Chapter: 11th Commerce : Chapter 19 : Sources of Business Finance
Classification of Business Finance
Source of Business Finance
Classification of Business Finance
Business finance is classified into
three types with reference to time period i.e. Long term finance (more than 5
years), Medium term finance (above 1 year but below 5 years) and Short term
finance (within one year) for carrying on business operations. Long term
finance can be mobilized by issue of shares and debentures, term loans from
commercial banks and financial institutions, and retained earnings. Medium term
finance can be mobilized by public deposits, leasing, medium term loans from
banks
and financial institutions. Short term
fiancé can be raised through public deposits, trade credit, customer advance, ,
hypothecation, cash credit, bank overdraft, pledge, mortgage etc.
The various sources of business finance can be classified into three categories on the basis of i) period basis ii) ownership basis iii) source of generation basis
On
the basis of period
The different sources of finance can be
further grouped into three categories on the basis of period
1) Short term finance 2) Medium term
finance 3) Long term finance
Source of Short Term Finance
Short term funds are those sources which
are required by the business firms for a period of within one year. Some of the
important sources of short term finance are briefly explained below.
1.
Loans and Advances
Loan is a direct advance made in lump
sum which is credited to a separate loan account in the name of borrower. The
borrower can withdraw the entire amount in cash immediately. It can be repaid
in one or more installments. But the interest on loans and advances is
calculated on the whole of the amount borrowed right from the date of sanction.
It may be secured or unsecured. Loans and advances are usually sanctioned by
pledge of specific assets like Fixed Deposit Receipts, Document of Title to the
Goods, Shares, Debentures, etc.
2.
Bank Overdraft
Bank overdraft refers to an arrangement
whereby the bank allows the customers to overdraw the required amount from its
current deposit account within a specified limit. Interest is charged only on
the amount actually overdrawn.
3.
Discounting Bills of Exchange
When goods are sold on credit, the
suppliers generally draw bills of exchange upon customers who are required to
accept it.
The duration of such bills of exchange
may be ranging from 15 days to 180 days. Instead of holding the bills till the
date of maturity, borrowers generally prefer to get them discounted with the
bank. Discounting bills of exchange refers to an act of selling a bill to
obtain payment for it before its maturity.
4.
Trade Credit
Trade credit is the
credit extended by one
trader to another for the purpose of purchasing goods and services. Purchaser
need not pay money immediately after the purchase. Such credit appears in
balance sheet as Trade Creditors, or Accounts Payable. Trade credit is very
simple and convenient method of raising short term finance. There is no
formality involved in availing this facility. There is no need to give any
security for trade credit. It is said to be more economical than bank loans.
5.
Pledge
A customer transfers the
possession of an article with the creditor (banker) and
receives loan. Till the repayment of loan, the article is under the custody of
the borrower. If the debtor fails to refund the loan, creditor (banker) will
auction the article pawned and adjust the outstanding loan from the sale
proceeds.
6.
Hypothecation
This is loan taken by depositing
document of title to the property with the banker. Of course the physical
possession of asset property is with the borrower. If the
borrower fails to repay the loan amount, the article hypothecated will
be sold in auction by the banker concerned. Business people hypothecate goods
or equipment to get this type of loan. It is a
loan taken on the security of movable asset.
7.
Mortgage
This is a type of loan taken from the
bank by lodging with the banker title deeds of immovable assets like land and
building. Business people raise loans by depositing the title deeds of the
properties with the bank.
8.
Loans Against the Securities
Banks accept various types of securities
like fixed deposit receipt, book debts, insurance policies, supply bills,
shares debentures, bonds of company, document of title to the goods like
railway receipt, bill of lading, trust receipt, warehouse keeper’s receipt,
book debt, and so on, and provides loan on the basis of the aforesaid
securities.
9.
Clean Loan
Banks provide clean loan to certain
customer of outstanding credit worthiness on the basis of their character,
capacity and capability. It simply grants loan without any physical security.
