Term 2 Chapter 2 | 6th Maths - Measurements | 6th Maths : Term 2 Unit 2 : Measurements
Chapter: 6th Maths : Term 2 Unit 2 : Measurements
Measurements
CHAPTER 2
MEASUREMENTS

Learning Objectives
* To understand the position of decimal point in
the conversion of smaller unit to larger unit and vice versa.
* To do the four fundamental operations on quantities
of different units.
* To read time in a clock and convert the 12 hour
format to the 24 hour format and vice versa.
* To find duration between 2 given time instances.
* To do conversion of units of time.
Introduction
Let us listen to the following conversation between
a teacher and a student:
Teacher: Have you ever noticed your mother buying
knotted flowers? How is it measured?
Student: Yes teacher. The flower seller measures
the string of flowers using her/his hand. She/He
measures in cubit (முழம் in tamil).
Teacher: If you
measure the same using your hand, what would you observe?
Student: It would measure more than one cubit,
because my hand is shorter.
Teacher: Yes, how far is your house from the
school?
Student: Just 100 feet, teacher.
Teacher: How do you buy rice, milk, cloth from
the shop?
Student: We buy the rice in kilogram, milk in litre , cloth
in metre.

Teacher: How much time do you spend on your homework?
Student: I usually spend an hour to do my homework.
Teacher: How do you measure height and weight?
Student: Height in centimetre, Weight in kilogram.
Teacher: Have you heard about any other measures
used in earlier days?
Student: My grandparents talk of measures
used in their days such as Padi (படி),
Uzhakku (உழக்கு), Aazhakku (ஆழாக்கு), Marakkal (மரக்கால்), Feet அடி), Span (சாண்), Cubit (முழம்).
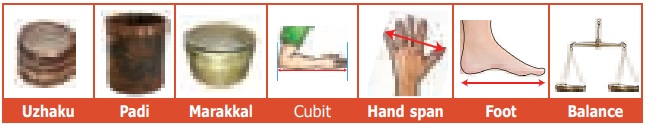
Teacher: Then why do we use kilogram, metre,
litre instead of those units?
Student: I don t know teacher, please tell us
why ?.
Teacher: As we started trading world wide, we found people
in various places using different measures. The ‘kings foot’, the ‘kings arm’ and
the ‘yard’ (the distance between the tip of his nose to the tip of the thumb) were
used
as units to measure small length in various places.
As these lengths differed from person to person and place to place, it was necessary
to standardize measurements throughout the world. The metric measures were defined in 1971 by the General Conference of Weights and Measures.

The basic metric units are Metre, Litre, Gram, Seconds
and so on. It is based on the decimal system (10), which is easier to convert from
one unit to another. We use kilometre, metre, centimetre, millimetre to measure
length; kilogram, gram, milligram for weight and kilolitre, litre, millilitre for
volume in shops, schools ,office, railways and many other places.
An eye blink represents a second; heart beats are
counted per minute; working time of an employee is calculated in hours.
MATHEMATICS ALIVE – MEASUREMENTS IN REAL
LIFE

Related Topics