Chapter: 12th Computer Science : Chapter 4 : Algorithmic Strategies
Algorithm for Searching Techniques
Algorithm for Searching Techniques
Linear Search
Linear search also called sequential search is
a sequential method for finding a particular value in a list. This method
checks the search element with each element in sequence until the desired
element is found or the list is exhausted. In this searching algorithm, list
need not be ordered.
Pseudo code
1. Traverse the array using for loop
2. In every iteration, compare the target
search key value with the current value of the list.
If the values match, display the current index and value of the
array
If the values do not match, move on to the next array element.
3. If no match is found, display the search
element not found.
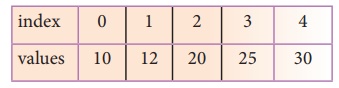
To search the number 25 in the array given
below, linear search will go step by step in a sequential order starting from
the first element in the given array if the search element is found that index
is returned otherwise the search is continued till the last index of the array.
In this example number 25 is found at index number 3.
Example 1:
Input: values[] = {5, 34, 65, 12, 77, 35}
target = 77
Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: values[] = {101, 392, 1, 54, 32, 22, 90, 93}
target = 200
Output: -1 (not found)
Binary Search
Binary search also called half-interval search
algorithm. It finds the position of a search element within a sorted array. The
binary search algorithm can be done as divide-and-conquer search algorithm and
executes in logarithmic time.
Pseudo code for Binary search
1. Start with the middle element:
If the search element is equal to the middle
element of the array i.e., the middle value = number of elements in array/2,
then return the index of the middle element.
If not, then compare the middle element with
the search value,
If the search element is greater than the
number in the middle index, then select the elements to the right side of the
middle index, and go to Step-1.
If the search element is less than the number
in the middle index, then select the elements to the left side of the middle
index, and start with Step-1.
2. When a match is found, display success
message with the index of the element matched.
3. If no match is found for all comparisons,
then display unsuccessful message.
Binary Search Working principles
List of elements in an array must be sorted first for Binary search. The following example describes the step by step operation of binary search. Consider the following array of elemnts, the array is being sorted so it enables to do the binary search algorithm. Let us assume that the search element is 60 and we need to search the location or index of search element 60 using binary search.
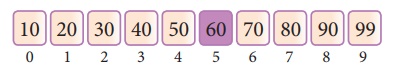
First, we find index of middle element of the
array by using this formula :
mid = low + (high - low) / 2
Here it is, 0 + (9 - 0 ) / 2 = 4 (fractional
part ignored). So, 4 is the mid value of the array.
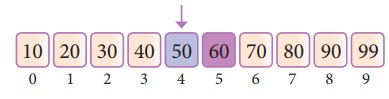
Now compare the search element with the value
stored at mid value location
The value stored at location or index 4 is 50,
which is not match with search element. As the search value 60 is greater than
50.
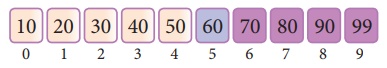
Now we change our low to mid + 1 and find the
new mid value again using the formula.
low to mid + 1
mid = low + (high - low) / 2
Our new mid is 7 now. We compare the value
stored at location 7 with our target value 31.
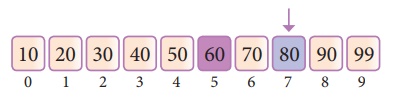
The value stored at location or index 7 is not
a match with search element, rather it is more than what we are looking for.
So, the search element must be in the lower part from the current mid value
location
The search element still not found. Hence, we
calculated the mid again by using the formula.
high = mid -1
mid = low + (high - low)/2
Now the mid value is 5.
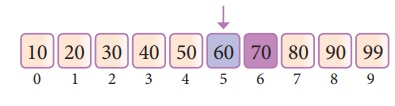
Now we compare the value stored at location 5
with our search element. We found that it is a match.
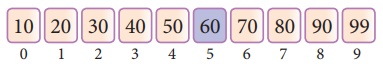
We can conclude that the search element 60 is
found at lcoation or index 5. For example if we take the search element as 95,
For this value this binary search algorithm return unsuccessful result.
Related Topics