Chapter: Information Security : Logical Design
Information Security Policy
INFORMATION SECURITY POLICY
PLANNING FOR SECURITY
ü Creation
of information security program begins with creation and/or review of
organization’s information security policies, standards, and practices
ü Then,
selection or creation of information security architecture and the development
and use of a detailed information security blueprint creates plan for future
success
ü Security
education and training to successfully implement policies and ensure secure
environment
Why Policy?
ü A quality
information security program begins and ends with policy
ü Policies
are least expensive means of control and often the most difficult to implement
ü Some
basic rules must be followed when shaping a policy:
–
Never
conflict with law
–
Stand up
in court
–
Properly
supported and administered
–
Contribute
to the success of the organization
–
Involve
end users of information systems
Definitions
· Policy: course of action used by an
organization to convey instructions from management to those who perform duties
–
Organizational
rules for acceptable/unacceptable behavior
–
Penalties
for violations
–
Appeals
process
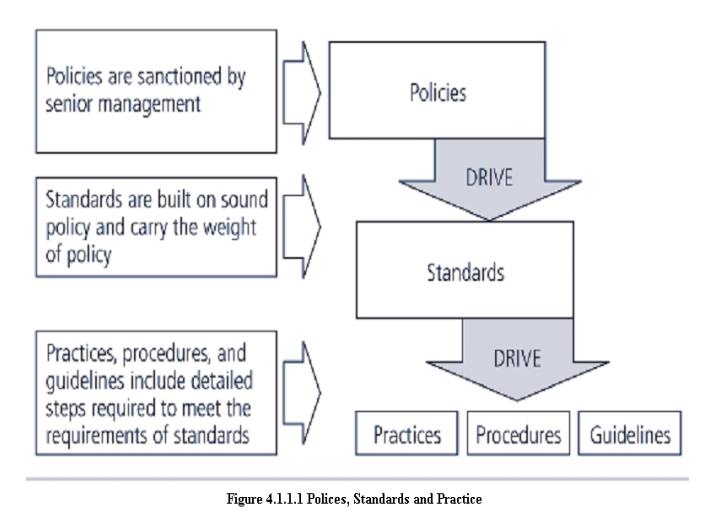
· Standards: more detailed statements of
what must be done to comply with policy
· Practices, procedures and guidelines effectively
explain how to comply with policy
· For a
policy to be effective it must be
–
Properly
disseminated
–
Read
–
Understood
–
Agreed to
by all members of organization
-
Types of
Policies
Enterprise information Security program
Policy(EISP)
Issue-specific information Security Policy ( ISSP)
Systems-specific information Security Policy
(SysSP)
1.Enterprise Information Security Policy (EISP)
Also
Known as a general Security policy, IT security policy, or information security
policy.
Sets
strategic direction, scope, and tone for all security efforts within the
organization
Assigns
responsibilities to various areas of information security
Guides
development, implementation, and management of information security program
2.Issue-Specific Security Policy (ISSP)
1. The ISSP:
–
Addresses
specific areas of technology
–
Requires
frequent updates
–
Contains
statement on position on specific issue
2. Approaches
to creating and managing ISSPs:
–
Create
number of independent ISSP documents
–
Create a
single comprehensive ISSP document
–
Create a
modular ISSP document
3. ISSP
topics could include:
– E-mail,
use of Web, configurations of computers to defend against worms and viruses, prohibitions against
hacking or testing organisation security controls, home use of company-owned
computer equipment, use of personal equipment on company networks, use of
telecommunications technologies(FAX and phone), use of photocopiers
Components
of the ISSP
4.4.4 Statement
of Policy
–
Scope and
Applicability
–
Definition
of Technology Addressed
–
Responsibilities
1. Authorized
Access and Usage of Equipment
–
User
Access
–
Fair and
Responsible Use
–
Protection
of Privacy
2. Prohibited
Usage of Equipment
–
Disruptive
Use or Misuse
–
Criminal
Use
–
Offensive
or Harassing Materials
–
Copyrighted,
Licensed or other Intellectual Property
–
Other
Restrictions
3. Systems Management
–
Management
of Stored Materials
–
Employer
Monitoring
–
Virus
Protection
–
Physical
Security
–
Encryption
4. Violations
of Policy
–
Procedures
for Reporting Violations
–
Penalties
for Violations
5. Policy
Review and Modification
–
Scheduled
Review of Policy and Procedures for Modification
6. Limitations
of Liability
– Statements of Liability or
Disclaimers
3.Systems-Specific Policy (SysSP)
6. SysSPs
are frequently codified as standards and procedures to be used when configuring
or maintaining systems
7. Systems-specific
policies fall into two groups:
8. Access control lists (ACLs) consist
of the access control lists, matrices, and capability tables governing the rights and privileges of a particular user to
a particular system
9. Configuration rules comprise
the specific configuration codes entered into security systems to guide the execution of the system
ACL Policies
Both
Microsoft Windows NT/2000 and Novell Netware 5.x/6.x families of systems
translate ACLs into sets of configurations that administrators use to control
access to their respective systems
ACLs
allow a configuration to restrict access from anyone and anywhere
ACLs
regulate:
–
Who can
use the system
–
What
authorized users can access
–
When
authorized users can access the system
–
Where
authorized users can access the system from
–
How
authorized users can access the system
THE INFORMATION SECURITY BLUEPRINT
It is the
basis for the design, selection, and implementation of all security policies,
education and training programs, and technological controls.
More
detailed version of security framework,
which is an outline of overall information security strategy for organization
and a road map for planned changes to the information security environment of
the organization.
Should
specify tasks to be accomplished and the order in which they are to be
realized.
Should
also serve as a scalable, upgradeable, and comprehensive plan for the
information security needs for coming years.
Related Topics