Term 3 Chapter 2 | 5th Science - Animals | 5th Science : Term 3 Unit 2 : Animals
Chapter: 5th Science : Term 3 Unit 2 : Animals
Animals
UNIT 2
ANIMALS

Learning Objectives
After the completion of this lesson,
students will be able to:
* Understand reproduction in animals.
* Differenitiate oviparous and
viviparous animals.
* Know about endangered animals and the
importance to save them.
* List out the importance of wildlife
sanctuaries and national parks.
* Understand the need for the prevention
of cruelty to animals.
Introduction
Our planet earth has countless number of
organisms including plants and animals. Among them, animals are the most
advanced organisms. Animals are a gift of nature to human beings. They are very
closely associated with us in our daily life and contribute a lot to us. Man is
exploiting nature nowadays more than ever before. Hence animals are affected
and many of the plant and animal species are disappearing from the surface of
the earth. We are going to study about this in this lesson. This lesson will
deal with reproduction in animals, extinction of animals and the ways to
preserve them.
I. Reproduction in Animals
Reproduction is the biological process
by which an organism gives rise to a new organism. This process is seen in all
living organisms – both plants and animals. Reproduction is essential for the
continuation of similar kinds of species, generation after generation. In
animals two types of reproduction are seen. They are: sexual reproduction and
asexual reproduction.
1. Sexual Reproduction
Sexual
reproduction is a natural way of reproduction in humans, animals and also in
most of the plants. This type of reproduction is more complex and lengthy as
compared to asexual reproduction. Different and unique offspring are produced
by sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction consists of the following stages.
a.
Pre-fertilization
b.
Fertilization
c.
Post-fertilization.
a. Pre-fertilisation
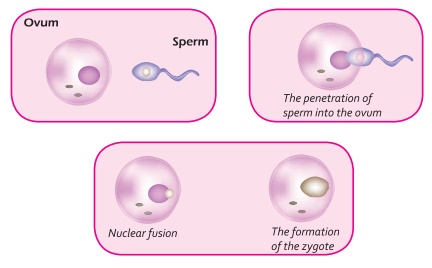
This
is the first stage of sexual reproduction. In this stage gamete (sex cells) formation and transfer of gametes take place. In
animals, males and females have different reproductive organs. The male
reproductive organ is called testes and the female reproductive organ is called
ovary. The testes produce the male gametes known as sperms and the ovaries
produce the female gametes known as ova or eggs. The male gametes reach the
female gamete during this stage. ![]()
b.
Fertilisation
When the
male gamete reaches the female gametes they begin to fuse together. The fusion
of gametes is known as fertilization. During fertilization, the nuclei of the
sperm and the egg form a single nucleus together, resulting in the formation of
a fertilized egg, known as zygote.
Fertilisation in animals takes place in
two ways. They are: External fertilization and Internal fertilization

External fertilization takes place outside the animal’s body. It usually takes place in aquatic environments where both eggs and sperm are released into the water. Fertilization in frogs and fish takes place by this method. When the fertilization takes place inside the animal’s body, it is called internal fertilization. Internal fertilization takes place in animals like cat, dog, cow etc.
c. Embryo
formation
The
zygote (fertilized egg) further divides repeatedly into group of cells. These cells develop into different tissues and
organs constituting a full body. This structure is known as embryo.
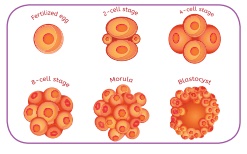
The embryo continues to develop in the uterus and it is developed into body parts such as head, face, hands, legs, etc. Based on whether the embryo develops outside or inside the body, animals are classified into oviparous and viviparous respectively.
* Oviparous animals
Animals
in which embryo develops outside the body are called oviparous animals. They
produce their offspring by laying eggs. In the case of birds new ones are
produced from the eggs. The egg shell protects the embryo from outer
environment and the embryo receives its nutrients from the egg yolk. In these
animals the new born one will have different developmental stages.

