Chapter: Electrical Drives & Control : Introduction to Electrical Drives
Important Short Questions and Answers: Introduction to Electrical Drives
Introduction
Define Drive and Electric Drive?
Drive: A
combination of prime mover, transmission equipment and mechanical Working load
is called a drive
Electric drive: An Electric Drive can be defined as an electromechanical device for
converting electrical energy to
mechanical energy to impart motion to different machines and mechanisms for
various kinds of process control.
List out some examples of prime movers?
Hydraulic Engine,
Steam engine,
Turbine or electric motors.
List out some advantages of electric drives?
Availability of electric drives
over a wide range of power a few watts to mega watts.
Ability to provide a wide
range of torques over wide range of speeds.
Electric motors are available
in a variety of design in order to make them compatible to any type of load.
Give some examples of Electric Drives?
Driving fans, ventilators,
compressors and pumps.
Lifting goods by hoists and
cranes.
Imparting motion to conveyors
in factories, mines and warehouses
Running excavators &
escalators, electric locomotives trains, cars trolley buses, lifts & drum
winders etc.
What are the types of electric drives?
Group electric drives (Shaft
drive),
Individual Drives,
Multi motor electric drives.
What is a Group Electric Drive (Shaft Drive)?
This drive consists of single
motor, which drives one or more line Shafts supported on bearings.
The line shaft may be fitted
with either pulleys & belts or gears, by means of which a group of machines
or mechanisms may be operated.
Classify electric drives based on the means of
control?
Manual,
Semiautomatic,
Automatic
What are the advantages and disadvantages of
Group drive (Shaft drive)?
A single large motor can be
used instead of a number of small motors.
The rating of the single
motor may be appropriately reduced taking into account the diversity factor of
loads.
Disadvantages:
There is no flexibility;
Addition of an extra machine to the main Shaft is difficult.
The efficiency of the drive
is low, because of the losses occurring in several transmitting mechanisms.
The complete drive system
requires shutdown if the motor, requires Servicing or repair.
The system is not very safe
to operate
The noise level at the work
spot is very high.
What is an individual electric drive? Give some
examples. (UQ)
In this drive, each individual machine is
driven by a separate motor. This motor also imparts motion to various other
parts of the machine.
Single spindle drilling machine, Lathe machines
etc.
What is a multi motor electric drive? Give some examples.
In this drive, there are several drives, each
of which serves to activate on of the working parts of the driven mechanisms.
Metal cutting machine tools, paper making
machines, rolling mills, traction drive, Traveling cranes etc.,
Write about manual control, semiautomatic control & Automatic
control?
Manual control: The electric drives with manual control can be as simple as a room
fan, incorporating on switch and a
resistance for setting the required speed.
Semiautomatic control: This control consists of a manual device for giving a certain
command (Starting, braking,
reversing, change of speed etc.,) and an automatic device that in response to
command operates the drive in accordance with a preset sequence or order.
Automatic control: The electric drives with automatic control have a control gear, Without manual devices
What are the typical elements of an Electric Drive?
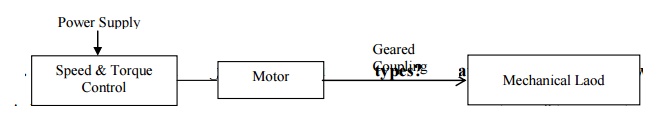
What is a load diagram? What are its types? What are required to
draw a load
A load diagram is the diagram which shows
graphically the variation of torque acting on the electric drive. The motor of
the electric drive has to overcome the load torque expressed as a function of
time.
Types:
One for the static or steady
state process
Other for the dynamic
process, when the dynamic components of torque are induced by the inertia of
the motor & load.
(Instantaneous speed, acceleration, Torque
& power) as a function of time are required to draw…..
What are the types drive systems?(UQ)
Electric Drives
Mechanical Drives
Electromechanical Drives
Hydraulic drives.
Give an expression for the losses occurring in
a machine?
The losses occurring in a machine is given by
W = Wc + x2 Wv
Where Wc =
Constant losses
Wv = Variable losses at full load
X = load
on the motor expressed as a function of rated load.
What are the assumptions made while performing
heating & cooling calculation of an electric motor?
The machine is considered to
be a homogeneous body having a uniform temperature gradient. All the points at
which heat generated have the same temperature. All the points at which heat is
dissipated are also at same temperature.
Heat dissipation taking place
is proportional to the difference of temperature of the body and surrounding
medium. No heat is radiated.
The rate of dissipation of
heat is constant at all temperatures.
What are the factors that influence the choice of Electrical
drives?
Shaft power & speed
Power range
Starting torque
Maintenance
Total purchase cost
Influence on power supply
Availability
Nature of electric supply
Types of drive
Service cost
Speed range
Efficiency
Influence on the supply network
Special competence
Cost of energy losses
Environment
Accessibility
Nature of load
Electrical Characteristics
Service capacity & rating
Indicate the importance of power rating & heating of electric
drives.
