Lithosphere – II Exogenetic Processes | Geography | Social Science - Distinguish between | 9th Social Science : Geography : Lithosphere – II Exogenetic Processes
Chapter: 9th Social Science : Geography : Lithosphere – II Exogenetic Processes
Distinguish between
Social Science : Geography
LITHOSPHERE – II
EXOGENETIC PROCESSES
VI. Distinguish between
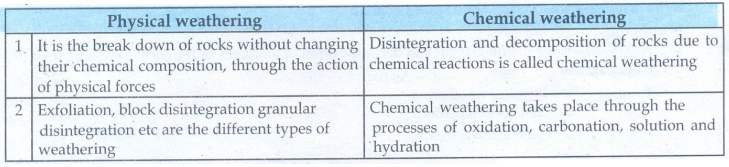
1. Physical and chemical weathering
Physical weathering
• It is the break down of rocks without changing their chemical composition, through the action of physical forces
• Exfoliation, block disintegration granular disintegration etc are the different types of weathering
Chemical weathering
• Disintegration and decomposition of rocks due to chemical reactions is called chemical weathering
• Chemical weathering takes place through the processes of oxidation, carbonation, solution and hydration
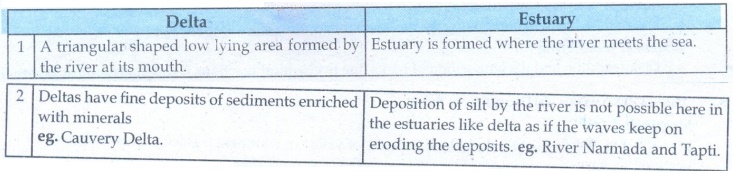
2. Delta and Estuary
Delta
• A triangular shaped low lying area formed by the river at its mouth.
• Deltas have fine deposits of sediments enriched with minerals eg. Cauvery Delta.
Estuary
• Estuary is formed where the river meets the sea.
• Deposition of silt by the river is not possible here in the estuaries like delta as if the waves keep on eroding the deposits, eg. River Narmada and Tapti.
3. Stalactite and Stalagmite

Stalactite
• When the water containing dissolved calcite gradually drips from the ceiling of the caves, water evaporates and the remaining calcite hangs from the ceiling. Thus stalactites are formed
Stalagmite
• When the calcite deposits rises upward like a pillar Stalagmites are formed.
4. Longitudinal and Transverse Sand dunes

Longitudinal sand dunes
• Longitudinal dunes are long narrow ridges of sand, which extend in a direction parallel to the prevailing winds. These dunes are called Seifs in Sahara
Transverse sand dunes
• Transverse dunes are asymmetrical in shape. They are formed by alternate slow and fast winds that blow from the same direction
5. Inselbergs and Yardangs.

Inselbergs
• Certain hard rocks like igneous rocks are more resistant to wind action.
• Such isolated residual hills rising abruptly from their surroundings are inselbergs. eg : Uluru, Ayers Rock, Australia
Yardang
• In arid regions, certain rocks have hard and soft layers arranged vertically.
• When winds blow over these rocks the soft layers get eroded leaving irregular crests and are called Yardangs.
6. Spit and Bar:

Spit
• A spit is a ridge or embankment of sediment, attached to the land on one end and terminating in open water on the other end. Spits are common at the mouth of estuaries.
Bar
• A bar is an elongated deposit of sand, shingle or mud found in the sea. It is almost parallel to the shoreline
Related Topics