Landforms | Term 1 Unit 2 | Geography | 7th Social Science - Exercises Questions with Answers | 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 1 Unit 2 : Landforms
Chapter: 7th Social Science : Geography : Term 1 Unit 2 : Landforms
Exercises Questions with Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the correct
answer
1.
____________ is a deposition of river sediments along the foot-hills.
a) Plunge pool
b) Alluvial fan
c) Flood plain
d) Delta
Answer: b. Alluvia
fan
2.
Courtallam falls is located across the____________ river.
a) Cauvery
b) Pennar
c) Chittar
d) Vaigai
Answer: c. Chittar
3.
The landform created by glacial deposition is
a) Cirque
b) Arete
c) Moraine
d) Tarn lake
Answer: c. Moraine
4.
Large deposits of loess are found in
a) USA
b) India
c) China
d) Brazil
Answer: c. China
5.
____________ are not associated with wave erosion
a) Cliff
b) Sea arch
c) Stack
d) Beaches
Answer: d. Beaches
II. Fill in the blanks
1. The process of breaking and
crumbling of rocks is Weathering.
2. The place where the river joins a
lake or a sea is known as River mouth.
3. Inselbergs are found in the Kalahari desert in South Africa.
4. A cirque is known as Kar in Germany.
5. The first longest beach in the world
is Miami beach.
III. Match the following
1. Breaking and crumbling of rocks – - Glacier
2. Abandoned meander loops - Barchans
3. Large body of moving ice - Lagoon
4. Crescent shaped sand dunes - Weathering
5. Vembanad lake - Oxbow lake
Answer: 1) Weathering
2) Oxbow lake 3) Glacier 4) Barchans 5) Lagoon
1. Breaking and crumbling of rocks : Weathering
2. Abandoned meander loops : Oxbow lake
3. Large body of moving ice : Glacier
4. Crescent shaped sand dunes : Barchans
5. Vembanad lake : Lagoon
IV. Consider the
following statement and tick
(✔) the
appropriate answer
1.
Assertion (A): The deltas are formed near the mouth of the river.
Reason
(R) : The velocity of the
river becomes slow when it approaches the sea.
a) Both A and R are correct
b) A is correct and R is wrong
c) A is wrong and R is correct
d) Both A and R are wrong
Answer: a) Both A
and R are correct
2.
Assertion (A): Sea arches
in turn become Sea Stacks.
Reason
(R) : Sea Stacks are the
results of wave deposition.
a) Both A and R are correct
b) A is correct and R is wrong
c) A is wrong and R is correct
d) Both A and R are wrong
Answer: b) A is correct and R is
wrong
V. Answer the following
1.
Define erosion.
Erosion is the wearing away of the landscape by different agents
like water, wind, ice and sea waves. The eroded material is carried away by
water, wind, etc. and eventually deposited. This process of erosion and
deposition create different landforms on the surface of the earth.
2.
What is a plunge pool?
Plunge pool is a hollow feature at the base of a waterfall which
is formed by cavitation.
3.
How are Ox – bow lakes formed?
Due to continuous erosion and deposition along the sides of the
meander, the ends of the meander loop comes closer and closer. In due course of
time the meander loop cuts off from the river and forms a cut-off lake, also
called an Ox-bow lake.
4.
Name the major landforms formed by glacial erosion.
Cirruc, Tam lake, Aretes, U shaped Valley.
5.
Give a note on Mushroom rocks.
In deserts we can see rocks in the shape of a mushroom, commonly
called mushroom rocks.
6.
What is a lagoon? Give an example.
Lagoon is a shallow stretch of water partially or completely
separated from the sea. E.g. Chilka lake in Odisha, Pulicat lake in Tamil Nadu
and Andhra Pradesh and Vembanad lake in Kerala are the famous lagoons in India.
VI. Distinguish the following
1.
Tributary and Distributary

Tributary
A stream or river that flows into and joins a main river.
Distributary
A stream that branches off and flows away from a main stream.
2.
‘V’ shaped valley and ‘U’ shaped valley