For
example, in butterfly, there are different developmental stages like egg,
larva, pupa and adult. Each stage is different. The process in which a
butterfly becomes an adult is called metamorphosis. The life cycle process can
take a month to year.
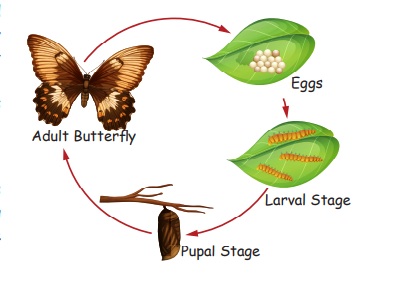
Stage
1: Eggs
In
the first stage a butterfly lays eggs on a leaf. These eggs are very small and
round. About five days after the eggs are laid, a tiny worm-like creature will
hatch from the egg.
Stage
2: Caterpillar (Larva)
The
second stage is the caterpillar. It is also called larva. It looks like a worm.
The caterpillar starts to eat leaves and flowers once it has hatched. It grows
very fast because it eats a lot. As it grows fast it sheds its old skin and
gets new skin. A caterpillar shedding its outgrown skin is called molting.
Stage
3: Chrysalis (Pupa)
The
third stage is the pupa. It is mostly brown or green. This is the resting stage
as well as the changing stage. The caterpillar turns into a butterfly.
Do
you know?
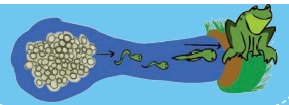
Amphibians are animals which have double life. The early part of
an amphibian’s life is spent in the water. As they get older, they spend time
on land. Amphibians like frog lay thousands and sometimes millions of small,
soft eggs in the water.
Stage
4: Butterly (Adult)
In the fourth stage the pupa opens and a
butterfly comes out. A butterfly is sometimes called an imago. It is also
called as adult. Butterflies are very colorful. When the butterfly first comes
out it is very tired and so it rests. Then the butterfly will lay eggs and the
lifecycle will start all over again.
* Viviparous animals
Animals in which the embryo develops
inside the body are called viviparous animals. These animals give birth to the
young ones. The developing embryo gets its nutrients from the mother. Humans,
cows, deer and dogs are examples for viviparous animals.

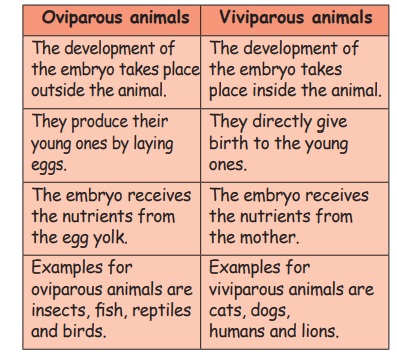
Oviparous animals
The development of the
embryo takes place outside the animal.
They produce their young
ones by laying eggs.
The embryo receives the
nutrients from the egg yolk.
Examples for oviparous
animals are insects, fish, reptiles and birds.
Viviparous animals
The development of the embryo takes
place inside the animal.
They directly give birth to the young
ones.
The embryo receives the nutrients from
the mother.
Examples for viviparous animals are
cats, dogs, humans and lions.
Activity 1
Write down the names of
any three oviparous and viviparous animals in the table given below.

2. Asexual Reproduction
The type of reproduction in which only a
single parent, gets divided into two new offspring, is known as asexual
reproduction. This type of reproduction takes place in micro organisms like
hydra and amoeba. Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are identical to
the parent. There are several ways by which animals reproduce asexually. Some
of them are explained below.
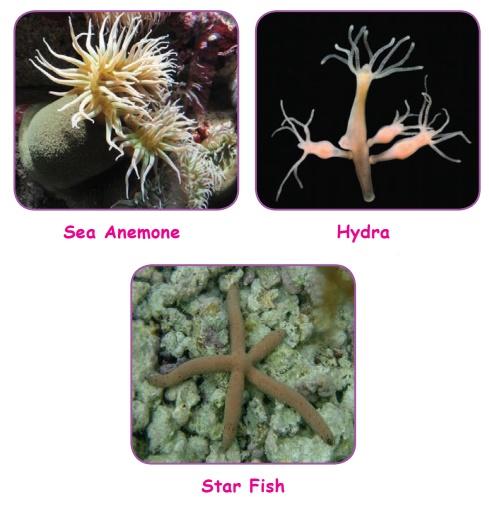
* Fission
Fission, occurs in some invertebrate
(organisams without back bone), multi-celled organisms. In this method, an
organism splits itself into two parts. For example, flatworms, sea anemones and
sea cucumbers divide into two halves and regenerate the other half in each of
the resulting individuals.
* Budding
Budding
is a form of asexual reproduction that results from the outgrowth of a part of
the body. Then the bud is separated from the original organism forming two
individuals. Budding occurs commonly in some invertebrate animals such as
hydras and corals.
* Fragmentation
Fragmentation
is the breaking of an individual into parts followed by regeneration.
Reproduction through fragmentation is observed in sponges and sea stars.
Fragmentation may occur through accidental damage, damage from predators, or as
a natural form of reproduction.

