Chapter: 12th Political Science : Chapter 10 : India and It’s Neighbours
India - Myanmar Relations
India – Myanmar Relations

Every Burmese Buddhist wish is to come to India at
least once in their lifetime and offer prayers in Bodh Gaya. Long before both
nations became independent states, diverse indigenous population living in the
border areas, mainly Mizos, Nagas, Kukis, Tangkhul and Paite, enjoyed close familial,
linguistic, religious and cultural ties. It’s only after the arrival of British
were the borders demarcated and the emergence of two different nations.
India – Myanmar (formerly known as
Burma) relations goes back to 2500 years. For the Burmese, Buddhist connections
binds both India and Burma together. According to the legend of Shwedagon
Pagoda – the heart of the temple is on the buried strands of Lord Buddha’s hair
gifted by him to two Burmese merchants. It’s this belief that made King Ashoka to
build pagodas in Burma and also for the spread of Buddhism.
Ethnic Composition
The defence of Burma is in fact the
defence of India and it is India’s primary concern no less than Burma’s to see
that its frontiers remain inviolate. In fact, no responsibility can be
considered too heavy for India when it comes to the question of defending
Myanmar. – K.M.Panikkar

Modern Era
The Historical close relations between Myanmar and
India found it’s low point during the British rule when the Indians had to face
resentment amongst the Burmese as the Indian soldiers (under the British Army)
fought against the BIA (Burma Independence Army). Burma always perceived that
Indian officers and staff functioned as tools of the British colonial regime.
Introduction
India shares a long land border of over 1600 Km
with Myanmar as well as a maritime boundary in the Bay of Bengal. Four
north-eastern states viz. Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram
share boundary with Myanmar.
These geo-strategic realities encompass our broader
interests in the Indian Ocean region. Both countries share a heritage of
religious, linguistic and ethnic ties.
Further, Myanmar is the only ASEAN country
adjoining India and, therefore, our gateway to South East Asia with which we
are seeking greater economic integration through India’s ‘Look East’ and now
‘Act East’ policy. Business opportunities that emerge from a surging economy in
Myanmar also provide new vistas for engagement.
1) India’s Look East Policy
India’s Look East policy represents its efforts to cultivate
extensive economic and strategic relations with the nations of Southeast Asia
in order to bolster its standing as a regional power and a counterweight to the
strategic influence of the People’s Republic of China.
Two highways involving Myanmar play a vital role in
improving connectivity in the South East Asian region.
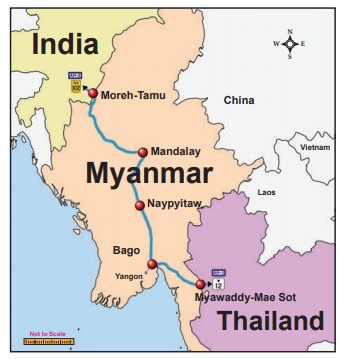
2) India-Myanmar-Thailand Friendship Highway
India and Myanmar have agreed to a 4-lane, 3200 km
triangular highway connecting India, Myanmar and Thailand. The route will run
from India’s northeastern states into Myanmar, where over 1,600 km of roads
will be built or improved. This is expected to be completed by April 2021.
3) Access to North-east
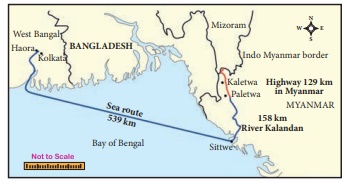
The Kaladan Multi-modal Transit Transport Project
will connect the eastern Indian seaport of Kolkata with Sittwe seaport in
Myanmar by sea; it will then link Sittwe seaport to Lashio in Myanmar via
Kaladan river boat route and then from Lashio on to Mizoram in India by road
transport.
Various Aspects of India – Myanmar Relationship
Defence
and Security Cooperation
1. It has strengthened over the years. Exchange of
high-level visits, signing of MoU on border cooperation, training army, air
force and naval staff are important indicators in this direction.
2. Myanmar side has provided assurances at the
highest levels that it will cooperate with India in taking necessary action in
preventing the use of Myanmar territory for anti-India activity.
Commercial Cooperation
1. A bilateral Trade Agreement was signed in 1970.
2. India is the fifth largest trading partner of
Myanmar but trade remains below potential.
3. India’s exports to Myanmar include sugar
pharmaceuticals, etc.
4. India is presently the tenth largest investor
with an approved investment of US$ 740.64 million.
5. Most India’s investments have been in oil &
gas sector. Indian companies have evinced interest in investing in Myanmar and
major contracts have been won by Indian companies.
6. Besides normal trade, both sides have also taken
steps to bolster trade across the land border. Cooperation in the banking
sector is crucial for investment and trade. United Bank of India signed banking
agreements with banks of Myanmar (MFTB, MICB, MEB, and 9 private banks) to facilitate
bilateral trade
7. Myanmar is an important partner in our energy
relations with other countries in the region.
Culture relations
India and Myanmar share close cultural ties and a
sense of deep kinship given India’s Buddhist heritage.
1. Restoration of the Ananda Temple in Bagan
2. GOI donation of a 16 foot replica of the Sarnath
Buddha Statue which has been installed at the premises of Shwedagon Pagoda in
Yangon.
3. The ‘Samvad-II’ Interfaith dialogue was held on
6-7 August 2017, Yangon.
4. ICCR and Sitagu International Buddhist Academy
organised an International Conference on Buddhist Cultural Heritage
5. India has responded to Myanmar’s interest in
restoring and renovating two historic temples in Bodh Gaya built by Myanmar
rulers King Mindon and King Baygyidaw. These temples and inscriptions will now
be restored with the assistance of the Archaeological Survey of India as a
bilateral friendship project.
Indian diaspora
1. The origin of the Indian community in Myanmar is
traced to the mid-19th century with the advent of the British rule in Lower
Burma in 1852.
2. The two cities Yangon and Mandalay had a
dominating presence of Indians in civil services, education, trade and commerce
during the British rule.
Bilateral Cooperation in Regional/Sub-regional context
ASEAN: As the
only ASEAN country which shares a
land border with India, Myanmar is a bridge between India and ASEAN.
BIMSTEC: Myanmar
is a signatory to the BIMSTEC Free
Trade Agreement. Myanmar is the lead country for the energy sector. Myanmar
trades mostly with Thailand and India in the BIMSTEC region. Myanmar’s major
exports to India are agricultural products like beans, pulses and maize and
forest products such as teak and hardwoods. Its imports from India include
chemical products, pharmaceuticals, electrical appliances and transport
equipment.
Mekong
Ganga Cooperation: Myanmar is a member of the Mekong Ganga Cooperation
(MGC) since its inception in November 2000. MGC is an initiative by six
countries – India and five ASEAN countries namely, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar,
Thailand and Vietnam – for cooperation in the fields of tourism, education,
culture, transport and communication. The chairmanship of MGC is assumed by
member countries in alphabetical order.
SAARC: Myanmar
was given the status of observer in
SAARC in August 2008.
1. In India, we often say Myanmar is our “gateway” to
the East. Against the rhetoric, the existing connectivity between the two neighbours
remains much to be desired. With long land and maritime boundaries, the
neighbours are yet to take full advantage of geography.
2. Historically, India has been a major player in
Myanmar’s socio-economic landscape till the 1960s. The advent of military
dictatorship and its economic policies reduced India’s interactions with
Myanmar.
3. As the political transition in Myanmar picks up
momentum, it provides an excellent opportunity to explore new avenues of
cooperation.
Related Topics