V Shaped Valley
The running water in the river erodes the landscape which
creates a steep sided valley like the letter 'V’ known as V shaped Valley.
U Shaped Valley
U shaped valley is found beneath the glaciers which is deepened
and widened by the lateral and vertical erosion. The material carried by the
glacier such as rocks - big and small, sand and silt get deposited.
3.
Continental glacier and Mountain glacier

Continental glacier
The glacier covering vast areas of a continent with thick ice
sheets.
E.g. Antarctica, Greenland.
Mountain glacier
Mountain glacier is a stream of ice flowing along a valley. It
usually follows former river courses and are banded by steep sides.
E.g: The Himalayas and the Alps.
VII. Give Reason
1.
The ends of the meander loops come closer and closer.
Due to continuous erosion and deposition along the sides of the
meander the ends come closer and closer.
2.
Flood plains are very fertile.
As the river floods, it deposits layers of fine soil and other
material called sediments along its
banks. This leads to the formation of a flat fertile floodplain.
3.
Sea caves are turn into stacks.
Erosion breaks the roof and only walls are left. These wall like
features are called stacks.
VIII. Answer in a paragraph
1.
Explain different landforms produced by river erosion.
The running water in the river erodes the landscape, which
creates a steep-sided valley like the letter 'V' known as 'V' shaped valley.
Falling of river water over a vertical step in the river bed is
called waterfall. It is formed when the soft rocks are removed by erosion. E.g.
Courtrallam falls across the river Chittar in Tamil Nadu.
The highest waterfall is Angel Falls of Venezuela in South
America. The other waterfalls are Nigara Falls located on the border between
Canada and USA in North America and Victoria Falls on the borders of Zambia and
Zimbabwe in Africa.
2.
Describe the landforms associated with wind.
Winds erode the lower section of the rock more than the upper
part. Therefore, such rocks have narrower base and wider top. An isolated
residual hill, standing like a pillar with rounded tops is called Inselberg. E.g. Inselberg in the
Kalahari Desert of South Africa.
When the wind blows, it lifts and transports sand from one place
to another. When it stops blowing the sand falls and gets deposited in low hill
- like structures. These are called sand
dunes. The crescent shaped sand dunes are called Barchans.
3.
How are aretes formed?
When two adjacent cirques erode towards each other, the
previously rounded landscape is transformed into a narrow rocky, steep - sided
ridge called Aretes.
Activity
1. Fill in the corresponding columns with reference to the
landform features given below
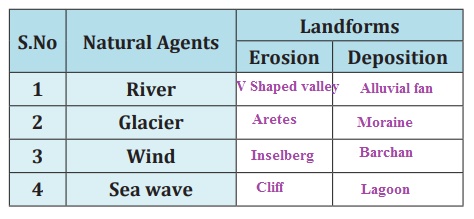
[Barchan, ‘V’ Shaped valley, Cliff,
Arete, Inselberg, Moraine, Alluvial fan, Lagoon]
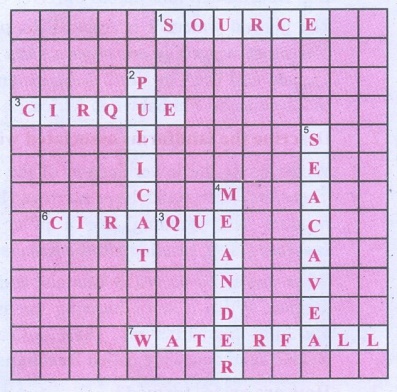
2. Crossword Puzzle

Across
1. Place of origin of the river.
3. Arm chair shaped glacial landform
6. Glacial Depositional feature
7. Vertical drop of water
Down
2. Lagoon in Tamil Nadu
4. Loops along the river course
5. Wave depositional feature
3. Identify any one of the following
features near your home town and write a note on them.
1. Hill
2. Waterfall
3. River (or) stream
4. Beach.
Related Topics