Plant Physiology | Biology | Science - Answer the following questions | 9th Science : Biology : Plant Physiology
Chapter: 9th Science : Biology : Plant Physiology
Answer the following questions
PLANT
PHYSIOLOGY
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES
V. Answer very briefly:
1. What is nastic movement?
Answer: Nastic
movement are non-directional response of a plant or part of a plant to
stimulus.
2. Name the plant part
a) Which bends in the direction
of gravity but away from the light.
b) Which bends towards light but
away from the force of gravity.
Answer:
a)
Root system
b)
Shoot system.
3. Differentiate phototropism
from photonasty.
Answer:

Phototropism
1.
Movement of a plant part towards light.
2.
Eg: Shoot of a plant.
Photonasty
1.
Movement of a plant part in response to light.
2.
Eg: Moon flower, Taraxacum officincle.
4. Photosynthesis converts energy
X into energy Y.
a) What are X and Y?
b) Green plants are autotrophic
in their mode of nutrition. Why?
Answer:
a)
X → light energy.
Y → Chemical energy.
b)
Green plants are autotrophic in their mode of nutrition because they prepare
their own food materials through photosynthesis.
5. Define transpiration.
Answer:
Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapour into the
atmosphere through stomata in leaves and stems.
6. Name the cell that surrounds
the stoma.
Answer: Each
stomata is surrounded by guard cells.
VI. Answer briefly:
1. Give the technical terms for
the following :
a) Growth dependent movement in
plants.
b) Growth independent movement in
plants.
Answer:
a)
Tropic movements,
b) Nastic movements
2. Explain the movement seen in
Pneumatophores of Avicennia.
Answer:
(i)
Pneumato [hores are specialised roots that can involve in the respiration of
plants.
(ii)
This type of roots intakes the gas through its lenticel. a small hole in their
both.
3. Fill in the blanks.

Answer:

4 What is chlorophyll?
Answer:
Chlorophyll is a green pigment present in all green plants which is responsible
for the absorption of light to provide energy for photosynthesis.
5. Name the part of plant which
shows positive geotropism. Why?
Answer:
(i)
Roots shows positive geotropism.
(ii)
Roots are the part of a plant which are responsible for anchoring the plant
firmly in the soil and helping them to hold the soil.
(iii)
Further the roots are responsible for absorbing water and mineral salts from
the soil and sending it to the leaves to help in photosynthesis and growth of
the plant.
(iv)
Hence the roots grow deep down into the soil and are positively geotropic.
6. What is the difference betw
een movement of flower in sunflower plant and closing of the leaves in the Mimosa pudica?
Answer:
Movement of flower
in sunflower plant:
In
sunflower plant the stem tip follows the path of the sun from dawn to dusk
(East to est) and in the night it moves from West to East. This is a growth
movement and takes place in response to the stimulus 'light'. It is an example
of tropic movement in response to light and is called phototropism.
Closing of the
leaves in the Mimosa pudica:
The
closing of leaves in Mimosa pudica occurs
in response to touch. It is not a growth movement and occurs independent of the
direction of stimulus. This is nastic movement and is called Thigmonasty.
7. Suppose you have a rose plant
growing in a pot, how will you demonstrate transpiration in it?
Answer:
Transpiration
in the plant can be demonstrated as follows:
(i)
A plastic bag must be tied over the leaf and the plant must be placed in sun
light.
(ii)
After some time, we can see water condensing inside the plastic bag. This has
been let out by the leaves and is called transpiration.
(iii)
Tiny microscopic holes called stomata are present in the leaves.
(iv)
The stomatal opening are guarded to guard cells.
(v)
The transpiration of water through the stomata are regulated by the opening and
closing of stomatal opening by the guard cells.
8. Mention the differences
between stomatal and lenticular transpiration.
Answer:

