Chapter: Engineering Economics and Financial Accounting : Financial Accounting (Elementary Treatment)
Cash Flow Statement(CFS)
CASH FLOW
STATEMENT
Complementing
the balance sheet and income statement, the cash flow statement (CFS), a
mandatory part of a company's financial reports since 1987, records the amounts
of cash and cash equivalents entering and leaving a company. The CFS allows
investors to understand how a company's operations are running, where its money
is coming from, and how it is being spent. Here you will learn how the CFS is
structured and how to use it as part of your analysis of a company.
A cash fl
ow statement is one of the most important fi nancial statements for a project
or business. The statement can be as simple as a one page analysis or may
involve several schedules that feed information into a central statement.
A cash fl
ow statement is a listing of the fl ows of cash into and out of the business or
project. Think of it as your checking account at the bank. Deposits are the
cash infl ow and withdrawals (checks) are the cash outfl ows. The balance in
your checking account is your net cash fl ow at a specifi c point in time.
The Structure of the CFS
The cash
flow statement is distinct from the income statement and balance sheet because
it does not include the amount of future incoming and outgoing cash that has
been recorded on credit. Therefore, cash is not the same as net income, which,
on the income statement and balance sheet, includes cash sales and sales made
on credit. (To learn more about the credit crisis, read Liquidity And Toxicity:
Will TARP Fix The Financial System?)
Cash flow
is determined by looking at three components by which cash enters and leaves a
company: core operations, investing and financing,
Operations
Measuring
the cash inflows and outflows caused by core business operations, the
operations component of cash flow reflects how much cash is generated from a
company's products or services. Generally, changes made in cash, accounts
receivable, depreciation, inventory and accounts payableare reflected in cash
from operations.
Cash flow
is calculated by making certain adjustments to net income by adding or
subtracting differences in revenue, expenses and credit transactions (appearing
on the balance sheet and income statement) resulting from transactions that
occur from one period to the next. These adjustments are made because non-cash
items are calculated into net income (income statement) and total assets and
liabilities (balance sheet). So, because not all transactions involve actual
cash items, many items have to be re-evaluated when calculating cash flow from
operations.
For
example, depreciation is not really a cash expense; it is an amount that is
deducted from the total value of an asset that has previously been accounted
for. That is why it is added back into net sales for calculating cash flow. The
only time income from an asset is accounted for in CFS calculations is when the
asset is sold.
Changes
in accounts receivable on the balance sheet from one accounting period to the
next must also be reflected in cash flow. If accounts receivable decreases,
this implies that more cash has entered the company from customers paying off
their credit accounts - the amount by which AR has decreased is then added to
net sales. If accounts receivable increase from one accounting period to the
next, the amount of the increase must be deducted from net sales because,
although the amounts represented in AR are revenue, they are not cash.
An
increase in inventory, on the other hand, signals that a company has spent more
money to purchase more raw materials. If the inventory was paid with cash, the
increase in the value of inventory is deducted from net sales. A decrease in
inventory would be added to net sales. If inventory was purchased on credit, an
increase in accounts payable would occur on the balance sheet, and the amount
of the increase from one year to the other would be added to net sales.
The same
logic holds true for taxes payable, salaries payable and prepaid insurance. If
something has been paid off, then the difference in the value owed from one
year to the next has to be subtracted from net income. If there is an amount
that is still owed, then any differences will have to be added to net earnings.
Investing
Changes
in equipment, assets or investments relate to cash from investing. Usually cash
changes from investing are a "cash out" item, because cash is used to
buy new equipment, buildings or short-term assets such as marketable
securities. However, when a company divests of an asset, the transaction is
considered "cash in" for calculating cash from investing.
Financing
Changes
in debt, loans or dividends are accounted for in cash from financing. Changes
in cash from financing are "cash in" when capital is raised, and
they're "cash out" when dividends are paid. Thus, if a company issues
a bond to the public, the company receives cash financing; however, when
interest is paid to bondholders, the company is reducing its cash.
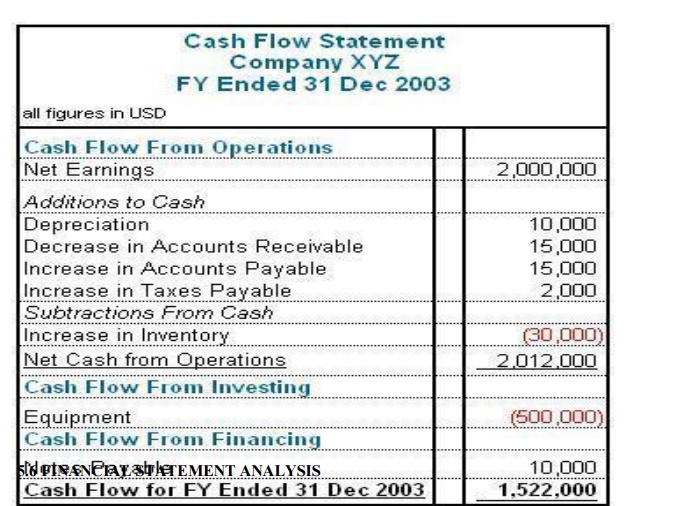
Analyzing
an Example of a CFS
Related Topics