Chapter: Mechanical and Electrical : Thermal Engineering : Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
Classification of Refrigeration System
CLASSIFICATION OF REFRIGERATION SYSTEM
Types of Refrigeration
• Vapour Compression Refrigeration (VCR): uses mechanical energy
• Vapour Absorption Re frigeration (VAR): uses thermal energy
Vapour Compression Refrigeration
• Highly compressed flu ids tend to get colder when allowed to expand
• If pressure high enough
• Compressed air hotter than source of cooling
• Expanded gas cooler than desired cold temperature
• Lot of heat can be rem oved (lot of thermal energy to change liquid to vapour)
• Heat transfer rate re mains high (temperature of working fluid mu ch lower than
what is being cooled)
Vapour Compression Refrig eration Cycle
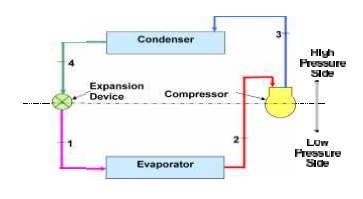
Evaporator
Low pressure liquid re frigerant in evaporator absorbs heat and changes to a gas
Compressor
The superheated vapo ur enters the compressor where its pressure is raised
Condenser
The high pressure sup erheated gas is cooled in several stages in the co ndenser
Expansion
Liquid passes through expansion device, which reduces its pressure an d controls the flow into the evaporator
Type of refrigerant
• Refrigerant determine d by the required cooling temperature
• Chlorinated fluorocarb ons (CFCs) or freons: R-11, R-12, R-21, R-22 and R-502
Choice of compressor, design of condenser, evaporator determined by
• Refrigerant
• Required cooling
• Load
• Ease of maintenance
• Physical space requirements
• Availability of utilities (water, power)
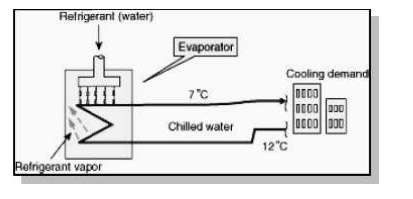
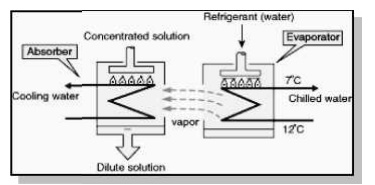
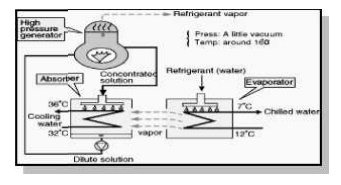
Vapour Absorption Refrigeration
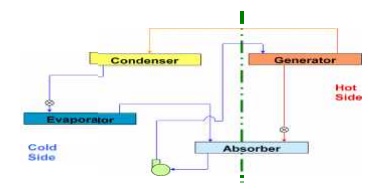
Evaporator
Absorber
High pressure generator
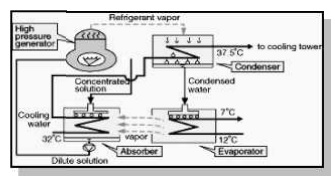
Condenser
Evaporative Cooling
• Air in contact with water to cool it close to ‘wet bulb temperature’
• Advantage: efficient cooling at low cost
• Disadvantage: air is ri ch in moisture
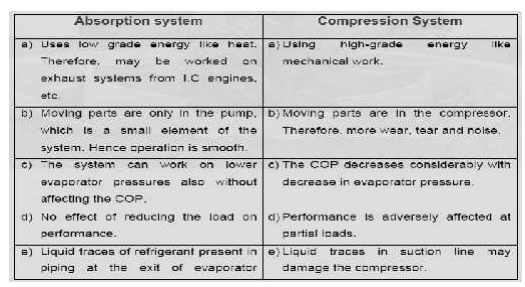
COMPARISON BETWEEN VAPOR COMPRESSION AND A BSORPTION SYSTEM
Related Topics