Stomatal
transpiration
1.
Loss of water from plants through stomata.
2.
90-95% of transpiration in a plant takes place through stomata only.
Lenticular
transpiration
1.
Loss of water from plants as vapour through the lenticels.
2.
A very small percentage of water is lost by through plants lenticular
transpiration.
9. To which directional stimuli
do (a) roots respond (b) shoots respond?
Answer:
(a)
Gravity
(b)
Light
VII. Answer in detail:
1. Differentiate between tropic
and nastic movements
Answer:
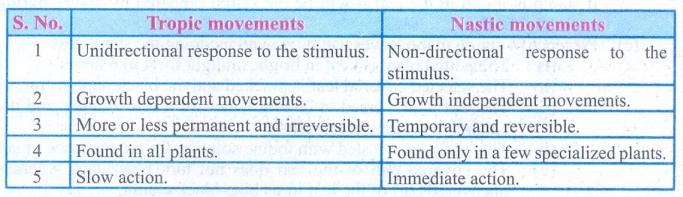
Tropic movements
1.
Unidirectional response to the stimulus.
2.
Growth dependent movements.
3.
More or less permanent and irreversible.
4.
Found in all plants.
5.
Slow action.
Nastic movements
1.
Non-directional response to the stimulus.
2.
Growth independent movements.
3.
Temporary and reversible.
4.
Found only in a few specialized plants.
5.
Immediate action.
2. How will you differentiate the
different types of transpiration?
Answer:
Transpiration in the plant can be differentiated by the loss of water in the
form of water vapour from the aerial parts of the plant body is called as
transpiration. The leaves have tiny, microscopic pores called stomata. Water
evaporates through these stomata. Each stomata is surrounded by guard cells.
These guard cells help in regulating the rate of transpiration by opening and
closing of stomata.
There are three
types of transpiration:
(i) Stomatal
transpiration: Loss of water from plants through stomata. It
accounts for 90-95% of the water transpired from leaves.
(ii) Cuticular
transpiration: Loss of water in plants through the cuticle.
(iii) Lenticular
transpiration: Loss of water from plants as vapour through the
lenticels. The lenticels are tiny openings that protrude from the barks in
woody stems and twigs as well as in other plant organs.
VIII. Higher Order
Thinking Skills:
1. There are 3 plants A, B and C.
The flowers of A open their petals in bright light during the day but closes
when it gets dark at night. On the other hand, the flowers of plant B open
their petals at night but closes during the day when there is bright light. The
leaves of plant C fold up and droop when touched with fingers or any other
solid object.
(a) Name the phenomenon shown by
the flowers of plant A and B.
(b) Name one plant each which
behaves like the flowers of plant A and B.
(c) Name the phenomenon exhibited
by the leaves of plant C.
(d) Name the plant which behaves
like the leaves of plant ’C’?
Answer:
(a)
Photonasty
(b)
Plant A - Common Dandelion - Taraxacum
officinale
Plant B - Moon flower - Ipomoea alba
(c)
Thigmonasty
(d)
Mimosa pudica, Dionaea muscipula
2. Imagine that student A studied
the importance of certain factors in photosynthesis. He took a potted plant and
kept it in dark for 24 hours. In the early hours of the next morning, he
covered one of the leaves with dark paper in the centre only. Then he placed
the plant in sunlight for a few hours and tested the leaf which was covered
with black paper for starch.
(a) What aspect of photosynthesis
was being investigated?
(b) Why was the plant kept in the
dark before the experiment?
(c) How will you prove that
starch is present in the leaves?
(d) Name the raw materials needed
for photosynthesis.
Answer:
(a)
Necessity of light as a factor for Photosynthesis.
(b)
To make the plant starch free before starting the experiment. After the
experiment if starch is found in the leaf it will be the starch prepared by
leaves during the experiment only.
(c)
Presence of starch in the leaves can be proved by doing the starch test.
(i)
The potted plant is kept in bright sunlight for 4 to 6 hours.
(ii)
The selected covered leaf is plucked and the black paper is removed.
(iii)
The leaf is immersed in boiling water for a few minutes and then in alcohol to
remove chlorophyll.
(iv)
The leaf is now tested with iodine solution for the presence of starch.
(v)
The covered part of the leaf does not turn blue-black whereas the uncovered
part of the leaf turns blue-black colour.
(vi)
The covered part of the leaf which did not receive the sunlight was unable to
synthesize starch.
(vii)
Hence it does not turn blue-black colour.
(viii)
But the uncovered part of the leaf which received sunlight was able to
synthesize starch and so it turns blue-black in colour.
(d)
1. Chlorophyll - Green pigment in leaves
2.
Water
3.
Carbon dioxide (from air)
4.
Sun light
Intext Activities
ACTIVITY - 1
Take a glass trough and fill it