* Spores
Some
protozoan, bacteria, plants and fungi reproduce via spores. Spores are the
structures naturally grown as part of an organism’s life cycle. They are
separated from the organism and dispersed through a medium such as air or
water. In a suitable environment, the spores will develop into a fully grown
organism.
Activity 2
Visit a nearby museum or a
higher secondary school lab in your area. Find the specimens of starfish,
cucumber and hydra there. Collect the pictures of these species and prepare an
album.
II. Endangered Species
An endangered species is an animal or a
plant that is at the risk of extinction. It means that they might extinct from
the earth soon. It is reported that nearly 132 species of plants and animals
are critically endangered in India. Snow Leopard, Bengal Tiger, Asiatic Lion,
Purple Frog and Indian Giant Squirrel are some of the endangered animals in
India. Similarly, plants like Umbrella Tree, Malabar Lily, Rafflesia Flower,
Indian Mallo and Musli Plant are endangered.


Activity 3
Collect the pictures of
different plants and animals. Prepare a poster showing the endangered animals and
plants in India. Also find out where they are found.
Do you know?
An animal is said to be endangered if its population is currently less than 50 or less than 250 for the past three years.
1. Causes for Endangerment
The following are the reasons why an
animal or a plant is endangered or extinct.
→
Forests which provide food and shelter to animals are destroyed for human
needs.
→
Large number of animals is hunted for their horns, skin, teeth and many other
valuable products.
Activity
4
Write few slogans for
conservation of forest and animals. Observe some important days related to
nature like World Wildlife Day and organise a rally on those days.
Do you know?
In the recent years more
number of animals is affected by wastes in the form of plastic. Animals mistake
plastic as their food and eat them. Surgeons in Tamil Nadu Veterinary
University, Chennai have removed 52kg of plastic from a cow.
→
Pollutions like air pollution and water pollution affect the animals.
→
Sometimes animals are taken to new habitat by people. They cannot survive
there.
→
Pesticides and chemicals which are used to get rid of insects, pests or weeds,
poison the plants and animals.
→
Natural disasters like flood, cyclones and fire also destroy animals.

2. Saving endangered Species
Nature is beautiful and it is filled
with varieties plants and animals. But they are endangered mainly due to human
activitys we need to take some measures to protect them.
→
Hunting and poaching animals should be prohibited.
→
We should not pollute the environment.
→
Limiting the usage of plastic and recycling it can save the endangered animals.
→
Pesticides and chemicals which pollute the environment should be avoided.
→
Planting native trees will provide food to the animals.
→
We should buy eco friendly products only.
Activity
5
Plant native trees like
Banyan Tree, Neem Tree, Umbrella Tree and Java Plum Tree in your school
area.These trees can benefit birds.
Do you know?
Project Tiger was
initiated in India in 1972 to protect the Bengal Tiger.It was launched on 1st
April 1973. Due to this project the population of Tiger has increased in India
from 1400 in 2006 to 2967 in 2018.
3. Red Data Book
The Red Data Book is a book maintained
for recording rare and endangered species of animals and plants. This book is
created to identify and protect the species which are about to extinct.

