Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Railway Track Gauge
Gauges on World Railways
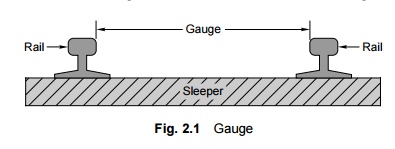
Gauge is
defined as the minimum distance between two rails. Indian Railways follows this
standard practice and the gauge is measured as the clear minimum distance
between the running faces of the two rails as shown in Fig. 2.1.
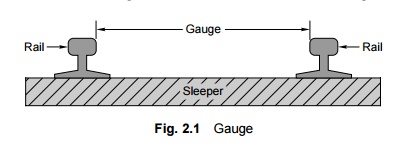
In European countries, the gauge
is measured between the inner faces of the two rails at a point 14 mm below the
top of the rail. This chapter describes the different gauge widths prevalent in
India and other countries. It also discusses the problems and implications of a
multiple-gauge system as adopted in India.
Gauges on World Railways
Various gauges have been adopted
by different railways in the world due to historical and other considerations.
In British Railways, a gauge of 1525 mm (5 feet) was initially adopted, but the
wheel flanges at that time were on the outside of the rails. Subsequently, in
order to guide the wheels better, the flanges were made inside the rails. The
gauge then became 1435 mm (4' 8.5" ), as at that time the
width of the rail at the top was 45 mm (1.75" ). The 1435-mm gauge
became the standard gauge in most European Railways. The approximate
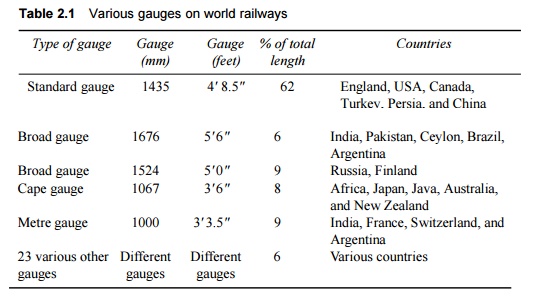
proportions of various gauges on world railways are given in Table 2.1.
Table
2.1 Various gauges on
world railways
Related Topics