Chemical Bonding | Chemistry | Science - Answer the following questions | 9th Science : Chemistry : Chemical Bonding
Chapter: 9th Science : Chemistry : Chemical Bonding
Answer the following questions
CHEMICAL
BONDING
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES
II. Answer briefly:
1. How do atoms attain Noble gas
electronic configuration?
Answer: Atoms
can combine either by transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another or
by sharing of valence electrons in order to achieve the stable noble gas
electronic configuration.
2. NaCl is insoluble in carbon
tetrachloride but soluble in water. Give reason.
Answer: NaCl is
an ionic compound, it is soluble in polar solvent (water). Whereas CCI4 is a covalent compound. So it is insoluble in polar solvent
(water). But it is soluble in non-polar solvents.
3. Explain Octet rule with an
example.
Answer: The
tendency of atoms to have eight electrons in the valence shell is known as the
‘Octet rule’ or the ‘Rule of eight’
For
example, Sodium with atomic number 11 will readily loose one electron to attain
Neon’s stable electronic configuration. Similarly, chlorine has electronic
configuration 2,8,7. To get the nearest noble gas (i.e. Argon) configuration,
it needs one more electron. So chlorine readily gains one electron from other
atom and obtains stable electronic configuration. Thus elements tend to have
stable valence shell (eight electrons) either by losing or gaining electrons.
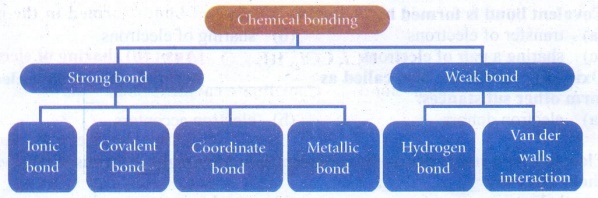
4. Write a note on different
types on bonds.
Answer: There are
different types of chemical bonding possible between atoms which make the
molecules. Depending on the type of bond they show different characteristics or
properties.
5. Correct the wrong statements.
(a) Ionic compounds dissolve in
non polar solvents.
(b) Covalent compounds conduct
electricity in molten or solution state.
Answer:
(a)
Covalent compounds dissolve in non-polar solvents, (or) Ionic compounds
dissolve in polar solvents.
(b)
Ionic compounds conducts electricity in molten or solution state.
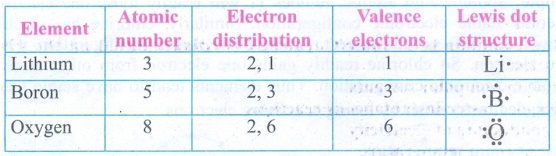
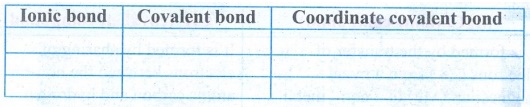
6. Complete the table give below.
Answer:
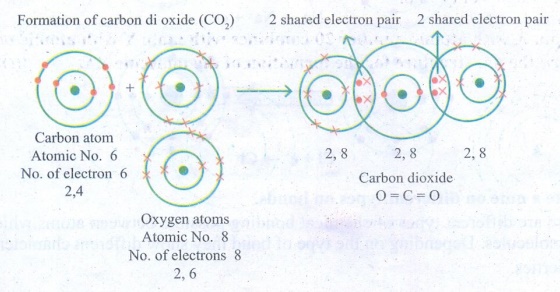
7. Draw the electron distribution
diagram for the formation of Carbon di oxide (CO2) molecule.
Answer:
8. Fill in the following table
according to the type of bonds formed in the given molecule.
CaCl2, H2O, CaO, CO,
KBr, HCl, CCl4, HF, CO2, AI2 Cl6
Answer:

9. The property which is
characteristics of an Ionic compound is that
(a) it often exists as gas at
room temperature.
(b) it is hard and brittle.
