Chapter: 12th standard bio zoology higher secondary school
Gaseous exchange in the alveoli
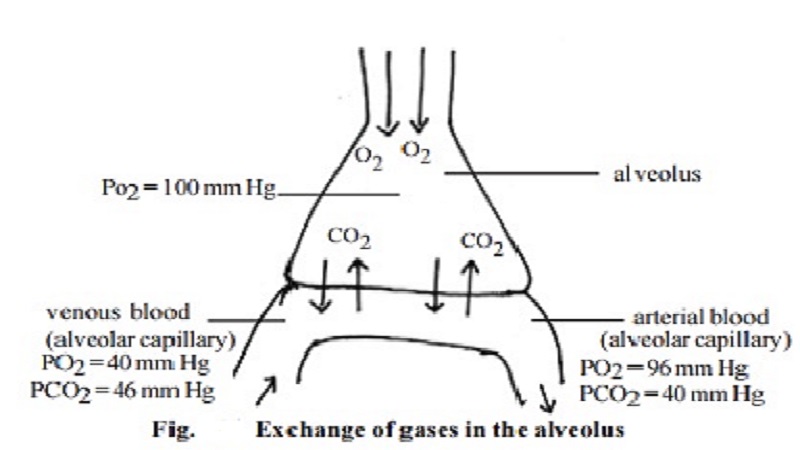
Gaseous exchange in the alveoli
Once the air is
within the lungs the process of gaseous exchange begins. Capillaries of the
pulmonary artery remains close to the wall of the alveloli. This enhances the
exchange of gases.
Oxygen and carbon-di-oxide are exchanged
across the alveolar membrane by diffusion from the site of higher to low
partial pressure until the partial pressure of the two regions are equal. This
process is a simple physical one which does not involve any secretary or active
transport mechanism.
In the atmospheric air there is a high
concentration of oxygen 20-95% (PO2 140mm Hg) while the proportion
of carbon dioxide is low (0.04%).
The alveolar PO2 is about 100mm Hg
and the PO2 of venous blood is about 40mm Hg. This pressure gradient
is sufficient for the transfer of O2. The PCO2 of venous
blood is 46mm.Hg and that of alveolar air is only 6mm.Hg (1/10th of
O2), it is adequate for CO2 transfer by diffusion. CO2
diffuses 20 times faster than O2.
Regulation of respiration :
In the brain the medulla oblongata contains a
respiratory center. This controls breathing. The respiratory center consists of
an inspiratory center and an expiratory center. The axons from the nerve cells
of these centres lead to the intercostals muscle through the intercostals
nerves and the diaphragm via the phrenic nerves. These nerve fibres transmit
impulses to the external intercostal muscles and internal intercostal muscles
alternately. The walls of the alveoli have sense endings which are stimulated
by changes in the tension of alveolar walls.
Mechanism of Breathing :
The process of inspiration and expiration
happens due to pressure changes in the thoracic cavity. The thorax is an
airtight compartment bounded by the sternum in front, the vertebral column at
the back, the ribs encircling the sides and the diaphragm found below. The rib
bones are provided with the two sets of muscles namely external and internal
intercostal muscles. By the contraction and expansion of these muscles the
volume of the thoracic cavity is reduced or increased. The floor of the
thoracic cavity is completely closed by the diaphragm. The act of breathing is
performed by expansion and contracton of the thoracic cavity.
Related Topics