with sand. Keep a flower pot containing water, plugged at the bottom at the
centre of the glass trough. Place some soaked pea or bean seeds around the pot
in the sand. What do you observe after 6 or 7 days? Record your observation.
Aim: To
demonstrate hydrotropism.
Materials required: Glass
trough, sand, flower pot, plugged at the bottom, pea or bean seeds and water.
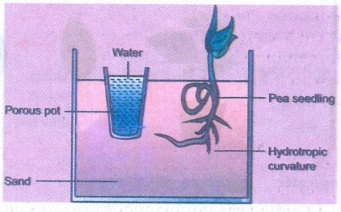
Procedure:
1.
A glass trough is taken and is filled with sand. A flower pot containing water,
plugged at the bottom is kept at the centre of the glass trough.
2.
Soaked pea or bean seeds are placed around the pot in the sand. It is observed
after 6 or 7 days.
Observation: Observed
that radicle has grown towards the pot and moisture instead of growing
vertically downward.
Inference: It
proves that primary root is positively hydrotropic.
Result:
Hydrotropism has been demonstrated by showing positive hydrotropism in roots.
ACTIVITY - 2
Take pea seeds soaked in water
overnight. Wait for the pea seeds to germinate.Once the seedling has grown put
it in a box with an opening for light on one side. After few hours, you can
clearly see how the stem has bent and grown towards the light.
Aim: To
demonstrate phototropism.
Materials required: Box,
water, light and pea seeds.
Procedure:
1.
Take pea seeds soaked in water overnight. Wait for the pea seeds to germinate.
2.
Once the seedling has grown put it in a box with an opening for light on one
side.
3.
After few hours, you can clearly see how the stem has bent and grown towards
the light.
Observation: Observed
that movement of a stem of a plant (pea seeds) towards light moist condition.
This is the way a new plant develops from a seed.
Inference: Positive
phototropism of a plant has been demonstrated.
ACTIVITY - 3
Pluck a variegated leaf from
Coleus plant kept in sunlight. De- starch it by keeping in dark room for 24
hours. Draw the picture of this leaf and mark the patches of cholorphyll on the
leaf. Immerse the leaf in boiling water followed by alcohol and test it for
starch using iodine solution. Record your observation.
Aim: To show
that chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis.
Materials required: Plant
with variegated leaves, boiling water, alcohol and iodine solution.
Procedure:
Variegated
leaf is plucked from Coleus plant
kept in sunlight. It is destarched by keeping it in dark room for 24 hours. The
picture of this leaf is drawn and the patches of cholorphyll on the leaf are
marked. After immersing the leaf in boiling water followed by alcohol it is
tested for starch with iodine solution.
Observation: The
patches of the leaf with chlorophyll turn blue-black. The other portions remain
colourless.
Inference: The
chlorophyll is essential for photosynthesis.
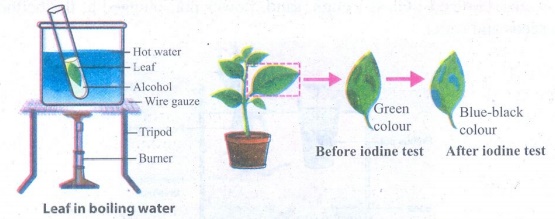
ACTIVITY - 4
Place a potted plant in a dark
room for about 2 days to de-starch its leaves. Cover one of its leaves with the
thin strip of black paper as shown in the picture, make sure that the leaf is
covered on both sides. Keep the potted plant in bright sunlight for 4 to 6
hours. Pluck the selected covered leaf and remove the black paper. Immerse the
leaf in boiling water for a few minutes and then in alcohol to remove
chlorophyll. Test the leaf now with iodine solution for the presence of starch.
The covered part of the leaf does not turn blue-black whereas the uncovered
part of the leaf turns blue-black colour. Why are the changes in colour noted
in the covered and uncovered part of the leaf?

Aim: To show
that light is essential for photosynthesis.
Materials required: Covered
leaf, boiling water, alcohol and iodine.
Procedure:
(i)
A potted plant is placed in a dark room for about 2 days to de-starch its
leaves.
(ii)
One of its leaves is covered with the thin strip of black paper as shown in the
picture.
(iii)
Make sure that the leaf is covered on both sides.
(iv)
The potted plant is kept in bright sunlight for 4 to 6 hours.
(v)
The selected covered leaf is plucked and the black paper is removed.
(vi)
The leaf is immersed in boiling water for a few minutes and then in alcohol to
remove chlorophyll.
(vii)
The leaf is now tested with iodine solution for the presence of starch.
Observation: The
covered part of the leaf does not turn blue-black whereas the uncovered part of
the leaf turns blue black colour. The covered part of the leaf which did not
receive sunlight was unable to synthesize starch.
Inference: The
light is essential for photosynthesis.
Related Topics