Environmental Science | Biology | Science - Answer the following questions | 9th Science : Biology : Environmental Science
Chapter: 9th Science : Biology : Environmental Science
Answer the following questions
ENVIRONMENTAL
SCIENCE
TEXT BOOK EXCERCISES
V. Answer briefly:
1. What are the two factors of
biosphere?
Answer:
(i)
Biotic (or) living factors, which include Plants, animals and all other living
organisms.
(ii)
Abiotic (or) non-living factors, which include temperature, pressure, air,
water, sunlight etc.
2. How do human activities affect
nitrogen cycle?
Answer: Human
activities,
1.
alters the biodiversity
2.
changes the food web structure
3.
destroys the general habitat.
3. What is adaptation?
Answer: Any
feature of an organism or its part that enables it to exist under conditions of
its habitat is called adaptation.
4. What are the challenges faced
by hydrophytes in their habitat?
Answer:
Challenges faced by
hydrophtes:
1.
More water availability than needed.
2.
Damaging of water body by water current.
3.
Regular change of water level.
4.
Maintenance of buoyancy in water.
5. Why is it important to
conserve water?
Answer: l. Water
is one of the precious natural resource.
2.
Clean and fresh water is essential for almost every human activity.
6. List some of the ways in which
you could save water in your home and school.
Answer: We could
save water by,
1.
Using low flow taps.
2.
Using recycled water for lawns.
3.
Repairing the leaks in the taps.
4.
Recycling (or) reusing water wherever it is possible.
7. What are the uses of recycled
water?
Answer:
Recycled water can
be used for
(i)
Agriculture
(ii)
Landscape
(iii)
Public parks.
(iv)
Cooling water for power plants and oil refineries
(v)
Toilet flushing
(vi)
Dust control
(vii)
Construction activities.
8. What is IUCN? What is the
vision of IUCN?
Answer:
IUCN:
International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources.
VISION: A just
world that values and conserves nature.
VI. Answer in detail:
1. Describe the processes
involved in the water cycle.
Answer: Process of
water cycle
1. Evaporation:
(i)
Conversion of liquid into gas (vapour) before reaching its boiling point.
(ii)
Water evaporates from the surface of the earth and water bodies such as the
oceans, seas, lakes, ponds and rivers turn into water vapour.
2. Sublimation:
Direct
conversion from solid to gas.
(e.g)-
(i)
Ice sheets and Ice caps from north and south pole,
(ii)
Ice caps on mountains converted into water vapour.
3. Transpiration:
The
process in which plants release water vapour to atmosphere through small pores
in leaves and stems.
4. Condensation:
Change
from gas phase into liquid phase. (e.g) Formation of clouds and fog.
5. Precipitation:
(i)
Clouds combine to make bigger droplets and pour down as precipitation (rain)
due to change in wind or temperature.
(ii)
Precipitation includes drizzle, rain, snow and hail.
6. Run off: Rain
water runs over the earth to form rivers, lakes and ends up into seas and Oceans.
7. Infiltration: Water
moves down the soil to increase ground water level.
8. Percolation: Water
moves through porous or fractured rock.
2. Explain carbon cycle with the
help of a flow chart.
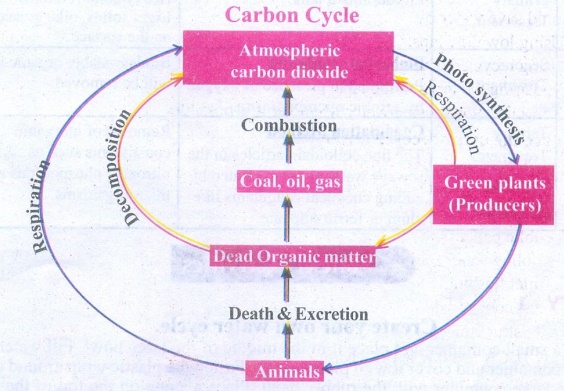
3. List out the adaptations of
xerophytes.
Answer: Adaptations of
xerophytes:
1.
Well developed roots. (e.g) Calotropis.
2.
Water storing parenchymatous tissues. (e.g) Aloe vera, Opuntia.
3.
Small sized leaves with waxy coating, (e.g) Acacia. In some plants, leaves are
modified into spines. (e.g) Opuntia.
4.
Complete life span in very short period on availing the moisture.
4. How does a bat adapt itself to
its habitat?
Answer: Adaptations
of BAT:
1.
Mostly, bats live in caves, which provide protection during the day from most
predators and maintain a stable temperature.
2.
Bats are active at night. This is a useful adaptation for them, as flight
requires a lot of energy during day.
3.
By Hibernation,
bats reduce body temperature with lowered metabolic rate during winter.
4.
Bats let their internal temperature reduce during rest.
5.
Bats use echolocation (High frequency ultrasonic sound waves) to identify and
locate the prey.
5. What is water recycling?
Explain the conventional wastewater recycling treatment methods.
Answer:
Water Recycling: Water
recycling is reusing treated waste water for beneficial purposes such as
agricultural and land irrigation, industrial processes, etc.
Conventional
wastewater recycling treatment: Conventional wastewater
treatment consists of combination of physical, chemical and biological
processes involving the following stages.

Intext Activities
ACTIVITY-1
Create your own water cycle.
Take a small container and place
it in the middle of the large bowl. Fill water in the large container and cover
it with plastic wrap. Fasten the plastic wrap around the rim of the large
container with the rubber band. Place a stone on the top of the plastic wrap.
Keep this under sun for few hours. Record your observation.
Aim:
To
understand utilisation and recycling of water
Materials:
A
large transparent bowl, plastic wrap, a stone, a smaller container and a rubber
band
Procedure:
(i)
The small container is placed in the middle of the large bowl. Water is filled
in the large container and it is covered with plastic wrap.
(ii)
The plastic wrap is fastened around the rim of the large container with the
rubber band.
(iii)
The stone is placed on the top of the plastic wrap.
This
is placed under the sun for few hours.
Observation:
1.
When we have a close look at the plastic wrap, water droplets would be formed
in the surface of plastic wrap. Thus, we can conclude there is condensation
process.
2.
The level of the water in bowl is reduced. It suggests that a part of water is
evaporated.
3.
After sometime, the droplets on the plastic wrap drip into the bowl which
indicates the phenonmenon of Precipitation.
Conclusion:
In this activity, the processes such as condensation, evaporation and precipitation have been demonstrated.
Related Topics