Natural Hazards - Understanding of Disaster Management in Practice | Term 3 Unit 3 | Geography | 7th Social Science - Exercises Questions with Answers | 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 3 Unit 3 : Natural Hazards - Understanding of Disaster Management in Practice
Chapter: 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 3 Unit 3 : Natural Hazards - Understanding of Disaster Management in Practice
Exercises Questions with Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the correct
Answer:
1._____________ is a
event which causes enormous physical damage to property, loss of life and
change in the environment.
a.
Hazard
b.
Disaster
c.
Recovery
d.
mitigation
[Answer : () (a)
and (b)]
2. Activities that
reduce the effects of disaster
a.
Preparation
b.
Response
c.
Mitigation
d. Recovery
[Answer: (c)
Mitigation]
3. A sudden movement
(or) trembling of the earth’s crust is called an _____________
a.
Tsunami
b.
Earthquake
c.
Fire
d.
Cyclone
[Answer: (b)
Earthquake]
4. A sudden overflow of
water in a large amount caused due to heavy rainfall is called _____________
a.
Flood
b.
Cyclone
c.
Drought
d.
Seasons
[Answer: (a) Flood]
5.
Road accidents can be avoided by permitting the persons who have _____________
is allowed to drive vehicle
a.
Ration card
b.
License
c.
permission
d.
Documents
[Answer: (b)
License]
II. Fill
in the blanks:
1.
A hazard is a dangerous event that can causes
harm or damage to human and his property
2.
Activities taken during a disaster is called Disaster management.
3.
Displacement of water can produce one or more huge destructive waves known as Tsunami.
4.
In case of fire accidents call the nearby police station or the no 101
for the fire service
5.
Disastermanagement refers to conservation of lives and property
during a natural or man-made disaster
III. Match
the following:
1.
Earthquake – Gigantic waves
2.
Cyclone – Creak / Fault
3.
Tsunami – Uneven rainfall
4.
Industrial accident – Eye of the storm
5.
Drought – Carelessness
Answer:
1. Earthquake -
Creak / Fault
2. Cyclone - Eye of
the storm
3. Tsunami -
Gigantic waves
4. Industrial
accident - Carelessness
5. Drought - Uneven
rainfall
IV.
Consider the following statement and tick the appropriate answer
1.
Assertion (A) : In the modern world
we can’t live happing everyday.
Reason (R) :
Due to pollution and environmental degradation we are undergoing natural hazard
and Disaster
a.
A and R are correct and A explains R
b.
A and R are correct but A does not explain R
c.
A is not correct but R is correct
d.
Both A and R are in correct
[Answer : (b) A and
R are correct but A does not explain R]
2.
Assertion (A) Sudden movement (or)
trembling of the earth’s crust is called an Earthquake Reason (R): Movement of
the tectonic plates, mass wasting, surface fault all leads to earthquake
a.
A and R are correct and A explains R
b.
A and R are correct but A does not explain R
c.
A is in correct but R is correct
d.
Both A and R are in correct
[Answer : (b) A and
R are correct but A does not explain R]
V. Answer
the following briefly
1. Define Hazard
Answer: A hazard is a dangerous phenomenon, substance, human activity or
condition that may cause loss of life, injury, health impacts, property damage,
loss of livelihoods, services, social and economic disruption or environmental
damage.
2. What is disaster ?
Answer: A disaster can be generally defined as “A serious disruption in
the society causing widespread material, economic, social or environmental
losses which exceed the ability of the affected society to cope using its own
resources”.
3. What are the six
concepts of Disaster management cycle?
Answer: Preparation, Mitigation, Preparedness, Response, Recovery and
Development are the six Disaster management cycles.
4. Name any two agency
which involves in warring system in Tamilnadu
Answer:
(i) TNSDMA
(ii) DDMA
(iii) SDRF
5. Write about any
three effects of flood
Answer: Effects:
(i) Loss of life and property,
(ii) Displacement of people and
(iii) Spread of contagious diseases such as cholera and Malaria
etc.,,
6. Give any four Rail
safety tips
Answer: (i) Stay alert. Trains can come from either direction at any time,
(ii) Never sit on the edge of the Station Platform,
(iii) Cross the tracks safely.