Power rating: Correct
selection of power rating of electric motor is of economic interest as it is associated with capital cost and
running cost of drives.
Heating: For
proper selection of power rating the most important considerations the heating
effect of load. In this connection
various forms of loading or duty cycles have to be considered.
How heating occurs in motor drives?
The heating of motor due to losses occurring
inside the motor while converting the electrical power into mechanical power
and these losses occur in steel core, motor winding & bearing friction.
What are the classes of duties?
Continuous duty
Short time duty operation of
motor Main classes of duties
Intermittent periodic duty
Intermittent periodic duty
with starting
Intermittent periodic duty
with starting & braking
Continuous duty with
intermittent periodic loading
Continuous duty with starting
& braking
Continuous duty with periodic
load changes
How will you classify electric drives based on
the method of speed control?
Reversible &non
reversible in controlled constant speed
Reversible and non reversible
step speed control
Reversible and non reversible
smooth speed control
Constant predetermined
position control
Variable position control
Composite control.
List out some applications for which continuous
duty is required.
Centrifugal pumps, fans,
conveyors & compressors
Why the losses at starting are not a factor of consideration in a
continuous duty motor?
While selecting a motor for this type of duty
it is not necessary to give importance to the heating caused by losses at
starting even though they are more than the losses at rated load. This is
because the motor does not require frequent start nit is started only once in
its duty cycle and the losses during starting do not have much influence on
heating.
What is meant by “short time rating of motor”?
Any electric motor that is rated for a power
rating P for continuous operation can be loaded for a short time duty (Psh)
that is much higher than P, if the temperature rise is the consideration.
What is meant by “load equalization”?
In the method of “load Equalization” intentionally
the motor inertia is increased By adding a flywheel on the motor shaft, if the
motor is not to be reversed. For Effectiveness of the flywheel, the motor
should have a prominent drooping characteristic so that on load there is a
considerable speed drop.
How a motor rating is determined in a
continuous duty and Variable load?
Method of Average losses, equivalent power,
equivalent Torque
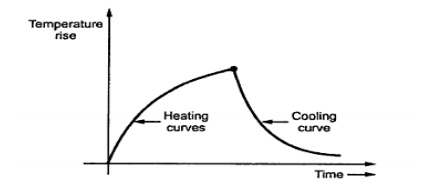
Define heating time constant & cooling time
constant?
Heating time constant is defined as the time
taken by the machine to attain 0.623 of its final steady temperature rise.
Cooling time constant is, therefore, defined as
the time required cooling the machine down to 0.368 times the initial
temperature rise above ambient temperature.
What are the various function performed by an
electric drive?
Driving fans, ventilators,
compressors & pumps etc.,
Lifting goods by hoists &
cranes
Imparting motion to conveyors
in factories, mines & warehouses and
Running excavators &
escalators, electric locomotives, trains, cars, Trolley buses and lifts etc.
Write down the heat balance equation?
Heat balance equation is given by Ghd0 + S0 .dt
= p.dt
What is ingress protection code? (UQ)
The protection code deals with the methods
employed for safeguarding the motor against the entry of external agents like
dust, water etc.
For example IP 21 deals with safeguarding motor
against foreign bodies like water. IP stands for ingress protection code.
What are
the mechanical considerations to be considered in Selection of motor (UQ)
Types of enclosures
Types of bearings
Types of mounting
Types of drive
Noise emitted
Mention four types of mechanical load?
Load torque remaining
constant irrespective of the speed
Load torque increasing with
the square of the speed
Load torque increasing with
speed, Load torque decreasing
Define continuous duty of a motor?
Continuous duty: This type drive is operated continuously for a duration which is
long enough to reach its steady
state value of temperature. This duty is characterized by constant motor torque
and constant motor loss operation. This type of duty can be accomplished by
single phase/ three phase induction motors and DC shunt motors.
Examples:
Paper mill drives
Compressors
Conveyors
Centrifugal pumps and
Fans
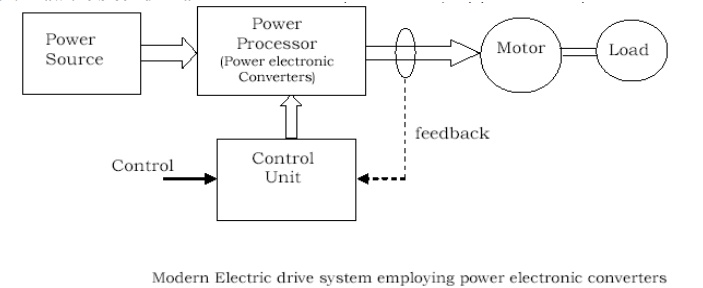
Draw the block diagram of electric drive?
Draw the heating and cooling curve?
Related Topics