Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Level Crossings
Classification of Railway Level Crossings
Level crossings are provided on
railway lines to allow road traffic to pass across the track. As the level of
the passing road traffic is the same as that of the railway track, the crossing
is referred to as a level crossing. Other types of crossings are road over
bridge or road under bridge, where road traffic passes over or under the
railway track. In both these cases, the necessary clearance between the road
bed and the railway track is kept as prescribed in the schedule of dimensions.
Classification of Level Crossings
Level crossings may be manned or
unmanned. One or more gatemen are posted at manned level crossings to regulate
the traffic. In an unmanned level crossing, there is no gateman and road users
cross the railway line at their own risk after taking the necessary
precautions.
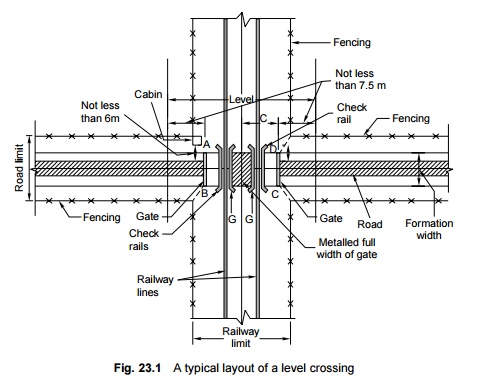
The typical layout of a square
level crossing is shown in Fig. 23.1. The sketch depicts the locations of guard
rails, gates, gate lodge, fencing, and railway boundary on a metalled road.
Level crossings can be classified
into different categories depending upon the class of the road, visibility
conditions, volume of road traffic, and the number of trains passing over the
level crossing. The classification of level crossings is as follows.
Special class
These are the busiest level
crossings in terms of road traffic. Most of the busy level crossings on the
national highway are special class level crossings. Normally the gates are open
to road traffic but whenever a train passes by, the gates are closed to road
traffic. The gates of the level crossings are interlocked with signals. They
are manned round the clock by three gatemen working 8-hour shifts.
'A' class
These
level crossings are also busy in terms of road traffic. All level crossings on
important roads are mostly A class level crossings. In this case also, the
gates are normally open to road traffic. All other provisions are the same as
for special class level crossings except that these level crossings are
provided with only two gatemen who work in 12-hour shifts, as these crossings
are not as busy as special class level crossings.
'B' class
These level crossings are
relatively less busy. Normal B class level crossings can be found on metalled
roads. The gates are normally closed to road traffic, but can be kept open to
road traffic provided that the gates are interlocked with signals. They are
provided with two gatemen working 12-hour shifts.
'C' class
These level crossings are mostly
provided on unmetalled roads. Some of these level crossings are unmanned
because of low volume of road traffic.
'D' class
These level crossing are provided
for cattle; they are normally used by cattle or pedestrians.
Indian Railways presently has about 42,000 level crossings, including about 20,000 unmanned level crossings and 3500 cattle crossings.
Related Topics