In other words clean loan is loan given without any security or with personal
security.
10.
Commercial Paper (CP)
Commercial paper (CP) is an unsecured
money market instrument in the form of
a promissory note. Corporates, Primary Dealers (PD), and All India
Financial Institutions are eligible to issue Commercial Paper. It was introduced
in India in 1990 under Section 45W of the Reserve Bank of India Act. It is issued by a firm to
raise funds for a short period. It can be issued for maturities between a
minimum of 7 days and a maximum of up to one year from the date of issue.
11.
Hire Purchase Finance
Small scale firms can acquire industrial
machinery, office equipments, vehicles etc., without making full payment
through hire purchase. With the help of assets acquired through hire purchase,
they can produce and sell. From the earnings, payments can easily be made in installments.
Ultimately the ownership of assets can be acquired. Now several agencies like
National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC) provide machinery and equipments
to small scale units on hire purchase basis.
12.
Factoring
Factoring is one of the methods of
raising business finance through sale or mortgage of book debts. Under this
method, business concerns sell the
accounts receivable to a
finance company called a factor at a discount.
Source of Medium Term Finance
1.
Loans from Banks
When the bank lends for a period ranging
from more than one year to less than five years, it is called medium term loan.
All aspects of bank finance have been discussed under the head long term
sources of finance.
2.
Loan from Financial Institutions
Where the financial institutions lends
for a period ranging from more than one year to less than five years, it is
called medium term loan. All aspects of institutional finance have been
discussed under the head long term sources of finance.
3.
Lease Financing
Lease financing denotes procurement of
assets through lease. For many small and medium enterprises, acquisition of
plant and equipment and other permanent assets will be difficult in the initial
stages. In such a situation Leasing is
helping them to a greater extent. Leasing here refers to the owning of an asset
by any individual or a corporate body which will be given for use to another
needy business enterprise on a rental basis.
The firm which owns the asset is called
‘Lessor’ and the business enterprise which hires the asset is called ‘Lessee’.
The contract is called ‘Lease’. The lessee pays a fixed rent on agreed basis to
the lessor for the use of the asset. The terms and conditions like lease
period, rent fixed, mode of payment and allocation of maintenance, are
mentioned in the lease contract. At the end of the lease period, the asset goes
back to the lessor. Alternatively lessee can own the asset taken on lease
by payimg the balance of price of asset concerned to lessor. Hence lease
finance is a popular method of medium term business finance.
Source of Long Term Finance
Long term sources of funds refer to
those sources which are required by the business firms for a period exceeding
five years. The various sources of long term business finance are briefly
explained below.
1.
Shares
Corporate enterprises generally obtain
capital mainly from share capital which
is divided into small units called shares. Each share has a nominal
value. The Indian Companies Act 2013
describes a share “to be a share in the share capital of a company”. The person holding a share is
called shareholder who has the interest in the assets and profit of the
company. There are two types of shares namely Equity shares and Preference
shares.
i.
Equity Shares
The fund raised by issuing equity shares
is termed as equity share capital. Equity share is the most important source of
raising long term capital by a company. These shares do not carry any special
or preferential rights in the matter of payment of annual dividend and repayment
of capital at the time of winding up . Equity shareholder enjoys more voting
rights in proportion to number of shares held by them.
Thus they take part in the management of the company.
ii.
Preference Shares
The fund raised by issue of preference
shares is called preference share capital. Preference shares are those shares
which enjoy priority regarding payment of dividend at a fixed rate out of the
net profits of the company. They will get their dividend every year before any
dividend is paid to equity shareholders. They will have a right to get their
settlement before the claims of equity shareholder are settled at the time of
liquidation of company. However they do not have voting rights.
2.
Debentures
Debentures are an important instrument
for raisinglongtermdebtcapital. Acompanycan
raisefundsthroughissueofdebentureswhich bear a fixed rate of interest. The
individual or person subscribing to debentures is called debenture holder. An
entity raising funds through debenture has to pay interest at the stipulated
date whether it earns profit or loss. Failure to pay interest leads to
liquidation of the company. Debenture holders do not have voting rights.
