich in anti-infective factors. It
contains high concentration of protein and other nutrients the baby needs.

Cord care
The stump is kept dry and clean. Nothing should be applied over
stump. Bandages should not be applied. Fold diaper below stump. If the stump is
wet, wash with clean water and soap, dry with clean cloth. Usually the stump
will fall in 7-10 days time. If umbilicus is red or draining pus or blood, the
mother should be advised to see the health worker.
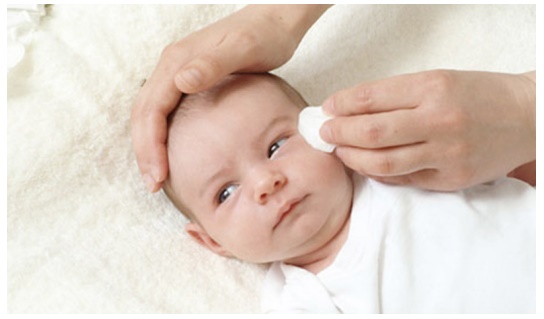
Eye care
Eyes of the babies are cleaned from inner canthus to outer canthus
using sterile wet gauze or cotton in the hospital and with a clean cloth at
home. Nothing should be poured into the eyes of the newborn unless medically
indicated.
Vitamin K injection: Vitamin K injectioning is given intra
muscularly to prevent bleeding.
Care of Skin: It is advisable to postpone the formal bath to the second
week. However sponge bath may be given after 24 hour of birth.
Urine and meconium: Check for passage of urine and meconium.
Immunization: Hepatitis B vaccine and zero doses of OPV and BCG is given
immediately. Thereafter, the child should be immunized on specific dates.
Harmful practices which should not be followed for newborn
·
Giving prelacteal feeds
soon after birth like sugar water or honey or donkey milk, jaggery water.
·
Discarding the
colostrums (the first milk secretion from the mother)
·
Applying ashes or soot
or powder or dry cow dung on the umbilical cord of the baby.
·
Applying kajal on the
baby’s face to prevent bad eye
·
Tying black thread or
bangles to the baby’s hand or leg to prevent bad eye.
·
Exposing baby to a
“holy” smoke (Sambirani) after bath.
·
Giving home remedies for
digestion like vasambu
·
Pouring of oil into eye
or ear.
·
Blowing of nose and ear
during bath
Red flag signs
These are danger signals to be identified at newborn. Presence of
one or more of these sings is an indication for prompt evaluation and
treatment.
·
Feeding difficulty
·
Persistent vomiting
·
Fast breathing (more
than 60 breaths per minute)
·
Hypothermia (temperature
less than 35.5°C
·
Hyperthermia or
Fever,Temperature more than 37.5°C
·
Seizures
·
Lethargy
Fatigue yellowish discoloration
Related Topics