Measuring Instruments - Measuring Mass | 9th Science : Measurement and Measuring Instruments
Chapter: 9th Science : Measurement and Measuring Instruments
Measuring Mass
Measuring Mass
We commonly use the term ‘weight’ which is actually
the ‘mass’. Many things are measured in terms of ‘mass’ in the commercial world.
The SI unit of mass is kilogram. In any case, the units are based on the items
purchased. For example, we buy gold in gram or milligram, medicines in
milligram, provisions in gram and kilogram and express cargo in tonnes.
Can we use the same instrument for measuring the
above listed items? Different measuring devices have to be used for items of
smaller and larger masses. In this section we will study about some of the
instruments used for measuring mass.
Common (beam) balance
A beam balance compares the sample mass with a
standard reference mass. (Standard reference masses are 5g, 10g, 20g, 50g,
100g, 200g, 500g, 1kg, 2kg, 5kg). is balance can measure mass accurately up to
5g (Figure 11).

Two pan balance
This type of balance is commonly used in provision
and grocery shops (Figure 12). is balance compares the sample mass with the
standard reference mass. The pans rest on top of the beam and can be
conveniently placed on a table top. is balance can measure mass accurately upto
5 g.

Physical balance
This balance is used in labs and is similar to the
beam balance but it is a lot more sensitive and can measure mass of an object
correct to a milligram (Figure 13).
The standard reference masses used in this physical
balance are 10 mg, 20 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg, 500 mg, 1 g, 2g, 5 g, 10 g, 20
g, 50 g, 100g, and 200 g.

Digital balance
Nowadays for accurate measurements digital balances
are used, which measures mass accurately even up to a few milligrams, the least
value being 10 mg (Figure 14). is electrical device is easy to handle and
commonly used in jewellery shops and labs.

Spring balance
This balance helps us to find the weight of an object.
It consists of a spring fixed at one end and a hook attached to a rod at the
other end. It works by ‘Hooke’s law’ which explains that the addition of weight
produces a proportional increase in the length of the spring (Figure 15). A
pointer is attached to the rod which slides over a graduated scale on the
right. The spring extends according to the weight attached to the hook and the
pointer reads the weight of the object on the scale.

Solve – The
mass of 40 apples in a box is 10 kg.
(i) Find the mass of a dozen of them (ii) Express the mass of one apple in
gram.
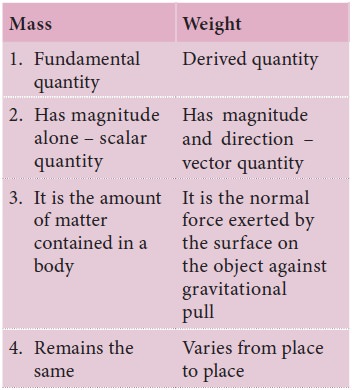
1. Difference between mass and weight
Mass (m) is the quantity of matter contained in a
body. Weight (w) is the normal force (N) exerted by the surface on the body to
balance against gravitational pull on the object. In the case of spring scale
the tension in the spring balances the gravitational pull on the object. When
the man is standing on the surface of the earth or floor, the surface exerts a
normal force on the body which is equivalent to gravitational force. The
gravitational force acting on the object is given by ‘mg’. Here m is mass of
the object and ‘g’ is acceleration due to gravity.
If a man has a mass 50 kg on the earth, then what
is his weight?
Weight
(w) = mg
Mass of a
man = 50 kg
His
weight = 50 × 9.8
w = 490
newton

The pull of gravity on the Moon is 1/6 times weaker
than that on the Earth. is causes the weight of the object on the Moon to be
less than that on the Earth.
Acceleration due to gravity on the Moon = 1.63m/s2
If the mass of a man is 70 kg then his weight on
the Earth is 686 N and on the Moon is 114 N. But his mass is still 70 kg on the
Moon.
Related Topics