Chapter: Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing : Induction of Labour
Induction of Labour
INDUCTION OF LABOUR
At the end of this chapter the students will be able to:
·
Identify indications of induction of labour
·
Mention standard protocol of induction
·
Define Augumentation
·
List indicators of failure of trial of labour
Definition: Induction is the initiation of
labour by artificial means Labour should be induced for medical or obstetrical reasons.
Type
i.
Medical - using drugs alone Syntocinon & prostaglandin E2
ii.
Surgical-aminiotomy or membranes sweep
iii.
Combined - medical & surgical.
Indications for Induction
·
Prolonged pregnancy (post term pregnancy)
·
Pre eclampsia, eclampsia and diabetes
·
Evidence of diminished fetal well being or growth
·
Elderly primigravida
·
Poor obstetric history
·
Spontaneous / premature rupture of membrane
·
Previous large baby
·
Rhesus iso - immunization
·
Unstable lie
·
Genital herpes
·
Previous precipitate labour
·
Placenta abruptio
· intrauterine death
Contraindication
·
Unreliable EDD
·
Malpresentation
·
Cephalopevic disproportion
·
Fetal distress
·
Psychological distress
Factors which affect induction of labour
A .Fetal maturity and viability
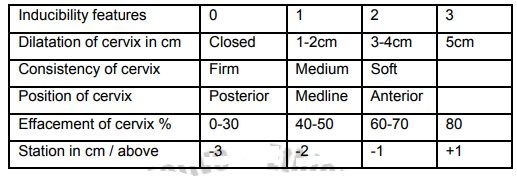
B .Favorability of cervix
Favorability of cervix is assessed by a score system called
‘’Bishop”score.It has to be done before induction. The score is scored out of
20.Score of greater or equal to 7is favorable. There are four factors
considered, each accounts a score of 0-3.
Preparations
·
Admit 24 hrs before hand
·
Sedate at night no breakfast
·
Vulval preparation
· Psychological preparations
Methods
Medical method
·
Prostaglandin E2
-
Vaginal prostaglandin
-
Endocervical prostaglandin
-
Extra amniotic prostaglandin
-
Oral
·
Intravenous oxytocin / syntocinon/ infusion
Aim - To achieve 3 contractions per 10 minutes lasting 40-60
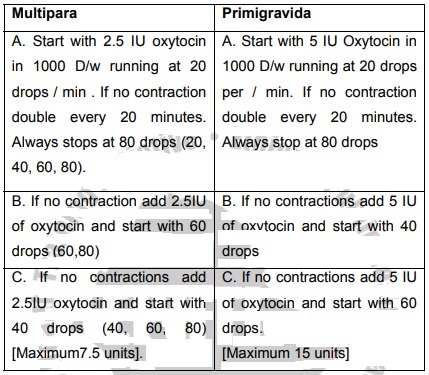
Table 7. Procedure of induction for multipara and primigravida
In induction
·
delivery interval doesn’t
exceed 18 hours;
if not ceaserean section is
indicated.
·
If no labour starts in 6 hours- consult
·
If contractions are very strong and tetanic stop drip, sedate and
consider ceaserean section.
Observation of mother and fetus
·
The fetal heart rate
·
Uterine contractions
·
Fluid balance chart
·
Urine test for ketoses
·
Progress in labour
·
Abdominal & cervical examination every 2-4 hours
After delivery continue oxytocin drops for one hour to prevent PPH.
Complications of medical induction
·
Over stimulation of the uterus causing fetal distress, precipitate
labour or uterine rupture.
Amniotomy (Surgical induction)
Amniotomy is artificial rupturing of amniotic bag or membranes.
Rupturing these if they do not rupture spontaneously allows the fetal head to
contact the cervix more directly and may increase the efficiency of
contractions. The membranes are torn and amniotic fluid is allowed to escape.
Complications:
·
Cord prolapse
·
Placental separation
·
Intrauterine infection if labour is not completed with is 24 hours of
rupture of membrane and prophylactic antibiotic is not given.
Contraindications:
·
High head
·
Unripe cervix
·
Malpresertaions
·
Intrauterine death
Related Topics