Chapter: Civil : Automobile Engineering : Transmission Systems
Hotchkiss drive
Hotchkiss drive
The Hotchkiss drive is a system of power transmission. It was
the dominant form of power transmission for front-engine, rear-wheel drive
layout cars in the 20th century. The name comes from the French automobile firm
of Hotchkiss, although it is clear that other makers (such as Peerless) used
similar systems before Hotchkiss.
During the early part of the 20th century the two major
competing systems of power transmission were the shaft-drive and chain-drive
configurations. The Hotchkiss drive is a shaft-drive system (another type of
direct-drive transmission system is the torque tube, which was also popular
until the 1950s).
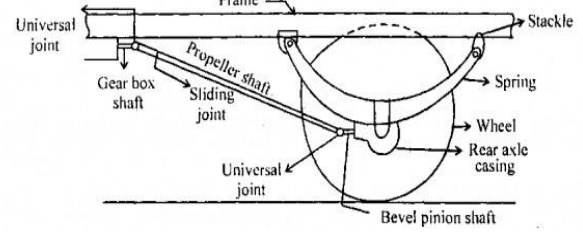
All shaft-drive
systems consist of a driveshaft (also called a
"propeller shaft" or Cardan
shaft) extending from the transmission
in front to the differential in the rear.
The differentiating characteristic
of the Hotchkiss drive is the fact that it uses universal joints at
both ends of the driveshaft, which is not enclosed. The use of two universal
joints, properly phased and with parallel alignment of the drive and driven
shafts, allows the use of simple cross-type universals. (In a torque-tube
arrangement only a single universal is used at the end of the transmission tail
shaft, and this universal should be a constant velocity joint.)
In the Hotchkiss drive, slip-splines or a plunge-type (ball
and trunnion u-joint) eliminate thrust transmitted back up the driveshaft from
the axle, allowing simple rear-axle positioning using parallel leaf springs.
(In the torque-tube type this thrust is taken by the torque tube to the
transmission and thence to the transmission and motor mounts to the frame.
While the torque-tube type requires additional locating elements, such as a
Panhard rod, this allows the use of coil springs.)
Some Hotchkiss drive shafts are made in two pieces with
another universal joint in the center for greater flexibility, typically in
trucks and specialty vehicles built on truck frames. Some installations use
rubber mounts to isolate noise and vibration. The 1984–1987 RWD
Toyota Corolla (i.e., Corolla SR5 and GT-S) coupe is another example of a car
that uses a 2-part Hotchkiss driveshaft with a rubber-mounted center bearing.
This design was the main form of power transmission for most
cars from the 1920s through the 1970s. Presently (circa 2012), it remains
common in pick-up trucks, and sport utility vehicles.

Related Topics