Chapter: Mechanical : Advanced IC Engines : Recent Trends
Gasoline Direct Ignition Engine
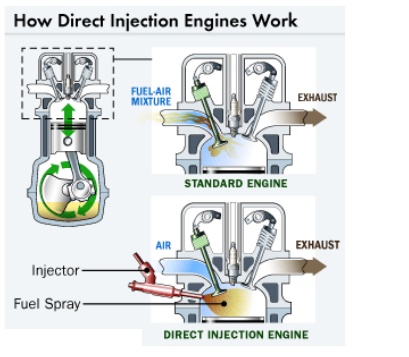
Gasoline Direct Ignition Engine
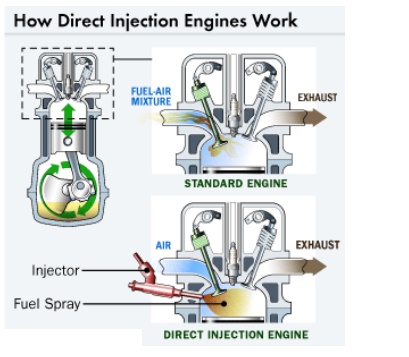
• First,
the fuel travels via pump from the fuel tank, through the fuel line and into
fuel injectors that are mounted into the engine.
• The
injectors spray gasoline into the air intake manifold, where fuel and air mix
together into a fine mist. At precisely timed intervals, intake valves open,
corresponding to the different cylinders of the engine.
• As a
cylinder's intake valve opens, a piston in that cylinder descends, sucking the
fuel-air mist from the air manifold above into the chamber below. As the piston
ascends once more, it squeezes (compresses) the fuel-air mix until it is nearly
nine times as dense as it was to begin with.
• Then,
that cylinder's designated spark plug fires, igniting the chamber into a
high-pressure, high-energy explosion.
• This
little bang pushes the piston back down with tremendous force, causing it to
turn the crankshaft and ultimately send power to the wheels.
• The ratio
of air to fuel as it burns in an engine will have certain, predictable effects
on engine performance, emissions of pollutants and fuel efficiency.
• When the
amount of air in the mixture is high, compared to the amount of fuel, it's
known as a "lean" mixture. When the reverse is the case, it's called
a "rich" fuel mixture.
• Direct
injection engines use a mixture of 40 or more parts air to one part fuel,
written as 40:1.
• That
compares to a normal gasoline engine's mix of 14.7:1. A leaner mixture allows
fuel to be burned much more conservatively.
• A second
efficiency plus for direct injection engines is that they can burn their fuel
more completely.
• The fuel
can be squirted directly where the combustion chamber is hottest -- in a
gasoline engine that means it ends up close to the spark.
•
With a traditional gasoline engine, the fuel air
mixture disperses widely within the chamber, leaving a substantial amount
unburned and therefore ineffective.
Related Topics