3.
Retained earnings
Retained earnings refer to the process
of retaining a part of net profit year
after year and reinvesting them
in the business. It is also termed as ploughing back of profit. An individual would like to save a
portion of his/her income for meeting the contingencies and growth needs.
Similarly profit making company would retain a portion of the net profit in
order to finance its growth and expansion in near future. It is described to be
the most convenient and economical method of finance.
4.
Public Deposits
Under this method, companies invite
public deposits by giving advertisement in the media. It offers deposit schemes
for a longer tenure. Person interested in making public deposit has to undergo
a simple formality. The interest rates offered by companies on public deposits
are relatively higher than the bank. Public deposits are perceived to be
economical for the company since the interest rate on deposits is less than the
cost of borrowing from the bank.
The company need not offer any of its
assets as security on accepting public deposits. Moreover the control of the
company is not diluted as the deposit holders do not enjoy the voting rights.
5.
Long Term Loan from Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are important sources
of raising business finance for various purposes as well as for different time
periods. Banks in modern times offer long tenured loans for a period beyond 5
years also. The long term loan taken from banks can be repaid either in
installment or in one lump sum. Banks provide long term loans on the security
of assets of the business firms. Nowadays the formalities for taking long term
loans are simplified by the Reserve Bank of India.
6.
The Loans from Financial Institutions
Central and State Governments have
established various financial
institutions in India to provide
finance to business enterprises for a longer period. These institutions aim at
promoting the industrial development
of a country.
In addition to loan assistance, they conduct market
surveys, provide technical assistant and supply managerial talents to borrowing
enterprises to manage the companies. They mainly provide large funds for longer
period for financing expansion,
reorganisation and modernisation of an enterprise. They allow longer
repayment period to repay the loan. Hence the borrowing companies do not feel
the stress of repayment. Financial institutions provide term loans mostly to
highly rated corporates by the credit rating companies.
On the Basis of Ownership
Business finance can be divided into two
categories based on ownership of funds.
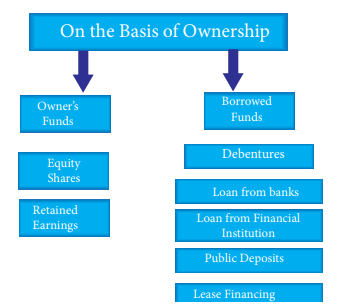
1.
Owner’s Funds
Owner’s funds mean funds which are
provided by the owner of the enterprises who may be an individual, or partners
or shareholders of a company. The profits reinvested in the business (ploughing
back of profit or retained earnings) come under owner’s funds. These funds are
not required to be refunded during the life time of business enterprise. It
provides the owner the right to control the management of the enterprise.
2.
Borrowed Funds
The term ‘borrowed funds’ denotes the
funds raised through loans or borrowings. For example debentures, loans from
banks and financial institutions, public deposits, trade credit, lease
financing, commercial papers, factoring, etc. represent borrowed funds.
·
These borrowed sources of funds provide
specific period before which the fund is to be returned.
·
Borrower is under legal obligation to
pay interest at given rate at regular intervals to the lender.
·
Generally borrowed funds are obtained on
the security of certain assets like bonds, land, building, stock, vehicles,
machinery, documents of title to the goods, and the like.
On the Basis of Generation of Funds
The sources of funds can be grouped into
two categories based on generation.
1.
Internal Sources
This includes all those sources
generated from within the business enterprises. For instance retained earnings,
collection from receivables (trade debtors and bills receivable), surplus from
disposal of old assets and so on. These sources can meet only limited needs of
business enterprise.
2.
External Sources
External sources of funds include all
those sources which generate funds from outside the business enterprise. For
example issue of shares and debentures, borrowings from banks and financial
institutions, public deposits, factoring, leasing, hire purchase, etc.
Related Topics