(c) it undergoes molecular
reactions
(d) it has low melting point.
Answer: (b) it
is hard and brittle
10. Identify the following
reactions as oxidation or reduction.
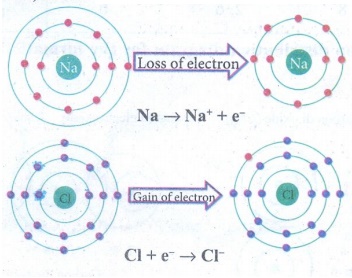
(a)
Na → Na+ + e−
(b)
Fe3+ + 2 e− → Fe+
Answer:
(a)
oxidation
(b)
reduction
11. Identify the compounds as
Ionic/Covalent/Coordinate based on the given characteristics.
(a) Soluble in non polar solvents
(b) Undergoes
faster/instantaneous reactions
(c) Non conductors of electricity
(d) Solids at room temperature
Answer:
(a)
Co-ordinate Covalent compound.
(b)
Ionic compound.
(c)
Covalent compound.
(d)
Ionic compound.
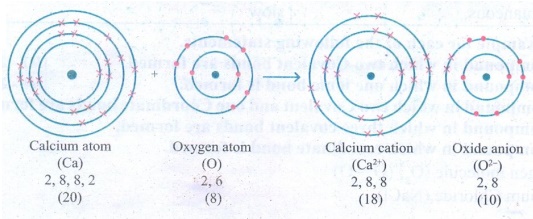
12. An atom X with atomic number
20 combines with atom Y with atomic number 8. Draw the dot structure for the
formation of the molecult XY.
Answer:
13. Considering MgCl2
as ionic compound and CH4 as covalent compound give any two
differences between these two compounds.
Answer:
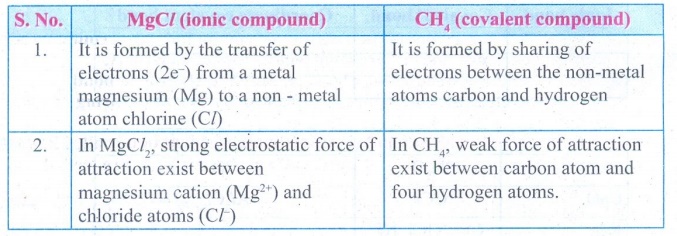
MgCI (Ionic compound)
1.
It is formed by the transfer of electrons (2e −) from a
metal magnesium (Mg) to a non - metal atom chlorine (CI)
2.
In Mg Cl2, strong
electrostatic force of attraction exist between magnesium cation (Mg2+)
and chloride atoms (Cl−)
CH4 (covalent
compound)
1.
It is formed by sharing of electrons between the non-metal atoms carbon and
hydrogen
2.
In CH4, weak force of attraction exist between carbon atom and four
hydrogen atoms.
14. Why are Noble gases inert in
nature?
Answer: Noble
gases have stable valence electronic configuration. So noble gas atoms neither
have any tendency to gain nor lose electrons and their valency is zero. Thus
they are said to be inert.
III. Answer in detail:
1. List down the differences
between Ionic and Covalent compounds.
Answer:
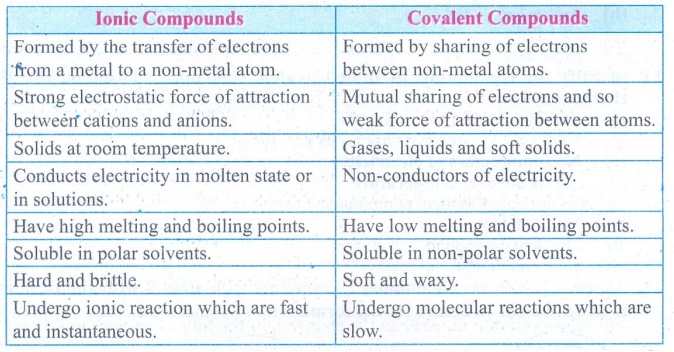
Ionic Compounds
•
Formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal atom.
