Information Processing | Term 2 Chapter 5 | 6th Maths - Conversion of Algebraic Expressions into Tree Diagrams | 6th Maths : Term 2 Unit 5 : Information Processing
Chapter: 6th Maths : Term 2 Unit 5 : Information Processing
Conversion of Algebraic Expressions into Tree Diagrams
Conversion
of Algebraic Expressions into Tree Diagrams
There is more fun with trees. Observe the following
trees
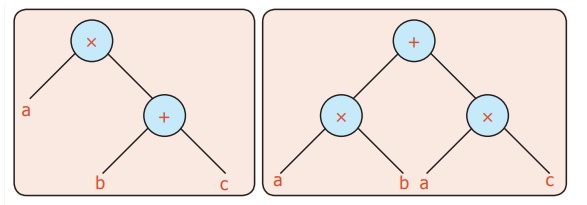
The above tree is nothing but the familiar equation
a × (b + c) = (a × b) + (a × c). Thus we can see the algebraic expressions as trees.
• The tree on the left has less number of nodes and
looks simple.
•
The tree on the right has more number of nodes
• Can we conclude
that the value of both the trees are different
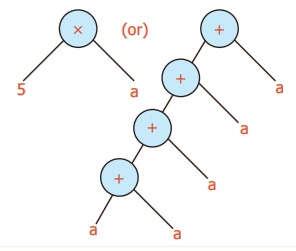
Example 15:
Convert ‘5a’ into Tree diagram
Solution:
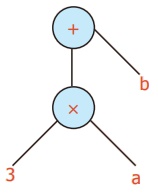
Example 16:
Convert '3a + b' into Tree diagram
Algebraic expression
3a+b
Tree diagram
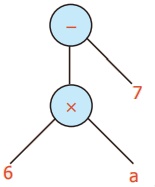
Example 17:
'6 times a and 7 less’ Convert into a Tree diagram.
Algebraic expression
6a − 7
Tree diagram
Example 18:
Convert the tree diagram into an algebraic expression.
Tree diagram
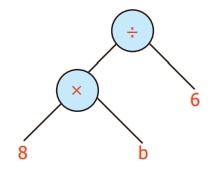
Algebraic expression
8b ÷ 6
Example 19:
Convert the tree diagram into an algebraic expression.
Tree diagram
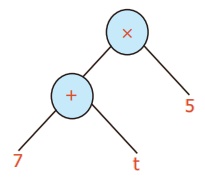
Algebraic expression
(7 + t) 5
Example 20:
Verify whether given trees are equal or not
Tree diagram
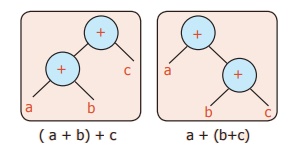
( a + b) + c = a + (b+c)
Yes, they are equal.
Try these
1. Check whether the Tree diagrams
are equal or not
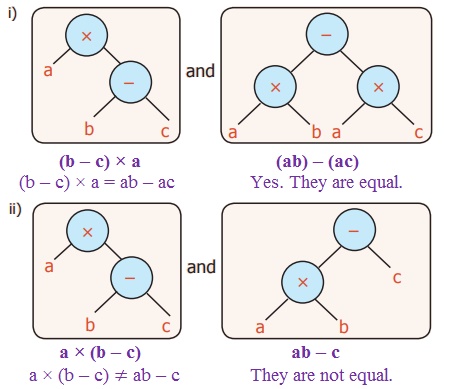
2. Check
whether the following algebraic expressions are equal or not by using Tree diagrams
i) (x −
y) + z and x − (y + z)
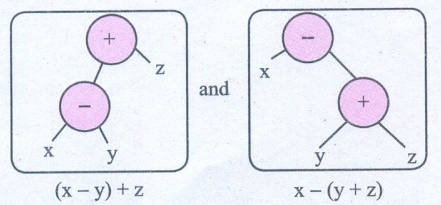
(x – y) + z ≠ x – (y + z).
They are not equal.
ii) (p ×
q) × r and p × (q × r)
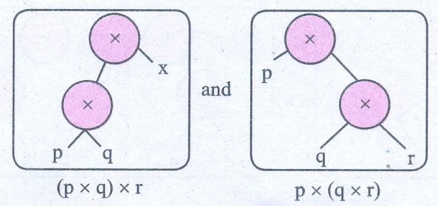
(p × q) × r = p × (q × r).
They are equal.
iii) a −
(b − c) and (a − b) − c
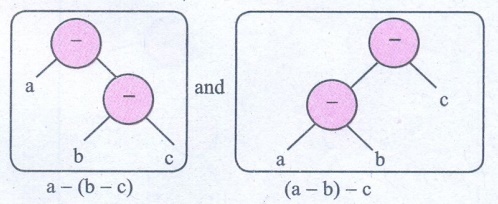
a – (b – c) ≠ (a – b) – c
They are not equal.
Do You Know
Consider
the numerical expression 9 – 4. which means 4 is to be subtracted from 9. 9 – 4
can be represented as – 9 4 (so far we have come across with operation in between
the operands)
Suppose
the expression is 9 – 4 × 2. This can be represented as × – 9 4 2 gives the meaning
of
Step 1: × 9 – 4
2
Step 2: (9 – 4)
× 2
Take the
expression + × − 9 4 2 5
Step 1: + × 9
− 4 2 5
Step 2: + (9 −
4 ) × 2 5
Step 3: [(9 − 4)
× 2] + 5
This is
reading an expression from “left to right”. Similarly, we can read expressions from
“right to left” also
9 4 2 5
+ × − can be read as “right to left” expression
which gives the meaning of
9 4 2 5
+ × => (9 − 4) 2 5 + ×
=> (9
− 4) × 2 5 +
=> [(9 − 4) × 2] + 5
Hence an
expression can be read as “left to right” or “right to left” giving the same answer
which is similar to name 4 as Naangu (நான்கு), Four, Nalagu (నాలుగు) and Char(चार), all of
them representing the collection of four objects. Similarly the numerical expression
[ (9 – 4)
× 8 ] ÷ [ (8 + 2) × 3] can be written as ÷ × – 9 4 8 × + 8 2 3 ( left to right)
or 8 9 4 – × 3 8 2 + × ÷ ( right to left ).
Try these: 1) × –
+ 9 7 8 2
2) ÷ × + 2 3 8 5
Related Topics