Chapter: Web or internet Programming : Scripting Elements
JavaScript - Arrays
Arrays
Declaring and Allocating Arrays
• Arrays
occupy space in memory. An array in JavaScript is an Array object. The programmer
uses operator new to allocate dynamically the number of elements required by
each array.
• The
process of creating new objects is also known as creating an instance, or
instantiating an object, and operator new is known as the dynamic memory allocation
operator. Array objects are allocated with new because arrays are considered to
be objects, and all objects must be created with new. To allocate 12 elements
for integer array c, use the statement
var c =
new Array( 12 );
• When
arrays are allocated, the elements are not initialized.
Examples Using Arrays
<head>
<title>Initializing
an Array</title> <script type = "text/javascript">
<!--
// this
function is called when the <body> element's
// onload
event occurs
function
initializeArrays()
{
var n1 =
new Array( 5 ); // allocate 5-element Array var n2 = new Array(); // allocate
empty Array
// assign values to each element of Array n1 for (
var i = 0; i < n1.length; ++i )
n1[ i ] =
i;
// create and initialize five-elements in Array n2
for ( i = 0; i < 5; ++i )
n2[ i ] =
i;
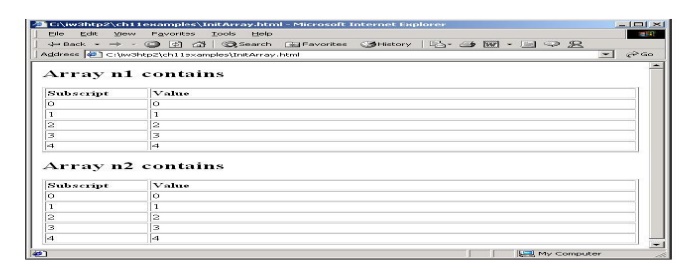
outputArray(
"Array n1 contains", n1 ); outputArray( "Array n2
contains", n2 );
}
// output
"header" followed by a two-column table
// containing
subscripts and elements of "theArray" function outputArray( header,
theArray )
{
document.writeln(
"<h2>" + header + "</h2>" );
document.writeln(
"<table border = \"1\" width =" +
"\"100%\">" ); document.writeln(
"<thead><th width = \"100\"" + "align =
\"left\">Subscript</th>" + "<th align =
\"left\">Value</th></thead><tbody>" );
for ( var i = 0; i < theArray.length; i++ )
document.writeln( "<tr><td>" + i +
"</td><td>" +
theArray[ i ] + "</td></tr>"
); document.writeln( "</tbody></table>" );
}
// -->
</script>
</head>
<body
onload = "initializeArrays()"></body>
</html>
Passing Arrays to Functions
• To pass
an array argument to a function, specify the name of the array (a reference to
the array) without brackets. For example, if array hourlyTemperatures has been
declared as
var
hourlyTemperatures = new Array( 24 );
then the
function call
modifyArray( hourlyTemperatures ); passes
array hourlyTemperatures to function modifyArray.
• In
JavaScript, every array object ―knows‖ its own size (via the length attribute).
Thus, when we pass an array object into a function, we do not pass the size of
the array separately as an argument.
• Although
entire arrays are passed by using call-by-reference, individual numeric and
boolean array elements are passed by call-by-value exactly as simple numeric
and Boolean variables are passed (the objects referred to by individual
elements of an Array of objects are still passed by call-by-reference). Such
simple single pieces of data are called scalars, or scalar quantities. To pass
an array element to a function, use the subscripted name of the element as an
argument in the function call.
Multiple-Subscripted Arrays
‖
Multiple-subscripted arrays with two subscripts often are used to represent
tables of values
• consisting
of information arranged in rows and columns.
• To
identify a particular table element, we must specify the two subscripts; by
convention, the first identifies the element‘s row, and the second identifies
the element‘s column. Arrays that require two subscripts to identify a
particular element are called double-subscripted arrays (also called
two-dimensional arrays).
• Multiple-subscripted
arrays can have more than two subscripts. JavaScript does not support
multiple-subscripted arrays directly, but does allow the programmer to specify
single-subscripted arrays whose elements are also single-subscripted arrays,
thus achieving the same effect.
• Every
element in array a is identified by an element name of the form a[i][j]; a is
the name of the array, and i and j are the subscripts that uniquely identify
the row and column, respectively, of each element in a.
• The names
of the elements in the first row all have a first subscript of 0; the names of
the elements in the fourth column all have a second subscript of 3.
Multiple-subscripted arrays can be initialized in declarations like a
single-subscripted array. Array b with two rows and two columns could be
declared and initialized with the statement
var b = [
[ 1, 2 ], [ 3, 4 ] ];
• The
values are grouped by row in square brackets. So, 1 and 2 initialize b[0][0]
and b[0][1], and 3 and 4 initialize b[1][0] and b[1][1]. The interpreter
determines the number of rows by counting the number of sub-initializer lists
(represented by sets of square brackets) in the main initializer list. The
interpreter determines the number of columns in each row by counting the number
of
initializer
values in the sub-initializer list for that row. Multiple-subscripted arrays
are maintained as arrays of arrays. The declaration
var b = [
[ 1, 2 ], [ 3, 4, 5 ] ];
creates
array b with row 0 containing two elements (1 and 2) and row 1 containing three
elements (3, 4 and 5).
Objects
The
built-in objects available in java script are,
String object
The
String object is used to manipulate a stored piece of text.
Example:
1. var
txt="Hello world!";
document.write(txt.length);
output:
12
2. var
txt="Hello world!";
document.write(txt.toUpperCase());
output: HELLO WORLD!
Related Topics