•
Strong electrostatic force of attraction between cations and anions.
•
Solids at room temperature.
•
Conducts electricity in molten state or in solutions.
•
Have high melting and boiling points.
•
Soluble in polar solvents.
•
Hard and brittle.
•
Undergo ionic reaction which are fast and instantaneous.
Covalent Compounds
•
Formed by sharing of electrons between non-metal atoms.
•
Mutual sharing of electrons and so weak force of attraction between atoms.
•
Gases, liquids and soft solids.
•
Non-conductors of electricity.
•
Have low melting and boiling points.
•
Soluble in non-polar solvents
•
Soft and waxy.
•
Undergo molecular reactions which are slow.
2. Give an example for each of
the following statements.
(a) A compound in which two
Covalent bonds are formed.
(b) A compound in which one ionic
bond is formed.
(c) A compound in which two
Covalent and one Coordinate bonds are formed.
(d) A compound in which three
covalent bonds are formed.
(e) A compound in which
coordinate bond is formed.
Answer:
(a)
Oxygen molecule (O2) (O = O)
(b)
Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
(c)
Carbon monoxide (C ![]() O)
O)
(d)
Nitrogen molecule (N2) (N ≡ N)
(e)
NH3 → BF3
3. Identify the incorrect
statement and correct them.
(a) Like covalent compounds,
coordinate compounds also contain charged particles (ions). So they are good
conductors of electricity.
(b) Ionic bond is a weak bond
when compared to Hydrogen bond.
(c) Ionic or electrovalent bonds
are formed by mutual sharing of electrons between atoms.
(d) Loss of electrons is called
Oxidation and gain of electron is called Reduction.
(e) The electrons which are not
involved in bonding are called valence electrons.
Answer:
(a)
Incorrect statement. Like covalent compounds, co-ordinate compounds also do not
contain charged particles (ions), so they are bad conductors of electricity.
(b)
Incorrect statement. Ionic bond is a strong bond when compared to hydrogen
bond.
(c)
Incorrect statement. Covalent bonds are formed by mutual sharing of electrons
between atoms. (or) Ionic or electrovalent bonds are formed by transfer of
electrons between atoms.
(d)
Correct statement
(e)
Incorrect statement. The electrons which are not involved in bonding are called
lone pair of electrons.
4. Discuss in brief about the
properties of coordinate covalent compounds.
Answer: The
compounds containing coordinate covalent bonds are called coordinate compounds.
(a)
Physical
state - These compounds exist as gases, liquids or solids.
(b)
Electrical
conductivity - Like covalent compounds, co-ordinate compounds also
do not contain charged particles (ions), so they are bad conductors of
electricity.
(c)
Melting
point - These compounds have melting and boiling points higher than
those of purely covalent compounds but lower than those of purely ionic
compounds.
(d)
Solubility -
Insoluble in polar solvents like water but are soluble in non-polar
solvents like benzene, CC14, and toluene.
(e) Reactions -
Co-ordinate covalent compounds undergo molecular reactions which are slow.
5. Find the oxidation number of
the elements in the following compounds.
(a) C in CO2
(b) Mn in MnSO4
(c) N in
HNO3
Answer:
(a) C in CO2
1(C)
+ 2(0) = 0
lx + 2(-2) = 0
x -
4 =0
x =
+4
ON
of C in CO2 is +4
(b)
Mn in MnSO4
1
(Mn)+ 1(S) + 4(0) = 0
x+1 (+6) +
4(-2) = 0
x + 6 - 8
= 0
x - 2 =0
x = +2
ON
of Mn in MnSO4 is +2
(c)
N in HNO3
1(H)
+ 1 (N) + 3(0) = 0
1
(+1)+ 1 (x) + 3(-2) = 0
+
1 + x - 6 = 0
x - 5 = 0
ON
of N in HNO3 is+ 5.
Related Topics