7. Name any four
different industry which goes under industrial disaster frequently
Answer: Defense, Energy, Food and Mining.
VI.
Distinguish between
1. Earthquake and
Tsunami
Answer:
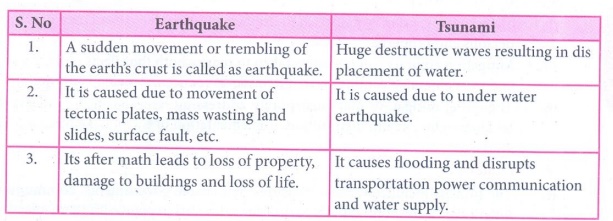
Earthquake
1. A sudden movement or trembling of the earth's crust is called
earthquake.
2. It caused due to movement of tectonic plants, mass wasting
land slides, surface fault, etc.
3. Its after math leads to loss of property, damage to buildings
and loss of life.
Tsunami
1. Huge destructive waves resulting in displacement of water.
2. It is caused due to under water earthquake.
3. It causes flooding disrupts transportation power
communication and water supply.
2. Flood and cyclone
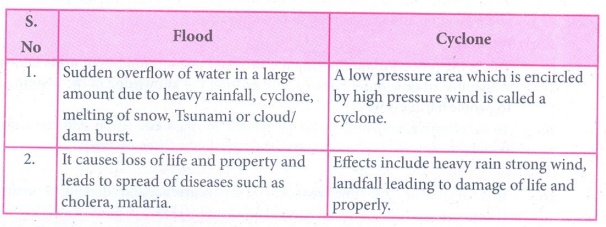
Flood
1.Sudden overflow of water in a large amount caused due to heavy
rainfall, cyclone, melting of snow, Tsunami or cloud/ dam burst.
2. It causes loss of life and property and leads to speard of
diseases such as cholera, malaria.
Cyclone
1. A low pressure area which is encircled by high pressure wind
is called a cyclone.
2. Effects include heavy rain strong wind, landfall leading to
damage of life and properly.
3. Hazard and disaster
Answer:
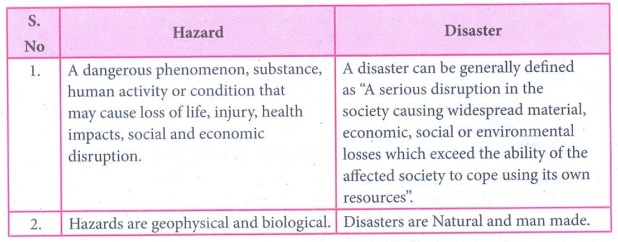
Hazard
1. A dangerous phenomenon, substance, human activity or
condition that may cause loss of life, injury, health impacts, social and
economic disruption.
2. Hazards are geophysical and biological.
Disaster
1. A disaster can be generally defined as “A serious disruption
in the society causing widespread material, economic, social or environmental
losses which exceed the ability of the affected society to cope using its own
resources”.
2. Disasters are Natural and man made.
VII.
Answer the following questions in detail
1. Write about disaster
management cycle
Answer: The six disaster management phases that have been used in the
concept of disaster cycle are as follows;
Pre-Disaster phase:
Prevention and
Mitigation:
(i) The term prevention is often used to embrace the wide diversity
of measures to protect persons and property.
(ii) Mitigation embraces all measures taken to reduce both the
effects of the hazard itself and the vulnerable conditions to it in order to
reduce the scale of a future disaster.
(iii) Therefore, mitigation may incorporate addressing issues such as
land ownership, tenancy rights, wealth distribution, implementation of
earthquake resistant building codes, etc.
Preparedness:
(i) The process includes various measures that enable governments,
communities and individuals to respond rapidly to disaster situations to cope
with them effectively.
(ii) Preparedness includes for example, the formulation of viable
emergency plans, the development of warning systems, the maintenance of
inventories, public awareness and education and the training of personnel.
Early Warning:
(i) This is the process of monitoring the situation in communities
or areas known to be vulnerable to slow onset hazards, and passing the
knowledge of the pending hazard to people harmless way.
(ii) To be effective, warnings must be related to mass education and
training of the population who know what actions they must take when warned.
