Chapter: Human Nervous System and Sensory Organs : Brain's Cerebrovascular and Ventricular Systems
Ependyma - Cerebrospinal Fluid Spaces
Ependyma
The
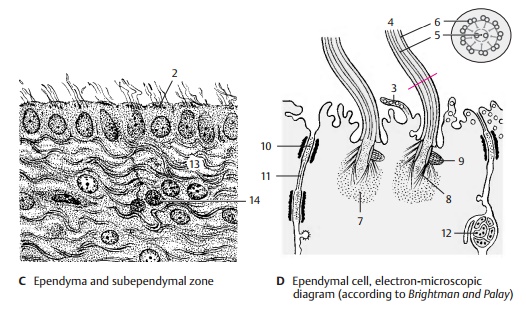
walls of the ventricular system are lined by a single cell layer, the ependyma (C). Each ependymal cell has a basal process, the ependymal fiber,
which extends into the brain. The cell surface facing the ventricular lumen
often carries several cilia, with the basal
bodies, or kinetosomes (C2), lined upbeneath the cell surface.
In the
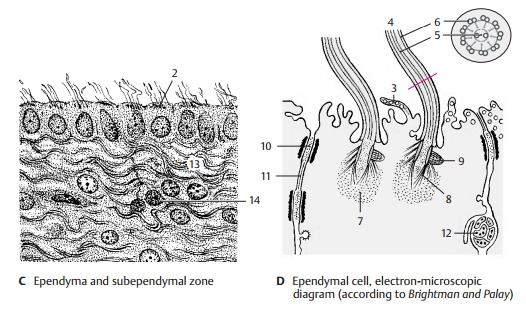
electron-microscopic image, the ventricular surface of the ependymal cells
exhibits numerous vesicle-containing pro-trusions (D3). The cilia (D4)
contain micro-tubules in the
characteristic 9 + 2 arrange-ment: two single microtubules in the center (D5) and nine microtubule doublets (D6) ar-ranged around them. The basal
body of each cilia is surrounded by a dense zone (D7) intowhich numerous short rootlets (D8) radiate. A basal foot
(D9) is located on one side of the
basal body; it may play a role in directing the beat of the cilia. The
ependymal cells are interconnected along their lateral surfaces by zonulae adherentes (adherent junctions)
(D10) and by zonulae occludentes (tight junctions) (D11); the latter seal the cere-brospinal fluid space against the
brain. Neu-ronal processes (D12) run
between the ependymal cells. The layer underneath the ependyma consists of
radially or horizon-tally running glial fibers (C13) and contains only few cells. Below it lies the subependy-mal cell layer (C14). It contains undifferen-tiated
cells in addition to astrocytes. Ac-cording to recent studies, not only glial
cells but also neurons are generated here throughout life. Intensive
investigations are under way to test whether neuronal stem cells of the
subependymal zone can be used for neuronal replacement in various forms of
neuronal degeneration.
The
structure of the ventricular wall varies widely in different regions. The
ependymal cover or the subependymal layer of glial fibers may be completely
absent in certain areas. The subependymal glial cell layer is most prominent
above the head of the cau-date nucleus and at the base of the anterior horn but
is absent above the hippocampus.
Related Topics