Chapter: RF and Microwave Engineering : Microwave Passive Components
Important Short Questions and Answers: Microwave Passive Components
MICROWAVE PASSIVE COMPONENTS
1)What
is Gyrator?
Gyrator is a two port device which provides a
relative phase shift of 180 degree for transmission from port 1 to port 2 as
compared to the phase for transmission from Port2 to port 1.
2)What
are the composition of ferrites
Ferrites are ceramic like materials. These are
by sintering a mixture of metallic oxides Properties
Specific resistivity‟s may be used as much as 1014 greater than that
of metals Dielectric constants around 10 to 15 or greater Relative permeability
is 1000 . Examples of ferrite devices: Isolator Circulator Phase shifters,
Modulators, Power limiters
3)What
are the high frequency limitation in conventional tubes
The high frequency effects in conventional
tubes are
i) Circuit reactance like Inter electrode
capacitance and Lead inductance
ii)Transit time effect
iii) Cathode emission
iv) Plate heat dissipation area
v)Power loss due to skin effect, radiation and
dielectric loss.
4) What
is Faraday’s rotation law?
If a circular polarized wave is made to pass through a ferrite rod which has been influenced by an Axial magnetic field B, then the axis of polarization gets tilted in clockwise direction and amount of tilt depends upon the strength of magnetic field and geometry of the ferrite.
5. What
is the S-matrix of 3 port circulators?

6)Give
the significance of Rat race junction
The rat race is particularly used for combining
2 signals or dividing a single signal into 2 equal halves
7)What
are ferrite? Why its needed in circulator
Ferrites are non metallic meterials with
resistives nearly 10 14 times greater than metals and also the
dielectric constant is in between 10 -15 and relative permeability
of the order of 1000
8)Mention
the application of gyrator and isolator
Gyrator :
(i)
In can
be in radar antenna as a duplexer
(i)
Isolator
are generally used to improve the frequency stability of microwave generators,
such as klystrons and magnetrons in which the reflection from the load affects
the generating frequency
8)Name the microwave passive devices which make
use of faraday rotation
ü Isolator
ü Gyrator
ü Circulator
9)What
are properties of S- Matrix
ü Zero diagonal elements for perfect matched
networks
ü Symmetry of reciprocal network
ü Unitary property
ü Phase shift property
10)
What are matched terminators
ü Low power co axial termination
ü Resistance strip
ü Standard mis matches
11)
Define isolator?
An isolator or uniline is two port non
reciprocal devices, which produce a minimum attenuation to wave in one
direction and very high attenuation in the opposite directio
12) Draw the Structure of Two hole Directional coupler
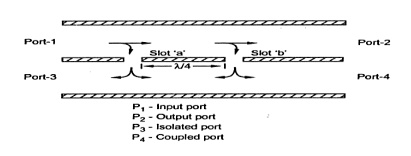
13) Draw
the diagram for H – plan tee?
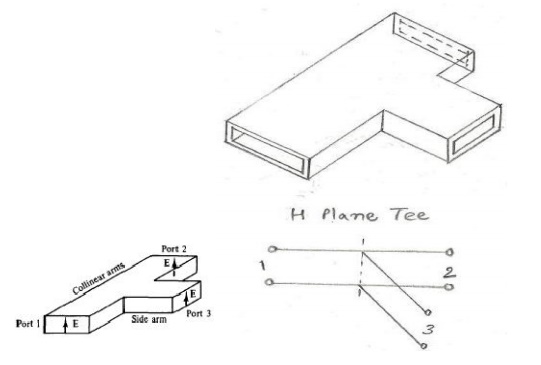
14 )What is H-Plane Tee?
It is a wave guide tee in which the axis of the
slide arm is shunting the E- field or parallel to the H-field of the main
guide.
15 )
Name some uses of waveguide twists?
(i) waveguide twists are used to change the plane of polarization of a
propagating wave.
(ii)
Waveguide twists are helpful in converting vertical to horizontal
polarizations or vice versa.
16 )
Give the applications of directional coupler
1.
Unidirectional
power measurement
2.
SWR
measurement
3.
Unidirectional
wave launching
4.
Reflectometer
5.
Balanced
duplexer.
17 )
What are waveguide corners, bends and twists?
These
wave guide components are normally used to change the direction of guide
through an arbitrary angle
Related Topics