The Disaster
Impact:
(i) This refers to the “real-time event of a hazard occurrence and
affecting elements at risk.
(ii) The duration of the event will depend on the type of threat;
ground shaking may only occur in a matter of seconds duri ng an earthquake
while flooding may take place over a longer sustained period.
During Disaster
Phase:
Response:
This refers to the first stage response to any calamity, which
include for examples such as setting up control rooms, putting the contingency
plan in action, issue warning, action for evacuation, taking people to safer
areas, rendering medical aid to the needy etc., simultaneously rendering relief
to the homeless, food, drinking water, clothing etc. to the needy, restoration
of communication, disbursement of assistance in cash or kind.
The Post- Disaster
Phase:
Recovery:
Recovery is used to describe the activities that encompass the
three overlapping phases of emergency relief, rehabilitation and
reconstruction.
Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation includes the provision of temporary public
utilities and housing as interim measures to assist long-term recovery.
Reconstruction: Reconstruction attempts to return communities with improved
pre-disaster functioning. It includes replacement of buildings; infrastructure
and lifeline facilities so that long-term development prospects are enhanced
rather than reproducing the same conditions, which made an area or population
vulnerable in the first place.
Development: In an evolving economy, the development process is an ongoing
activity. Longterm prevention/disaster reduction measures. For examples like
construction of embankments against flooding, irrigation facilities as drought
proofing measures, increasing plant cover to reduce the occurrences of
landslides, etc.
2. Write about flood
its effects and the mitigation
Answer: Flood:
Sudden overflow of water in a large amount caused due to heavy
rainfall, cyclone, melting of snow, Tsunami or a dam burst.
Effects:
(i) Loss of life and property,
(ii) Displacement of people and
(iii) Spread of contagious diseases such as cholera and Malaria etc.,
Mitigation for
flood:
They include flood walls / sea walls, flood gates, levees and
evacuation routes. Non structural measures reduce damage by removing people and
property out of risk areas. They induce elevated structures, property buyouts,
permanent relocation, zoning, subdivision and building codes.
3. Write about any five
general survival techniques
Answer: General
Survival Techniques:
(i) During the earthquake be under the table, chair, kneel to the
floor and protect yourself. Go near a sturdy wall, sit on the floor and hold
the floor strongly and protect yourself. Use only torch lights,
(ii) During flood forecast, store up necessary things like first
aid, etc. Listen to the local Radio/TV for instructions. Cut off all the
electrical supplies during flood and earthquake,
(iii) In case of fire accidents call fire service (No. 101)
(iv) If clothes are on fire, Don’t Run; stop, Drop and Roll,”
(v) Stay alert. Trains can come from either direction at any time,
(vi) Never sit on the edge of the Station Platform,
(vii) Cross the tracks safely.
4. Write about earthquake,
its effects, and mitigation steps
Answer: Earthquake:
A sudden movement (or) trembling of the earth crust is called as
earthquake. The movement of the tectonic plates, mass wasting, landslides,
surface fault, etc., causes earthquake.
Effects:
Due to a strong earthquake, loss of lives, buildings, roads,
bridges and dams are damaged. Earthquake cause floods, tsunamis, landslides,
fires, break down of water supply and electrical lines. It may change the
course of a river too.
Mitigation steps:
(i) Construct Earthquake resistant building.
(ii) Seek shelter under stable tables.
(iii) Move to open areas.
(iv) Secure your belonging.
(v) Put latches on cabinet doors and file cabinets.
(vi) Store hazardous materials in a sturdy place.
(vii) Keep fire extinguishers.
VIII. HOTs
1. Why should we know
about the natural disasters?
Answer: (i) To Prevent loss of life.
(ii) To Protect our belongings.
(iii) To create awareness among youngsters.
(iv) To be prepared with emergency phone nos.
(v) To be stocked with food, water medicine.
(vi) For children and old age people.
2. Name four places in
India which undergoes land slide .
Answer: Four places in India prone to landslider.
(i) Western ghats and Konkan hills.
(ii) Darjeeling and Sikkim (NE Himalayas)
(iii) North west Himalayas (Uttarakand, Himachal pradesh, Jammu and
Kashmir)
(iv) Eastern ghats (Araku region in Andhra pradesh)
Related Topics