Chapter: 11th Political Science : Chapter 1 : Introduction of Political Science
Approaches to the Study of Political Science
Approaches to the Study of Political
Science
An approach is the way of looking
at a political phenomenon and then explaining it. The approaches and methods to
the study of Political Science are many. There are both traditional and modern
or scientific approaches. The traditional approaches are highly speculative and
normative and the modern approaches are more empirical and scientific in
nature.
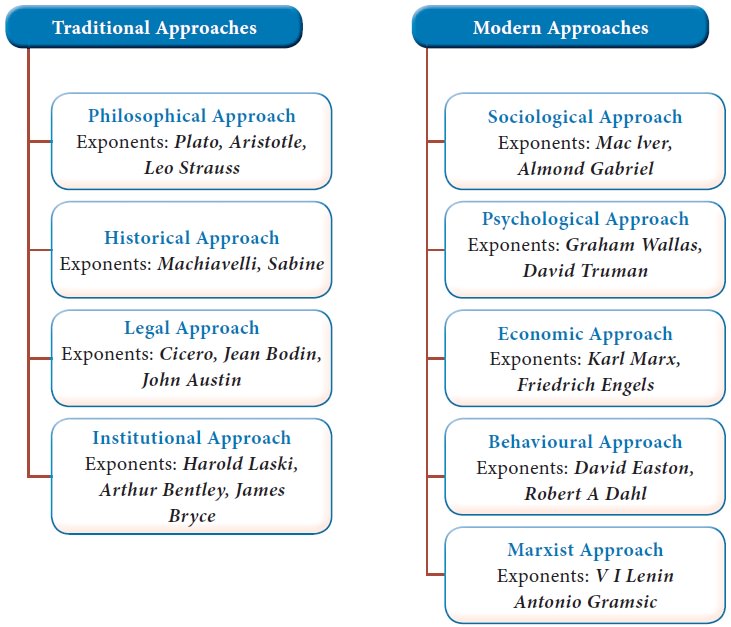
I. Traditional Approaches
i. Philosophical Approach
It is the oldest approach to the
study of politics. It is also known as speculative, metaphysical or ethical
approach. The study of state, government and the political behaviour of man is
intricately linked with the quest for achieving certain goals, morals or
truths. Here, the discipline moves closer to the world of ethics. The approach
is criticized for being highly speculative and abstract.
ii.Historical Approach
This approach throws light on the
past and traces the origin and development of the political institutions. It
seeks to study the role of individuals and their motives, accomplishments and
failures in the past and its implications for the future. In understanding the
political issues of today, the help of historical parallels are sought.
However, critics argue that historical parallels can be illuminating, but at
the same time they can also be misleading as it is loaded with superficial resemblances.
iii. Legal Approach
The study of politics is linked with the study of
legal institutions created by the State for the maintenance of the political
organization. As the State is engaged in the maintenance of law and order, the
study of judicial institutions become the concern of political theorists. This
approach looks at the State as an organization primarily concerned with the
creation and enforcement of law. However, critics argue that this approach has
a narrow perspective. The State has various other functions to perform other
than enforcement of law and order. Laws deal with only one aspect of an
individual’s life and do not enable the complete understanding of his political
behaviour.
iv. Institutional Approach
This approach is also known as the structural
approach. It lays stress on the formal structures of the political organization
such as legislature, executive and judiciary. The informal structures are also
studied and a comparative study of the governmental systems are encouraged.
However, this approach is criticized for laying too much emphasis on formal and
informal structures and ignoring the role of individual in those institutions.
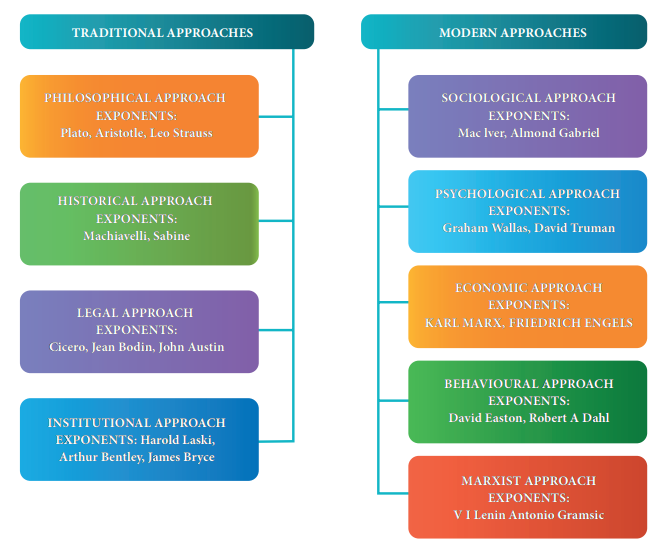
II. Modern Approaches
i. Sociological Approach
This approach emphasizes on the understanding of the social context to explain the political behaviour of the members of the community. The state is considered primarily as a social organism and politics is understood through the sociological factors. But critics are of the opinion that too much of emphasis on the social context can affect the very autonomy of the discipline.
