Chapter: Mechanical : Advanced IC Engines : Recent Trends
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI)
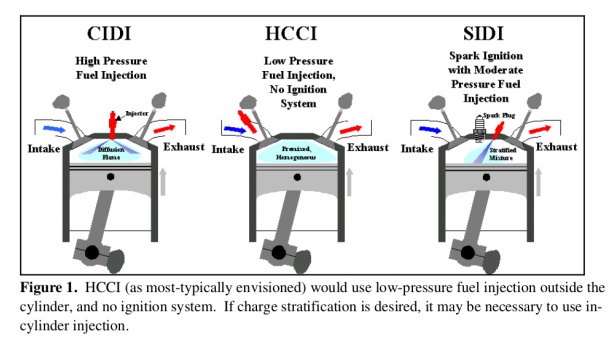
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI)
● HCCI is
an alternative piston-engine combustion process that can provide efficiencies
as high as compression-ignition, direct-injection (CIDI) engines (an advanced
version of the commonly known diesel engine) while, unlike CIDI engines,
producing ultra-low oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and particulate matter (PM)
emissions.
WORKING PRINCIPLE OF HCCI
Homogenous
charge is drawn in to the cylinder during suction and compress to high enough
temperature to achieve spontaneous ignition of the charge.
After
Combustion initiation the temperature rapidly increases and whole fuel burn
simultaneously.
As whole
mixture burns simultaneously and no flame propagation, combustion temp can be
controlled less than 700°
Centigrade and thus NOx formation is avoided.
Advantages
of HCCI:
● HCCI
engines are more efficient thus eliminating of throttling losses, the use of
high compression ratios, and a shorter combustion duration.
●
HCCI engines also have lower engine-out NOx than SI
engines.
● Lower
emissions of PM and Nox
● Because
flame propagation is not required, dilution levels can be much higher than the
levels tolerated by either SI or CIDI engines.
● The
combustion duration in HCCI engines is much shorter than in CIDI engines since
it is not limited by the rate of fuel/air mixing. This leads to higher efficiency.
● HCCI
engines may be lower cost than CIDI engines since they would likely use
lower-pressure fuel-injection equipment.
Challenges of HCCI:
● Controlling
Ignition Timing over a Range of Speeds and Loads.
● Extending
the Operating Range to High Loads.
● Cold-Start
Capability.
● Hydrocarbon
and Carbon Monoxide Emissions.
Related Topics