Chapter: Diseases of The Brain and Nervous System(A Health Education Guide): Neuroradiology : Theimaging of The Brain
Causes of Coma - Unconscious Tate
Causes :
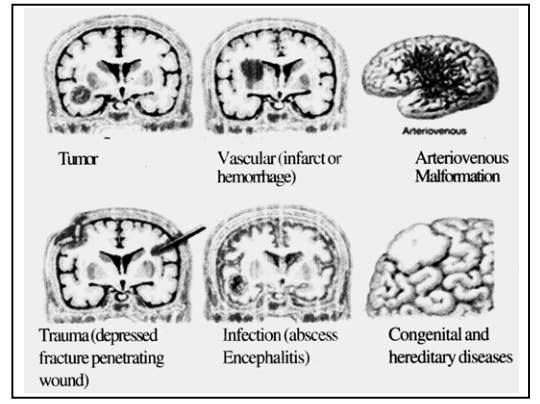
1. Road Accidents: Brain Trauma: Concussion, Contusion,Hemorrhage (Subdural, Epidural)
2. Diseases related to blood circulation of the brain :
Thrombosis (clotting of blood in the vessels), Embolism, Hemorrhage, and Sub-arachnoid Hemorrhage.
3. Infections of the brain: Falciparum malaria, Meningitis,TB, Viral-Encephalitis, AIDS, and other opportunistic diseases like fungal; parasite infection, syphilis etc.
4. Brain Tumor: Cancerous tumors (primary or secondary)like Glioma or Metastasis, simple tumors like meningioma. In all these tumors, symptoms like headaches, vertigo, convulsions, vomiting, and paralysis of one or both the sides are seen. Differential diagnosis can be done on the basis of medical examination, CT scan and MRI.
5. Metabolic diseases: Diabetic coma is the commonest inthese diseases. The tense lifestyle, mental stress, busy schedule etc. play a very important role in this. Oxygen deficiency, fluctuation in the blood sugar level, liver diseases, kidney diseases, respiratory disorders etc. cause debility in various organs of the body and eventually the efficiency of the brain is affected, causing coma.
6. Nutritional deficiency or dehydration can also lead tocoma. Extreme deficiency of important elements like vitamin B1, B12 etc. can also cause coma. Decrease in sodium level can also lead to coma, which is known as Hyponatremic Coma.
7. Hormonal Imbalance: Imbalance in the hormones ofthyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pituitary glands can also lead to coma.
8. Epilepsy: Epileptic attacks can also lead to coma.
9. Alzheimer’s Disease: during the last stage of thedisease one might lapse into coma.
10. Poison: Organophospherous poisoning or heavy metalslike arsenic or lead used for murder or suicide, overdose of sleeping pills, can also lead to coma.
11. Drug Addiction.
12. Psychogenic Coma: (the patient is not actually in coma) The treatment of coma should be done systematically. Usually, the patient is thoroughly examined and his/her history, pulse, temperature, respiration are noted. The Nervous system and the eyes are also examined along with certain specific tests of the body and brain, which include various blood tests, MRI, CT scan, E.E.G. If necessary cerebrospinal fluid is also examined. These are very helpful for the treatment. Before a coma patient is considered brain dead, the brain death has to be ascertained very carefully and the rules and regulations made specifically for this purpose are to be followed before declaring it. In this situation, the brain never regains consciousness, so such a patient can donate his/her kidney and other parts to save the life of another patient before his/her heart stops functioning.
Related Topics