It
is maintained by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), an
international organization working in the field of nature conservation. The Red
Data Book contains colour-coded information sheets.
* Advantages of the Red
Data Book
→
It helps to evaluate the population of a particular species.
→
The data given in this book can be used at the global level.
→
The risk of a species becoming globally extinct can be estimated with the help
of this book.
→
It provides the necessary guidelines for implementing protective measures.
Do
you know?
Red Data Book of India
contains the conservation status of animals and plants which are found in the
Indian subcontinent. Surveys conducted by the Zoological Survey of India and
the Botanical Survey of India provide the data for this book.
III. Conservation of Animals
Biodiversity is the term used to
describe different plants, animals, microorganisms, and insects etc. that are
found on the earth. Conservation of biodiversity helps us to protect, maintain
and recover the endangered animals and plant species. Conservation is the
protection, preservation, management of wildlife and natural resources.
Endangered species are maintained in certain protected areas such as national
parks and wild life sanctuaries. In India, there are about 73 national parks
and 416 wild life sanctuaries.
1. National Parks
A National park is an area which is
strictly reserved for the betterment of the wild life. In these areas,
activities like forestry, grazing or cultivation are not permitted. Even
private ownership rights are not allowed in these areas. The national parks
cover an area of 100 – 500 square kilometers.
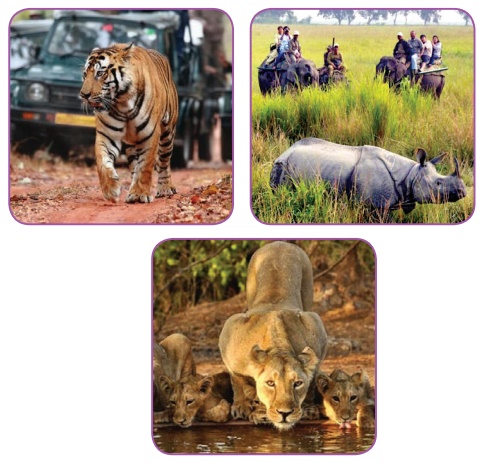

* Jim Corbett National Park
Jim
Corbett National Park is located close to Nainital, in Uttarakhand. Tigers are
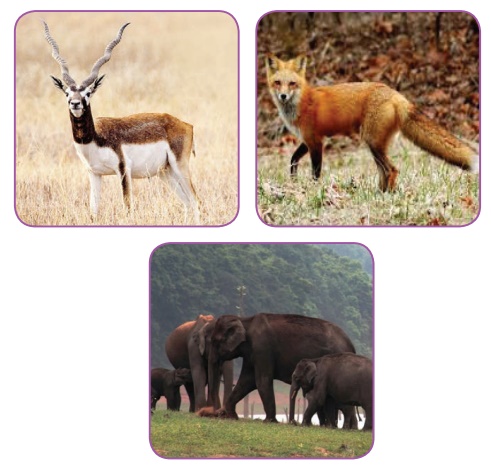
found in this park. Other animals found here include several species of deer,
leopards, jackals, red foxes, black bear, sloth bear, and monkeys.
*
Gir Forest National Park
It
is located in Gujarat. Asiatic lions in their natural habitat can be seen here.
Other animals that are found here include sambar, chinkara, chital, porcupine,
wild boar and black buck.
* Kaziranga National Park
Wild
animals such as Rhinoceros, Tiger, Elephant, Wild Buffalo and Swamp Deer are
seen here. This park also has bears, leopards, and several species of local and
migratory birds. This park is famous for one horned Rhino.