ii. Psychological Approach
This approach studies and explains political and
social institutions through psychological laws. It assumes that the
psychological analysis of political leaders reveals significant knowledge about
politics. However, this approach ignores the sociological, legal and economic
factors in the study of politics.
iii. Economic Approach
As matters pertaining to production and
distribution of goods are regulated by the State, the economic matters also
become a concern for the political theorists. This approach emphasizes on the
role of the State in regulating the economic matters and argues that economic
affairs are intimately linked to the political process of the State. The
approach is inclined towards linking and understanding the political and
economic life of individuals. However, the approach takes into account only the
economic factors and ignores other factors such as social and psychological
factors.
iv. Behavioural Approach
This approach focuses on
political behaviour and studies the attitudes and preferences of humans in the
political context. Thus, the study of politics moved its focus from formalism
and normativism to the study of political behaviour. However, critics argue
that this approach is based on a false conception of scientific methods.
v. Marxist Approach
This approach is basically different from the other
modern approaches. It perceives State as an inevitable consequence of class
contradictions. It assumes that there is a continuous interaction between the
political and economic forces and separating one from the other is not
possible. However, this approach gives undue importance to the economic factors
and ignores the other important factors.
After careful analysis of the approaches, it is
understood that each approach has its own relevance in the study of political
phenomenon and also suffer from certain limitations.
III. Relationship with other Social Sciences
i. Political Science and History
The state and its institutions are a product of
slow historical growth and Political Science uses historical facts to discover
general laws and principles. Political History is the narrative of political
events and movements. The relationship between History and Political Science is
well explained by Freeman as he says ‘History is past Politics and Politics is
present History’. John Seeley adds to it through his quote, ‘History without
Political Science has no fruit, Political Science without History has no root’.
ii. Political Science and Economics
Economics was considered a branch of Political
Science and in fact, the Greeks called Political Science by the name of
Political Economy. Political Economy attempts to understand how political
institutions, political environment and economy influence each other.
Historians have explained as to how groups with common economic interests have
utilized the political process and environment to effect changes for their own
benefit. The study of Political Science and Economics are directed towards the
same end providing the best possible life for its people.
![]()
iii. Political Science and Ethics
Philosophy is closely associated with ethics.
Ethics deals with morality and formulates rules and regulations governing the
behaviour of individuals in the society. Ethics is the science of moral order
and Political Science is the science of political order. Both Political Science
and Ethics aim at the noble and righteous life of humans.
iv. Political Science and Sociology
Political Science and Sociology
are intimately related and it is Sociology that provides the basic information
regarding the origin and evolution of state and other political institutions.
Political Science is also called as Policy Science and policies of the State
cannot be formulated without the careful analysis of the social needs of the
people. Political Science provides information to Sociology about the
organization and functions of the state and how the policies and programmes of
the State affect the society at large.
v. Political Science and Psychology
Psychology deals with all the aspects of human
behaviour while Political Science deals only with the political behaviour of
humans. Psychology throws light on why individuals and groups behave in a
certain manner. It aids Political Science in understanding the behaviour of
political parties and varied other groups in the state. Barker rightly says, ‘The
application of psychological clue to the riddles of human activity has indeed
become the fashion of the day. If our forefathers thought biologically, we
think psychologically’.
vi. Political Science and Public Administration
Political Science is closely related to Public Administration and in fact, the term ‘public’ denotes ‘government’ though Public Administration also includes the study of non-governmental organizations. Public Administration is the implementation of governmental policies and Political Science deals with the process of policy formulation. There is a similarity in the objective of Political Science and Public Administration as they both aim at optimum use of resources and social welfare.
Thus, we understand that
Political Science is the systematic study of governance by the application of
empirical and scientific methods of analysis. Though it involves empirical
investigations, it does not generally produce precise predictions. Political
Science examines the state and its organs and institutions. It also encompasses
the study of societal, cultural, economic and psychological factors that
influence the government. It borrows heavily from the other social sciences but
its focus on power differentiates it from the other disciplines. Apart from
power, Political Science also focuses on comparative politics, international
relations, political theory, public law and public policy. Most importantly,
the study of Political Science gives us the basic understanding of the
political process, the system of government and the way in which it affects the
life of every citizen.
ACTIVITY
Write a short note
on how politics affects your daily life.
ACTIVITY
Collect pictures on
the life and works of your favorite political thinker and explain to the class
about his contributions to the discipline.
Related Topics