Do you know?
UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation) has declared Kaziranga National Park as a World Heritage Site.
* Sundarban National Park
Located
in West Bengal, the Sundarban National Park is a Tiger and Biosphere Reserve on
the Ganges Delta. Bengal tiger, saltwater crocodile, wild boars, foxes, leopard
cats, huge turtles, Ganges river dolphins and several other varieties of
mammals and reptiles, along with a huge variety of local and migratory birds
can be seen here.
* Kanha National Park
Kanha
National Park located in Madhya pradesh was established as a part of Project
Tiger. Apart from tiger, animals such as elephants, jackals, leopards, striped
hyenas, monkeys, and several varieties of deer including black buck, swamp
deer, chital, and sambhar are seen here.
* Periyar National Park
Periyar National Park is in Thekkady,
Kerala. Various species including the majestic elephants, royal tigers, and
fishes, reptiles and birds can be seen here.
Name
of the Park : District
Gulf of Munnar National
Park - Ramanathapuram
Indira Gandhi National
Park - Coimbatore
Mudumalai National Park - The Nilgiris
Mukurthi National Park - The Nilgiris
* Guindy National Park
This park is located at the heart of the
Chennai city. It is a home to spotted deer, black bucks, white bucks, river
otter, hyena, bonnet monkey, civet cat, jackals, pangolin, hedgehog and common
mongoose etc.
2. Wildlife Sanctuaries
A sanctuary is a protected area which is
reserved for the conservation of animals only. Harvesting of timber, collection
of forest products and private ownership rights are allowed here. Tourist visit
is also allowed in these places.
* Kalakkad Wildlife Sanctuary
The Kalakkad wildlife sanctuary is
famous for Tigers. Lion tailed macaque, Nilgiri langur, bonnet macaque, langur,
Nilgiri tahr, sambar, sloth bear, gaur, elephant, flying squirrel, panther,
wild dog and pangolin are some of the animals found here.
Activity 6
List out the national
parks and wild life santuaries in Tamil Nadu. Visit such places that are close
to you and collect more information about the animlas found there.
* Mudumalai Wildife Sanctuary
It is located in Ooty. Bengal Tiger, Giant Elephant and Leopard are found here.
Elephant safari is famous in this sanctuary.
* Mundanthrai Wildlife Sanctuary
It is located in Thirunelveli District.
Major wild life animal found here is Tiger.
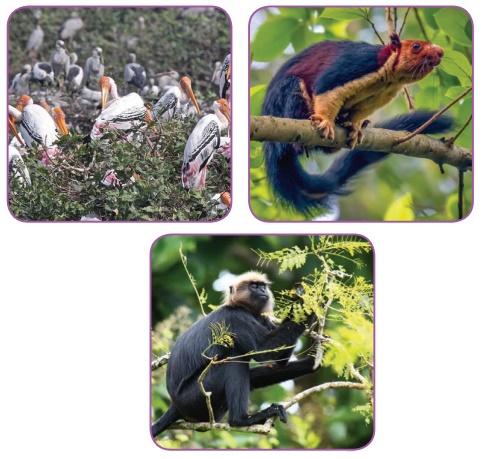

* Anaimalai Wildlife
Sanctuary
It
is also called as Indira Gandhi Wildlife Sanctuary. It is situated in
Coimbatore District. Dhole, Wild dog and Giant Squirrel are seen here.
* Vedanthangal Bird
Sanctuary
It
is a very old sanctuary in Tamil Nadu. It is located in Kancheepuram District.
It has many migratory birds like Spoon bills, Open billed storks, Pelicans etc.
Name of the Santuary : District
Meghamalai
Wildlife Sanctuary : Then
Vandaloor
Wildlife Sanctuary : Chennai
Kalakkad
Wildlife Sanctuary : Thirunelveli
Grizzled
Squirrel Wildlife Sanctuary : Virudhunagar
3.
Advantages of Conservation
→
Species can be adapted to their
habitat.
→
Species can interact with each other.
→
Natural habitat of the animals is
maintained.
→
It is less expensive and easy to
manage.
Do
you know?
Point Calimere Sancturary - Nagappattinam
Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary - Ariyalur
Vaduvur Bird Sanctuary - Tiruvarur.
Vallanadu Black Buck Sancturary
- Tuticorin
Viralimalai Bird Sanctury - Trichi
Grizzled Squirred Sancturary - Virudhunaga
V.
Prevention of Cruelty to Animals
Cruelty
to animals includes capturing, trapping, poisoning of any wild animal
collectively. There are many animal welfare organizations concerned with the
health, safety and psychological wellness of animals. They include animal
rescue groups which help animals in distress, and others which help animals
suffering from some epidemic. Animal Welfare Board of India and National
Institute of Animal Welfare are the government organizations which work for the
welfare of animals. There are some private welfare organizations also.
1.
Blue Cross
Blue
Cross is a registered animal welfare charity in the United Kingdom. It was
established in 1897 with the vision that every pet will enjoy a healthy life in
a happy home. The charity provides support for pet owners who cannot afford
private veterinary treatment, helps to find homes for unwanted animals, and
educates the public in the responsibilities of animal ownership.
Blue
Cross of India was established at Chennai in the year 1959. Now, Blue Cross of
India is one of the largest animal welfare organizations in India. The main
office is located at Guindy, Chennai, with all amenities like hospitals,
shelters, ambulance services and animal birth controls, etc. Activities of the
organization include, providing shelters, adoption, maintaining hospitals and
mobile dispensary and providing ambulance services.

Activity 7
Make a visit to a
veterinary clinic near your area. Find how animals are affected by people.
Discuss how you can prevent cruelty to animals.
Do you know?
Blue Cross of India was founded by Captain V. Sundaram of Chennai. He was an Indian pilot and animal welfare activist.

Related Topics